c语言,购票、盗墓者是个丑奴儿
第一个源文件:
#include
pthread_mutex_t s;
int fei=1000; //飞机票
int huo=1000; //火车票
int lun=1000; //轮船票
int getfei(){ //购买飞机票方法
pthread_mutex_lock(&s);
fei--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&s);
return 1;
}
int gethuo(){ //购买火车票方法
pthread_mutex_lock(&s);
huo--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&s);
return 1;
}
int getlun(){ //购买轮船票方法
pthread_mutex_lock(&s);
lun--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&s);
return 1;
}
//根据全局变量ran的数值,决定开启的线程购买哪种票,要保证ran不被刷掉,还要回收线程资源,达不到线程相互争抢的效果
第二个源文件:
头文件引入
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "piao.h"
int ran=0; //随机数
int countf=0; //记录购买的飞机票数
int counth=0; //记录购买的火车票数
int countl=0; //记录购买的轮船票数
//购票方法,下面使用了join阻塞回收线程,不需互斥锁
void * run(void * nu){
switch (ran){
case 0:
if(getfei()==1)
countf++;
break;
case 1:
if(gethuo()==1)
counth++;
break;
case 2:
if(getlun()==1)
countl++;
break;
default :
exit(0);
break;
}
}
//main测试
int main(void){
int ix=700;
srand(time(NULL)); //设置随机数种子
for(int i=1;i<=ix;i++){
ran=rand()%3; //随机
pthread_t ind=-1;
int fid=pthread_create(&ind,NULL,run,NULL); //开启线程
pthread_join(ind,NULL); //阻塞回收线程
}
sleep(1);
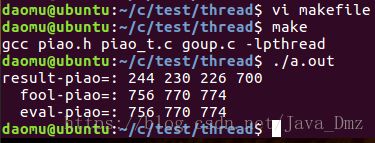
printf("result-piao=: %d %d %d %d \n",countf,counth,countl,countf+counth+countl);
printf(" fool-piao=: %d %d %d \n",fei,huo,lun);
printf(" eval-piao=: %d %d %d \n",1000-countf,1000-counth,1000-countl);
return 0;
}
头文件:
#ifndef _CAL_H
#define _CAL_H
extern int fei;
extern int huo;
extern int lun;
int getfei();
int gethuo();
int getlun();
#endif
makefile:
all:
gcc piao.h piao_t.c goup.c -lpthread
运行结果: