android从放弃到坚持放弃第七课
跨程序共享数据,使用内部提供器
- 跨程序共享数据使用内部提供器
- 简介
- 运行时权限
- Android权限机制详解
- 在程序运行时申请权限
- 访问其他程序中的数据
- ContentResolver基本用法
- 举个例子读取系统联系人
- 实现自己的内容提供器
- 创建内容提供器的步骤
- 实践
- Git
- 忽略文件
- 查看修改内容
- 查看提交记录
- 问题
生了一场病,拖了好久,⊙﹏⊙
简介
内部提供器主要用于在不同的应用程序之间实现数据共享的功能,不仅可以允许一个程序访问另一个程序,还可以保证数据的安全性。
不同于文件存储和SharedPreferences存储中的两种全局可读可写操作模式,内容提供器可以选择只对哪一部分数据进行共享,从而保证我们程序中的隐私数据不会泄露。
首先我们要先介绍一下Android运行时权限:
运行时权限
Android在Android 6.0系统中引用了运行时权限这个功能,从而更好的保障用户的安全和隐私。
Android权限机制详解
我们在写Broadcast的时候有用过一次
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED"/>因为访问系统的网络状态以及监听开机广播设计了用户设备的安全性,因此必须在AndroidManifest.xml加入权限声明,否则程序就会GG.
在安装程序的时候,低于6.0的系统会提示程序的权限申请情况。如果有不认可的权限就不安装。但是现实很残酷。很多常用软件都存在这滥用权限的情况,不管用不用,都会把权限申请(比如微信)。
Android开发团队于是在6.0系统中加入了运行时权限功能。即可以在运行时再对某一项权限进行授权。就算我们拒绝了这个权限,也可以使用这个应用的其他功能。
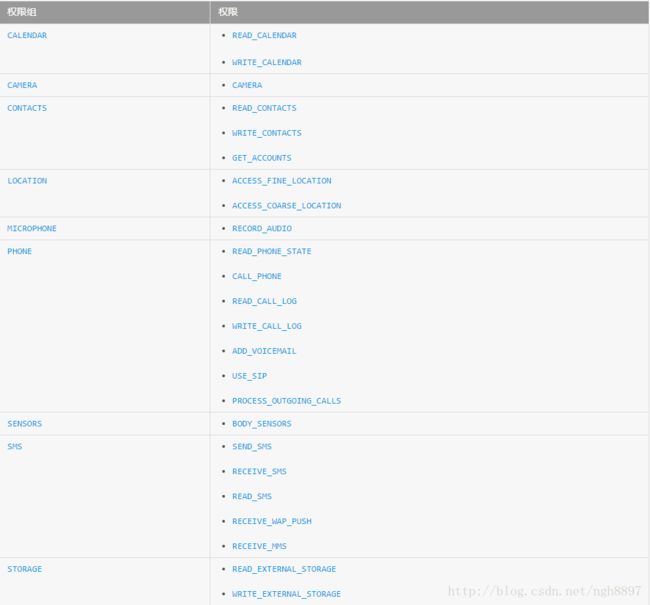
当让不停的授权也很繁琐。所以权限被分为了普通权限和危险权限两类。系统会帮我们自动授权那些不会危险用户安全和隐私的普通权限,比如上面的两个。但是危险权限就需要用户手动点击授权才可以。
上图都是危险权限,可以当作一个参照表。方便查询。
在程序运行时申请权限:
这里举CALL_PHONE这个权限的例子。因为拨打电话会扣除手机资费,所以被列为是危险权限。添加一个Button
<Button
android:id="@+id/make_call"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Make call"
android:textAllCaps="false"
/>添加Manifest.xml:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CALL_PHONE" />修改MainActivity:
Button makeCall = (Button) findViewById(R.id.make_call);
makeCall.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
try{
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_CALL);
intent.setData(Uri.parse("tel:10086"));
startActivity(intent);
}catch (SecurityException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});我们构建了一个隐式Intent,Intent的action指定为Intent.ACTION_CALL,这是系统内置的一个打电话的动作。data部分的协议是tel,但发现报错了。。。。因为现在使用危险权限需要使用危险权限,重新修改一下:
Button makeCall = (Button) findViewById(R.id.make_call);
makeCall.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if(ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(MainActivity.this, Manifest.permission.CALL_PHONE)
!= PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED){
ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(MainActivity.this, new String[]{Manifest.permission.CALL_PHONE}, 1);
}else {
call();
}
}
});
}
private void call(){
try{
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_CALL);
intent.setData(Uri.parse("tel:10086"));
startActivity(intent);
}catch (SecurityException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onRequestPermissionsResult(int requestCode, @NonNull String[] permissions, @NonNull int[] grantResults) {
switch (requestCode){
case 1:
if(grantResults.length > 0 && grantResults[0] == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED){
call();
}else{
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "You denied the permission!", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}break;
default:
}
}Tips:android 版本低时,效果可能不一样
可以看到Button里面首先判断了是否授权。借用了ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission()方法,接受两个参数,一个是上下文,还有一个权限名,源码如下
/**
* Determine whether you have been granted a particular permission.
*
* @param permission The name of the permission being checked.
*
* @return {@link android.content.pm.PackageManager#PERMISSION_GRANTED} if you have the
* permission, or {@link android.content.pm.PackageManager#PERMISSION_DENIED} if not.
*
* @see android.content.pm.PackageManager#checkPermission(String, String)
*/
public static int checkSelfPermission(@NonNull Context context, @NonNull String permission) {
if (permission == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("permission is null");
}
return context.checkPermission(permission, android.os.Process.myPid(), Process.myUid());
}已经授权的话就拨打电话。还未授权的话就调用ActivityCompat.requestPermission()方法来向用户申请权限,调用这个方法后会弹出一个对话框。然后我们判断一下返回的结果
/**
* Requests permissions to be granted to this application. These permissions
* must be requested in your manifest, they should not be granted to your app,
* and they should have protection level {@link android.content.pm.PermissionInfo
* #PROTECTION_DANGEROUS dangerous}, regardless whether they are declared by
* the platform or a third-party app.
*
* Normal permissions {@link android.content.pm.PermissionInfo#PROTECTION_NORMAL}
* are granted at install time if requested in the manifest. Signature permissions
* {@link android.content.pm.PermissionInfo#PROTECTION_SIGNATURE} are granted at
* install time if requested in the manifest and the signature of your app matches
* the signature of the app declaring the permissions.
*
*
* If your app does not have the requested permissions the user will be presented
* with UI for accepting them. After the user has accepted or rejected the
* requested permissions you will receive a callback reporting whether the
* permissions were granted or not. Your activity has to implement {@link
* android.support.v4.app.ActivityCompat.OnRequestPermissionsResultCallback}
* and the results of permission requests will be delivered to its {@link
* android.support.v4.app.ActivityCompat.OnRequestPermissionsResultCallback#onRequestPermissionsResult(
* int, String[], int[])} method.
*
*
* Note that requesting a permission does not guarantee it will be granted and
* your app should be able to run without having this permission.
*
*
* This method may start an activity allowing the user to choose which permissions
* to grant and which to reject. Hence, you should be prepared that your activity
* may be paused and resumed. Further, granting some permissions may require
* a restart of you application. In such a case, the system will recreate the
* activity stack before delivering the result to your
* {@link OnRequestPermissionsResultCallback#onRequestPermissionsResult(int, String[], int[])}.
*
*
* When checking whether you have a permission you should use {@link
* #checkSelfPermission(android.content.Context, String)}.
*
*
* Calling this API for permissions already granted to your app would show UI
* to the user to decided whether the app can still hold these permissions. This
* can be useful if the way your app uses the data guarded by the permissions
* changes significantly.
*
*
* You cannot request a permission if your activity sets {@link
* android.R.attr#noHistory noHistory} to true in the manifest
* because in this case the activity would not receive result callbacks including
* {@link OnRequestPermissionsResultCallback#onRequestPermissionsResult(int, String[], int[])}.
*
*
* The
* RuntimePermissions sample app demonstrates how to use this method to
* request permissions at run time.
*
*
* @param activity The target activity.
* @param permissions The requested permissions. Must me non-null and not empty.
* @param requestCode Application specific request code to match with a result
* reported to {@link OnRequestPermissionsResultCallback#onRequestPermissionsResult(int, String[], int[])}.
* Should be >= 0.
*
* @see OnRequestPermissionsResultCallback#onRequestPermissionsResult(int, String[], int[])
* @see #checkSelfPermission(android.content.Context, String)
* @see #shouldShowRequestPermissionRationale(android.app.Activity, String)
*/
public static void requestPermissions(final @NonNull Activity activity,
final @NonNull String[] permissions, final @IntRange(from = 0) int requestCode) {
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 23) {
ActivityCompatApi23.requestPermissions(activity, permissions, requestCode);
} else if (activity instanceof OnRequestPermissionsResultCallback) {
Handler handler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper());
handler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
final int[] grantResults = new int[permissions.length];
PackageManager packageManager = activity.getPackageManager();
String packageName = activity.getPackageName();
final int permissionCount = permissions.length;
for (int i = 0; i < permissionCount; i++) {
grantResults[i] = packageManager.checkPermission(
permissions[i], packageName);
}
((OnRequestPermissionsResultCallback) activity).onRequestPermissionsResult(
requestCode, permissions, grantResults);
}
});
}
}我们重写了onRequest.PermissionsResult()方法中,因为会回调到那个方法中。然后再判一下就ok了。
如果我们已经授权过权限的时候,只要进入Setting→Apps→RuntimePermissionTest→Permissions然后把它关了就ok了。
访问其他程序中的数据
内容提供器有两种,一种是使用现有的内容提供器来读取和操作相应程序的数据,另一种是创建自己的内容提供器给我们程序的数据提供外部访问接口。
如果一个程序通过内容提供器对其数据提供外部访问接口,那么任何其他程序就可以对这部分数据进行访问(比如Android系统自带的电话薄,短信等等)
ContentResolver基本用法
想要访问内容提供器中共享的数据,就需要使用ContentResolver类,通过Context中的getContentResolver()方法获取该类的实例。ContentResolver中提供了一系列的方法用于对数据进行CRUD操作,其中insert(),update(),delete(),query()等操作数据。
不同于SQLiteDatabase,ContentResolver中的增删改查方法都是不接受表名参数的,而是使用Uri参数代替,这个参数被称为内容URI。内容URI给内容提供器中的数据建立了唯一标识符,它主要由两部分组成:authority,path.authority是用于对不同的应用程序做区分的,一般为了避免冲突,都会采用程序包名的方式来命名。比如一个程序包名是com.example.app,那么该程序对的authority就可以命名为com.example.app.provider。path则是用于对同一个应用程序中不同的表做区分,通常会加到authority的后面。比如这个程序数据库中有两个表table1,table2,于是内容URI就是com.example.app.provider/table1,另一个略;再加上协议就是标准的格式了:
content://com.example.app.provider/table1这样ContentResolver就可以接受内容URI对象实现CRUD操作了。我们之前知道的Uri.parse()方法是可以解析字符串的。
Uri uri = Uri.parse("content://com.example.app.provider/table1");然后就利用Crusor这个对象来得到表中的数据
Cursor cursor = getContentResolver().query(
uri,
projection,
selection,
selectionArgs,
sortOrder;
) /**
* Query the given URI, returning a {@link Cursor} over the result set.
*
* For best performance, the caller should follow these guidelines:
*
* - Provide an explicit projection, to prevent
* reading data from storage that aren't going to be used.
* - Use question mark parameter markers such as 'phone=?' instead of
* explicit values in the {@code selection} parameter, so that queries
* that differ only by those values will be recognized as the same
* for caching purposes.
*
*
*
* @param uri The URI, using the content:// scheme, for the content to
* retrieve.
* @param projection A list of which columns to return. Passing null will
* return all columns, which is inefficient.
* @param selection A filter declaring which rows to return, formatted as an
* SQL WHERE clause (excluding the WHERE itself). Passing null will
* return all rows for the given URI.
* @param selectionArgs You may include ?s in selection, which will be
* replaced by the values from selectionArgs, in the order that they
* appear in the selection. The values will be bound as Strings.
* @param sortOrder How to order the rows, formatted as an SQL ORDER BY
* clause (excluding the ORDER BY itself). Passing null will use the
* default sort order, which may be unordered.
* @return A Cursor object, which is positioned before the first entry, or null
* @see Cursor
*/
public final @Nullable Cursor query(@RequiresPermission.Read @NonNull Uri uri,
@Nullable String[] projection, @Nullable String selection,
@Nullable String[] selectionArgs, @Nullable String sortOrder) {
return query(uri, projection, selection, selectionArgs, sortOrder, null);
}可以看到参数的描述。
然后就可以利用遍历的代码:
if(cursor != null){
while(cursor.moveToNext){
String column1 = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("column1"));
int column2 = cursor.getInt(cursor.getColumnIndex("column2"));
}
cursor.close();
}添加数据:
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("column1","text");
values.put("column2",1);
getContentResolver().insert(uri, values);更新:
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("column1","");
getContentResolver().update(uri, values, "column1 = ? and column2 = ?", new String[] {"text","1"});删除:
getContentResolver().delete(uri, "column2 = ?", new String[] {"1"});举个例子读取系统联系人
我使用的真机,使用虚拟机的可以选择自己创建几个联系人。
首先是布局:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/activity_contacts"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.example.wrjjrw.litepaltest.ContactsActivity">
<android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/contacts_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView>
LinearLayout>
这里我们使用的是RecyclerView所以要改一下dependencies:
compile 'com.android.support:recyclerview-v7:25.3.1'因为用的是这个布局,贴一个item的xml:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/contacts_layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/contacts_man"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/contacts_tel"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="3"
android:gravity="center"
/>
LinearLayout>然后加一个Contacts类:
public class Contacts {
private String name;
private String tel;
public Contacts(String name, String tel) {
this.name = name;
this.tel = tel;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getTel() {
return tel;
}
}然后加一个ContactsAdapter类:
public class ContactsAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<ContactsAdapter.ViewHolder> {
private List mContactsList;
static class ViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder{
TextView contactsName;
TextView contactsTel;
LinearLayout contactsLayout;
public ViewHolder(View view){
super(view);
contactsName = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.contacts_man);
contactsTel = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.contacts_tel);
contactsLayout = (LinearLayout) view.findViewById(R.id.contacts_layout);
}
}
public ContactsAdapter(List contactsList){
mContactsList = contactsList;
}
@Override
public ViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
View view = LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext()).
inflate(R.layout.simple_item, parent, false);
final ViewHolder holder = new ViewHolder(view);
holder.contactsLayout.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
int position = holder.getAdapterPosition();
Contacts contacts = mContactsList.get(position);
Toast.makeText(v.getContext(), "you click "+ contacts.getName() +
":"+contacts.getTel(), Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
});
return holder;
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(ViewHolder holder, int position) {
Contacts contacts = mContactsList.get(position);
holder.contactsName.setText(contacts.getName());
holder.contactsTel.setText(contacts.getTel());
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return mContactsList.size();
}
} 最后对活动的一个更改:
public class ContactsActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private List contactList = new ArrayList<>();
ContactsAdapter adapter = new ContactsAdapter(contactList);
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_contacts);
RecyclerView recyclerView = (RecyclerView) findViewById(R.id.contacts_view);
LinearLayoutManager layoutManager = new LinearLayoutManager(this);
recyclerView.setLayoutManager(layoutManager);
//ContactsAdapter adapter = new ContactsAdapter(contactList);
recyclerView.setAdapter(adapter);
if(ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(this, Manifest.permission.READ_CONTACTS)
!= PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED){
ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this,
new String[]{Manifest.permission.READ_CONTACTS}, 1);
}else{
readContacts();
}
}
private void readContacts(){
Cursor cursor = null;
try{
//find
cursor = getContentResolver().query(ContactsContract.
CommonDataKinds.Phone.CONTENT_URI, null, null, null, null);
if(cursor != null){
while(cursor.moveToNext()){
String name = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex(ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.DISPLAY_NAME));
String tel = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex(ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.NUMBER));
Contacts temp = new Contacts(name, tel);
contactList.add(temp);
}
adapter.notifyDataSetChanged();
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(cursor != null)
cursor.close();
}
}
@Override
public void onRequestPermissionsResult(int requestCode, @NonNull String[] permissions, @NonNull int[] grantResults) {
switch (requestCode){
case 1:
if(grantResults.length > 0 && grantResults[0] == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED){
readContacts();
}else{
Toast.makeText(this, "SHABI has denied the permission", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}break;
default:
}
}
} 仿照之前的call方法,这里我们写了readContact方法,CONTENT_URI已经是封装过的结果,不需要Uri.parse()。
还有权限别忘了:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_CONTACTS" />实现自己的内容提供器
访问其他程序的数据大概如此,只需要获取其应用程序的内容URI,然后借助ContentResolver进行CRUD操作。
创建内容提供器的步骤
官方推荐的方式是使用内容提供器,可以通过新建一个类去继承ContentProvider的方式来创建一个自己的内容提供器。ContentProvider类中有6个抽象方法,我们在使用子类继承的时候需要将这6个方法重写。
public class Myprovider extends ContentProvider{
@Override
public boolean onCreate() {
return false;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public Cursor query(Uri uri, String[] projection, String selection, String[] selectionArgs, String sortOrder) {
return null;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public Uri insert(Uri uri, ContentValues values) {
return null;
}
@Override
public int update(Uri uri, ContentValues values, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) {
return 0;
}
@Override
public int delete(Uri uri, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) {
return 0;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public String getType(Uri uri) {
return null;
}
}快捷键可以很快都自动生成。
/*
* @return true if the provider was successfully loaded, false otherwise
*/
public abstract boolean onCreate();
/*
* @param uri The URI to query. This will be the full URI sent by the client;
* if the client is requesting a specific record, the URI will end in a record number
* that the implementation should parse and add to a WHERE or HAVING clause, specifying
* that _id value.
* @param projection The list of columns to put into the cursor. If
* {@code null} all columns are included.
* @param selection A selection criteria to apply when filtering rows.
* If {@code null} then all rows are included.
* @param selectionArgs You may include ?s in selection, which will be replaced by
* the values from selectionArgs, in order that they appear in the selection.
* The values will be bound as Strings.
* @param sortOrder How the rows in the cursor should be sorted.
* If {@code null} then the provider is free to define the sort order.
* @return a Cursor or {@code null}.
*/
public abstract @Nullable Cursor query(@NonNull Uri uri, @Nullable String[] projection,
@Nullable String selection, @Nullable String[] selectionArgs,
@Nullable String sortOrder);
/**
* Implement this to handle requests to insert a new row.
* As a courtesy, call {@link ContentResolver#notifyChange(android.net.Uri ,android.database.ContentObserver) notifyChange()}
* after inserting.
* This method can be called from multiple threads, as described in
* Processes
* and Threads.
* @param uri The content:// URI of the insertion request. This must not be {@code null}.
* @param values A set of column_name/value pairs to add to the database.
* This must not be {@code null}.
* @return The URI for the newly inserted item.
*/
public abstract @Nullable Uri insert(@NonNull Uri uri, @Nullable ContentValues values);
/**
* Implement this to handle requests to update one or more rows.
* The implementation should update all rows matching the selection
* to set the columns according to the provided values map.
* As a courtesy, call {@link ContentResolver#notifyChange(android.net.Uri ,android.database.ContentObserver) notifyChange()}
* after updating.
* This method can be called from multiple threads, as described in
* Processes
* and Threads.
*
* @param uri The URI to query. This can potentially have a record ID if this
* is an update request for a specific record.
* @param values A set of column_name/value pairs to update in the database.
* This must not be {@code null}.
* @param selection An optional filter to match rows to update.
* @return the number of rows affected.
*/
public abstract int update(@NonNull Uri uri, @Nullable ContentValues values,
@Nullable String selection, @Nullable String[] selectionArgs);
/**
* Implement this to handle requests to delete one or more rows.
* The implementation should apply the selection clause when performing
* deletion, allowing the operation to affect multiple rows in a directory.
* As a courtesy, call {@link ContentResolver#notifyChange(android.net.Uri ,android.database.ContentObserver) notifyChange()}
* after deleting.
* This method can be called from multiple threads, as described in
* Processes
* and Threads.
*
* The implementation is responsible for parsing out a row ID at the end
* of the URI, if a specific row is being deleted. That is, the client would
* pass in content://contacts/people/22 and the implementation is
* responsible for parsing the record number (22) when creating a SQL statement.
*
* @param uri The full URI to query, including a row ID (if a specific record is requested).
* @param selection An optional restriction to apply to rows when deleting.
* @return The number of rows affected.
* @throws SQLException
*/
public abstract int delete(@NonNull Uri uri, @Nullable String selection,
@Nullable String[] selectionArgs);
/**
* Implement this to handle requests for the MIME type of the data at the
* given URI. The returned MIME type should start with
* vnd.android.cursor.item for a single record,
* or vnd.android.cursor.dir/ for multiple items.
* This method can be called from multiple threads, as described in
* Processes
* and Threads.
*
* Note that there are no permissions needed for an application to
* access this information; if your content provider requires read and/or
* write permissions, or is not exported, all applications can still call
* this method regardless of their access permissions. This allows them
* to retrieve the MIME type for a URI when dispatching intents.
*
* @param uri the URI to query.
* @return a MIME type string, or {@code null} if there is no type.
*/
public abstract @Nullable String getType(@NonNull Uri uri);
上面的除了最后一个,其他都见过。温故而知新可以弃坑也。
可以发现基本每个方法都有URI,这个参数也正是调用ContentResolver的增删改查方法传递过来的。但我们需要对传入的Uri参数进行解析,丛中分析出调用方期望访问的表和数据。
一个标准的内容URI:
content://com.example.app.provider/table1我们可以在之后添加一个/1
content://com.example.app.provider/table1/1这样就代表我们想要访问的是table1表中id为1的数据。以路径结尾则代表访问所有数据,以id结尾则访问该表中拥有相应id的数据。我们可以使用通配符的方式来分别匹配这两种格式内容的URI. *代表任意长度的任意字符。#这个代表任意长度的数字。
上面的两个可以改写成这样:
content://com.example.app.provider/*
content://com.example.app.provider/table1/#我们再通过UriMatcher这个类就可以轻松地实现匹配内容URI的功能。UriMatcher中提供了addURI()的方法。
/**
* @param authority the authority to match
* @param path the path to match. * may be used as a wild card for
* any text, and # may be used as a wild card for numbers.
* @param code the code that is returned when a URI is matched
* against the given components. Must be positive.
*/
public void addURI(String authority, String path, int code)改一下:
public class Myprovider extends ContentProvider{
public static final int TABLE1_DIR = 0;
public static final int TABLE1_ITEM = 1;
public static final int TABLE2_DIR = 2;
public static final int TABLE2_ITEM = 3;
private static UriMatcher uriMatcher;
static {
uriMatcher = new UriMatcher(UriMatcher.NO_MATCH);
uriMatcher.addURI("com.example.wrjjrw.litepaltest","table1",TABLE1_DIR);
uriMatcher.addURI("com.example.wrjjrw.litepaltest","table1/#",TABLE1_ITEM);
uriMatcher.addURI("com.example.wrjjrw.litepaltest","table2",TABLE2_DIR);
uriMatcher.addURI("com.example.wrjjrw.litepaltest","table2/#",TABLE2_ITEM);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreate() {
return false;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public Cursor query(Uri uri, String[] projection, String selection, String[] selectionArgs, String sortOrder) {
switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)){
case TABLE1_DIR:
//query all data in table1
break;
case TABLE1_ITEM:
//query single data in table1
break;
case TABLE2_DIR:
//query all data in table2
break;
case TABLE2_ITEM:
//query single data in table2
break;
default:
}
return null;
}
...
}insert(),update(),delete()这三个方法和query()其实差不多的。还有一个是getType().用于获取Uri对象所对应的MIME类型。一个内容Uri所对应的MIME字符串主要由3部分组成,Android对这三个部分做了规定:
- 必须以vnd开头
- 如内容URI以路径结尾,则后接
android.cursor.dir/,如果以id结尾,则后接android.cursor.item/ - 最后接上vnd..
举个例子:
content://com.example.app.provider/table1
//↓
vnd.android.cursor.dir/vnd.com.example.app.provider.table1
content://com.example.app.provider/table1/1
//↓
vnd.android.cursor.item/vnd.com.example.app.provider.table1修改getType():
@Nullable
@Override
public String getType(Uri uri) {
switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)){
case TABLE1_DIR:
return "vnd.android.cursor.dir/vnd.com.example.wrjjrw.litepaltest.provider.table1";
case TABLE1_ITEM:
return "vnd.android.cursor.item/vnd.com.example.wrjjrw.litepaltest.provider.table1";
case TABLE2_DIR:
return "vnd.android.cursor.dir/vnd.com.example.wrjjrw.litepaltest.provider.table2";
case TABLE2_ITEM:
return "vnd.android.cursor.item/vnd.com.example.wrjjrw.litepaltest.provider.table2";
}
return null;
}理论上,一个内容提供器已经完成,理论上你也可能一脸蒙蔽。
实践
借用上次的项目基础继续开发。
右键包名→New→Other→Content Provider新建一个DatabaseProvider,authority写com.example.wrjjrw.broadcastbestpractise.provider。两个属性都勾上。Exported是指是否允许外部程序访问我们的内容提供器,Enabled属性是指是否启用这个内容提供器。FInish
修改:
package com.example.wrjjrw.broadcastbestpractise;
import android.content.ContentProvider;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.content.UriMatcher;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.net.Uri;
public class DatabaseProvider extends ContentProvider {
public static final int BOOK_DIR = 0;
public static final int BOOK_ITEM = 1;
public static final int CATEGORY_DIR = 2;
public static final int CATEGORY_ITEM = 3;
public static final String AUTHORITY = "com.example.wrjjrw.broadcastbestpractise.provider";
private static UriMatcher uriMatcher;
private MyDatabaseHelper dbHelper;
static {
uriMatcher = new UriMatcher(UriMatcher.NO_MATCH);
uriMatcher.addURI(AUTHORITY, "book", BOOK_DIR);
uriMatcher.addURI(AUTHORITY, "book/#", BOOK_ITEM);
uriMatcher.addURI(AUTHORITY, "category", CATEGORY_DIR);
uriMatcher.addURI(AUTHORITY, "category/#", CATEGORY_ITEM);
}
public DatabaseProvider() {
}
@Override
public int delete(Uri uri, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) {
// Implement this to handle requests to delete one or more rows.
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
int deletedRows = 0;
switch(uriMatcher.match(uri)){
case BOOK_DIR:
deletedRows = db.delete("Book", selection, selectionArgs);
break;
case BOOK_ITEM:
String bookId = uri.getPathSegments().get(1);
deletedRows = db.delete("Book", "id = ?",new String[]{ bookId });
break;
case CATEGORY_DIR:
deletedRows = db.delete("Category", selection, selectionArgs);
break;
case CATEGORY_ITEM:
String categoryId = uri.getPathSegments().get(1);
deletedRows = db.delete("Category", "id = ?", new String[]{categoryId});
break;
}
return deletedRows;
}
@Override
public String getType(Uri uri) {
// TODO: Implement this to handle requests for the MIME type of the data
// at the given URI.
switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)){
case BOOK_DIR:
return "vnd.android.cursor.dir/vnd.com.example.wrjjrw.broadcastbestpractise.provider.book";
case BOOK_ITEM:
return "vnd.android.cursor.item/vnd.com.example.wrjjrw.broadcastbestpractise.provider.book";
case CATEGORY_DIR:
return "vnd.android.cursor.dir/vnd.com.example.wrjjrw.broadcastbestpractise.provider.category";
case CATEGORY_ITEM:
return "vnd.android.cursor.item/vnd.com.example.wrjjrw.broadcastbestpractise.provider.category";
}
return null;
}
@Override
public Uri insert(Uri uri, ContentValues values) {
// TODO: Implement this to handle requests to insert a new row.
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
Uri uriReturn = null;
switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)){
case BOOK_DIR:
case BOOK_ITEM:
long newBookId = db.insert("Book", null, values);
uriReturn = Uri.parse("content://" + AUTHORITY + "/book/" + newBookId);
break;
case CATEGORY_DIR:
case CATEGORY_ITEM:
long newCategoryId = db.insert("Category", null, values);
uriReturn = Uri.parse("content://" + AUTHORITY + "/category" + newCategoryId);
break;
default:
break;
}
return uriReturn;
}
@Override
public boolean onCreate() {
// TODO: Implement this to initialize your content provider on startup.
dbHelper = new MyDatabaseHelper(getContext(), "BookStore.db", null, 2);
return true;
}
@Override
public Cursor query(Uri uri, String[] projection, String selection,
String[] selectionArgs, String sortOrder) {
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getReadableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = null;
switch(uriMatcher.match(uri)){
case BOOK_DIR:
cursor = db.query("Book", projection,selection,selectionArgs, null, null, sortOrder);
break;
case BOOK_ITEM:
String bookId = uri.getPathSegments().get(1);
cursor = db.query("Book",projection, "id = ?", new String[]{bookId}, null, null, sortOrder);
break;
case CATEGORY_DIR:
cursor = db.query("Category", projection, selection, selectionArgs, null, null, sortOrder);
break;
case CATEGORY_ITEM:
String categoryId = uri.getPathSegments().get(1);
cursor = db.query("Category" ,projection, "id = ?" , new String[]{categoryId}, null, null, sortOrder);
break;
default:
break;
}
return cursor;
}
@Override
public int update(Uri uri, ContentValues values, String selection,
String[] selectionArgs) {
// TODO: Implement this to handle requests to update one or more rows.
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
int updateRows = 0;
switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)){
case BOOK_DIR:
updateRows = db.update("Book", values,selection,selectionArgs);
break;
case BOOK_ITEM:
String bookId = uri.getPathSegments().get(1);
updateRows = db.update("Book",values, "id = ?", new String[]{bookId});
break;
case CATEGORY_DIR:
updateRows = db.update("Category", values, selection, selectionArgs);
break;
case CATEGORY_ITEM:
String categoryId = uri.getPathSegments().get(1);
updateRows = db.update("Category" ,values, "id = ?" , new String[]{categoryId});
break;
default:
break;
}
return updateRows;
}
}静态方法
这里添加了几个方法,onCreate()方法,这个方法的代码很短,只是创建MyDatabaseHelper的实例,然后返回true表示提供器初始化成功,query()方法同样先得到实例,然后传入Uri参数,访问单条数据的时候,这里使用了getPathSegments()方法,它会将内容URI权限之后的部分以“/”符号分割,并把分割后的结果放入到一个字符串列表中,这个列表中第0个位置就是路径,第一个位置就是存放的id.得到id之后,在通过selection和selectioArgs参数进行约束。其他方法也相同.
insert()方法需要返回一个能够代表这条新增数据的URI,所以我们需要调用Uri.parse()方法把内容URI转化成URI对象,最后返回。update()返回一下受影响的行数,delete()返回一下删除的行数,getType()方法则是按照之前讲的获取Uri对象所对应的MIME类型。同时可以发现AndroidManifest.xml中也多了一些代码:
<provider
android:name=".DatabaseProvider"
android:authorities="com.example.wrjjrw.broadcastbestpractise.provider"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true">
provider>它已经帮我们注册过了。
新建一个ProviderTest工程来测试一下。
MainActivity.xml:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/activity_main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.example.wrjjrw.providertest.MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/add_Book"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAllCaps="false"
android:text="Add to Book"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/query_Book"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAllCaps="false"
android:text="Query from Book"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/update_Book"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAllCaps="false"
android:text="Update Book"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/delete_Book"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAllCaps="false"
android:text="Delete from Book"
/>
LinearLayout>MainActivity:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private String newId;
private final static String Tag = "MainActivity";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button addData = (Button) findViewById(R.id.add_Book);
addData.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Uri uri = Uri.parse("content://com.example.wrjjrw.broadcastbestpractise.provider/book");
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("name", "A Clash of Kings");
values.put("author", "George Martin");
values.put("pages", 1040);
values.put("price", 22.85);
Uri newUri = getContentResolver().insert(uri, values);
// newId = newUri.getPathSegments().get(1);
}
});
Button queryData = (Button) findViewById(R.id.query_Book);
queryData.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Uri uri = Uri.parse("content://com.example.wrjjrw.broadcastbestpractise.provider/book");
Cursor cursor = getContentResolver().query(uri, null, null, null, null);
if(cursor != null){
while(cursor.moveToNext()) {
String name = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("name"));
String author = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("author"));
int pages = cursor.getInt(cursor.getColumnIndex("pages"));
double price = cursor.getDouble(cursor.getColumnIndex("price"));
Log.d(Tag, "Book name is " + name + ",and it's price is " + price);
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, name + " costs me " + price, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
cursor.close();
}
}
});
Button updateData = (Button) findViewById(R.id.update_Book);
updateData.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Uri uri = Uri.parse("content://com.example.wrjjrw.broadcastbestpractise.provider/book" + newId);
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("name", "A storm of Swords");
values.put("pages", 1216);
values.put("price", 24.05);
getContentResolver().update(uri, values, null, null);
}
});
Button deleteData = (Button) findViewById(R.id.delete_Book);
deleteData.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Uri uri = Uri.parse("content://com.example.wrjjrw.broadcastbestpractise.provider/book" + newId);
getContentResolver().delete(uri, null, null);
}
});
}
}这里写了四个按钮负责CRUD,方法和之前的类似,不做详解。
Git
书上又一次提到了Git,就稍微复习一下。
打开所在盘,git init.
忽略文件
代码仓库意见建好了,但是不是所有的文件都需要加入到版本控制中。build下的文件都是编译项目时产生的,不应该加入。
Git提供了一种可配性强机制来允许用户将指定的文件或目录排除在版本控制外,它会检查代码仓库的目录下是否有一个名为.gitignore的这样的文件,如果存在就读取,并把里面指定的文件或目录排除在外。.gitignore中指定的文件是可以使用*通配符的。
AS在创建项目的时候会创建连个.gitignore文件,一个在根目录下,一个在app模块下。
这是根目录下的:
*.iml
.gradle
/local.properties
/.idea/workspace.xml
/.idea/libraries
.DS_Store
/build
/captures
.externalNativeBuild还有一个我就不贴了,当然这两个文件我们都可以修改来满足特定的需求。比如说把test里的文件都忽略,只需要修改在app下的.gitignore
/build
/src/test配置完就可以了提交代码。 git add .然后一个`git commit -m "First commit"
查看修改内容
当我们在进行项目的修改或者维护时,会容易忘记(可能程序都容易健忘吧),不过问题不大。
git status可以查看修改情况。
我们对这个代码下一点毒。
然后`git status发现有一串红字说我们对代码下了毒,是的没错,我们应该告诉他们,我们的确下了毒。
git diff就可以查看我们对所有文件修改的内容了。
git diff app/src/main/java/com/example/wrjjrw/providertest/MainActivity.java这样就可以具体查看我在哪个杯子里下的哪种毒了(小心毒死自己)
然后就来一个git add .;如果你后悔了,不要紧,还可以吐出来。git reset或者git reset HEAD app/src/main/java/com/example/wrjjrw/providertest/MainActivity.java这样也可以。
查看提交记录
如果一个项目开发几个月了,我们可能已经执行过上百次的提交动作,然后就可以使用git log这个命令来看看。可以看到每次的修改的人和id号,根据id号又可以进行查看更详细的内容。
git log ec69cb85cd599a624ecb86869f11c5a726a33005 -1 -p表示我们只想看一行记录,-p表示我们想要查看具体修改了哪些内容。
问题:
- MIME是什么:
Click me
- 在此,我碰到了两次空指针问题
都是因为db没有初始化。。。。。