【Python】基于候选数的解数独算法 + 使用wxPython编写程序界面
0、本文提供了一种基于候选数的解数独算法,并使用wxPython编写了简单的程序界面
wxPython的安装和安装后的路径配置问题可参见:
【Eclipse+PyDev+wxPython】wxPython的安装注意事项&&安装后Eclipse中仍然报错问题的解决
1、基于候选数的解数独算法具体流程如下:
该算法类似于人工求解数独时所用到的假设解法,假设->回溯->假设->回溯……->得解
由于数独本身的规则所限,每行每列每个小区域都只能是1~9,而不能有任何重复的数字
所以,对应于每一个求解状态,每一个空格都会存在一组候选数集合,即可以填入该空格的候选数字(可以为空集)
(1)首先,找到一个候选数最少的空格,逐一假设填入
(2)如果在某一求解状态下,有空格的候选数集合为空(即没有合法数字可供填入),则回溯到上一状态继续尝试
(3)如果某一空格遍历假设了所有候选数而仍未得到解,则回溯到上一个假设空格继续尝试
(4)重复这一过程,直到得到一个解返回结果,或搜索完所有可能的解
(5)为实现这一算法,还需要一个栈用来存储过程中的状态,每次填入数字前入栈,而每次回溯时出栈
2、使用这一算法,实测能够秒解所有入门级数独,对于骨灰级的数独大概需要1到2min的时间
程序函数伪代码:
Solve_Sudoku(*Map, mode)
{
if Have_Find_Single_Solution
return
if Complete
Output_Solution()
if Stack!=empty
Erase_out()
Stack_out()
return
else
Update_Candidate()
Find_MIN_Candidate()
if MIN==0
Erase_out()
Stack_out()
return;
else
for i=1:MIN
Stack_in()
Fill_in()
Solve_Sudoku()
if Have_Find_Single_Solution
return
if Stack!=empty
Erase_out()
Stack_out()
return
}
Update_Candidate()
{
for Map[i][j]
if Map[i][j]!=0
for Candidate[i][:]
if Map[i][:]==0
Candidate[i][:][Map[i][j]-1]=0
for Candidate[:][j]
if Map[:][j]==0
Candidate[:][j][Map[i][j]-1]=0
for Candidate[3*(i//3):3*(i//3)+2][3*(j//3):3*(j//3)+2]
if Map[:][:]==0
Candidate[:][:][Map[i][j]-1]=0
}
Find_MIN_Candidate()
{
Min=9
for candidate[i][j][:]
count=sum(candidate[i][j][:])
if countPython具体实现代码:(使用递归函数实现,0表示空格,各模块代码在注释中均有比较详细的说明)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""##################
基于候选数的数独求解
Author: Alex_P @UCAS
##################"""
from numpy import array, zeros, ones, int32
"""#################数独#################"""
Sudoku = array([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 8, 5, 0, 0],
[2, 0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 0, 3, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 6, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[4, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 9, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 5, 0, 8, 0, 0],
[7, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 6],
[0, 3, 9, 7, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 2, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 7, 0]], dtype = int32)
#Notice:坐标轴(0~8, 0~8),表示为range(0, 9)
Solution = zeros((9, 9), dtype = int32)# 解阵列
"""#################栈类#################"""
class Stack:
# self
def __init__(self):
self.items = []
# 检查栈是否为空
def isEmpty(self):
return len(self.items) == 0
# 入栈
def push(self, item):
self.items.append(item)
# 出栈
def pop(self):
return self.items.pop()
# 提取栈顶元素
def peek(self):
if not self.isEmpty():
return self.items[len(self.items) - 1]
# 获取栈中元素个数
def size(self):
return len(self.items)
"""#################定义栈等#################"""
# 栈类
S = Stack()
# 栈内元素
for p in range(1, 81):
# S_Map1, S_Map2, S_Map3, ……, S_Map80
S_Map = "S_Map" + "%d" %p
exec(S_Map + " = zeros((9, 9), dtype = int32)")
# 单解标识
FSingleSolution = False
"""#################打印函数#################"""
def Print_Sudoku(Map):
print "—————————"
for i in range(0, 3):
for j in range(0, 3):
Map_str = "|"
for m in range(0, 3):
for n in range(0, 3):
Map_str = Map_str + " %d" %Map[i * 3 + j][m * 3 + n]
Map_str = Map_str + " |"
print Map_str
print "—————————"
"""#################求解函数#################"""
#Map->Sudoku
#mode->0(仅搜索单解,返回解),非0(搜索所有解,返回未求解原数独)
def Solve_Sudoku(Map, mode):
# 单解跳出
global FSingleSolution
if FSingleSolution == True:
return Map
# 候选数阵列
Candidates = ones((9, 9, 9), dtype = int32)
# 检查是否求解完毕
FComplete = True
for i in range(0, 9):
for j in range(0, 9):
if Map[i][j] == 0:
FComplete = False
break
# 求解完毕
if FComplete == True:
# 输出解
print "Solution Accomplished!"
global Solution
Solution = Map.copy()# 独立复制
Print_Sudoku(Solution)
# 找到单解后返回
if mode == 0:
FSingleSolution = True
return Map
# 返回操作并出栈
if S.isEmpty() == False:
Map = S.peek().copy()
S.pop()
#print "Stack OUT... (size:", S.size(), ")"
return Map
# 未求解完毕
else:
# 更新候选数阵列
#print "Updating Candidates..."
for i in range(0, 9):
for j in range(0, 9):
if Map[i][j] != 0:
# 列
for m in range(0, 9):
if Map[m][j] == 0:
Candidates[m][j][Map[i][j] - 1] = 0
# 行
for n in range(0, 9):
if Map[i][n] == 0:
Candidates[i][n][Map[i][j] - 1] = 0
# 单元九宫格
for m in range(3 * (i // 3), 3 * (i // 3) + 3):
for n in range(3 * (j // 3), 3 * (j // 3) + 3):
if Map[m][n] == 0:
Candidates[m][n][Map[i][j] - 1] = 0
# 寻找最少候选数
#print "Finding MIN Candidates..."
Min = 9
for m in range(0, 9):
for n in range(0, 9):
count = sum(Candidates[m][n][:])
if count < Min:
Min = count
Min_i = m
Min_j = n
#print Min, "candidate(s) available at (", Min_i + 1, ",", Min_j + 1, ")"
# 候选数为0(无解分支)
if Min == 0:
# 返回操作并出栈
Map = S.peek().copy()
S.pop()
#print "Stack OUT... (size:", S.size(), ")"
return Map
# 存在候选数
else:
# 逐一假设
for k in range(1, Min + 1):
# 入栈
p = "%d" %(S.size() + 1)
S_Map = "S_Map" + p
exec(S_Map + " = Map.copy()")
exec("S.push(" + S_Map + ")")# S.push(S_Map【S.size()+1】)
#print "Stack IN... (size:", S.size(), ")"
# 填入候选数
count = 0
for o in range(0, 9):
count = count + Candidates[Min_i][Min_j][o]
if count == k:
break
Map[Min_i][Min_j] = o + 1
#Print_Sudoku(Map)
# 使用递归函数进行回溯求解
Map = Solve_Sudoku(Map, mode)
# 单解跳出
if FSingleSolution == True:
return Map
# 返回操作并出栈
if S.isEmpty() == False:
Map = S.peek().copy()
S.pop()
#print "Stack OUT... (size:", S.size(), ")"
return Map
"""#################主函数#################"""
def main():
Print_Sudoku(Sudoku)
Solve_Sudoku(Sudoku, 0)# 搜索单解
#Solve_Sudoku(Sudoku, 1)# 搜索所有解
#Print_Sudoku(Solution)
"""#################main#################"""
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()3、使用wxPython编写程序界面,大致效果如下:(求解完成后可清除并重复使用)
具体实现代码:(需调用前述Sudoku,各模块代码在注释中均有比较详细的说明)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""###################
基于候选数的数独求解UI界面
Author: Alex_P @UCAS
###################"""
import wx
import Sudoku
from numpy import zeros, int32
"""#################wx.App类#################"""
class App(wx.App):
def OnInit(self):
self.frame = Frame()
self.frame.Show(True)# 显示窗口
#self.frame.Show(False)# 隐藏窗口
self.SetTopWindow(self.frame)# 设置为顶层窗口
return True
"""#################wx.Frame瀛愮被#################"""
class Frame(wx.Frame):
# 初始化界面
def __init__(self):
wx.Frame.__init__(self, None, -1, "An Easy Sukudo Solver", size = (400, 500))
self.setupMenuBar()# 菜单
panel = wx.Panel(self, -1)# 面板
wx.StaticText(panel, -1, "Sukudo", (150, 20), (80, -1), wx.ALIGN_CENTER)
# (位置), (大小), 居中
mapPosX = 30# 左上角起始点x坐标
mapPosY = 50# 左上角起始点y坐标
textWidth = 25# 文本框宽度
idleWidth = 10# 横向间距
idleHeight = 35# 纵向间距
sperateLength = 10# 九宫格间距
# 初始化数独输入框
for i in range(0, 9):
for j in range(0, 9):
Map_i_j = "self.Map_" + "%d" %i + "_" +"%d" %j# self.Map_0_0...Map_i_j...Map_8_8
exec(Map_i_j + " = wx.TextCtrl(panel, -1, '0', pos = (mapPosX + j * (textWidth + idleWidth) + j // 3 * sperateLength, mapPosY + i * idleHeight + i // 3 * sperateLength), size = (textWidth, -1), style = wx.TE_CENTER)")
# 初始化按钮
self.button = wx.Button(panel, -1, "Solve", pos = (152, 385), size = (80, 30))
self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnClickButton, self.button)# 事件绑定
self.button.SetDefault()# 设置为默认按钮
# 初始化阵列
self.Sudoku = zeros((9, 9), dtype = int32)# 数独阵列
self.Solution = zeros((9, 9), dtype = int32)# 解阵列
# 点击按钮的事件响应
def OnClickButton(self, event):
Label = self.button.GetLabel()# 获取按钮状态
# 解数独
if Label == "Solve":
self.button.SetLabel("Waiting...")# 按钮提示等待
FAllZero = True# 全零标识
for i in range(0, 9):
for j in range(0, 9):
# self.Map_0_0...Map_i_j...Map_8_8
Map_i_j = "self.Map_" + "%d" %i + "_" +"%d" %j
# 读取输入阵列
exec("self.Sudoku[i][j] = " + Map_i_j + ".GetValue()")
# 检验输入数独阵列是否合乎要求(0~9)
if self.Sudoku[i][j] != 0 and self.Sudoku[i][j] != 1 and self.Sudoku[i][j] != 2 and self.Sudoku[i][j] != 3 and self.Sudoku[i][j] != 4 and self.Sudoku[i][j] != 5 and self.Sudoku[i][j] != 6 and self.Sudoku[i][j] != 7 and self.Sudoku[i][j] != 8 and self.Sudoku[i][j] != 9:
dlg = wx.MessageDialog(self, "Only numbers (0~9, 0 for blank) allowed!", "Error", wx.OK)
dlg.ShowModal()
dlg.Destroy()
self.button.SetLabel("Solve")# 刷新按钮
return
# 检验数独阵列是否输入
if FAllZero == True and self.Sudoku[i][j] != 0:
FAllZero = False
# 错误提示
if FAllZero == True:
dlg = wx.MessageDialog(self, "Please input your Sukudo!", "Error", wx.OK)
dlg.ShowModal()
dlg.Destroy()
self.button.SetLabel("Solve")# 刷新按钮
return
#Sudoku.Print_Sudoku(self.Sudoku)
self.Solution = Sudoku.Solve_Sudoku(self.Sudoku, 0)# 解数独
Sudoku.FSingleSolution = False# 刷新求解函数状态
#Sudoku.Print_Sudoku(self.Solution)
for i in range(0, 9):
for j in range(0, 9):
Map_i_j = "self.Map_" + "%d" %i + "_" +"%d" %j# self.Map_0_0...Map_i_j...Map_8_8
exec(Map_i_j + ".SetValue(str(self.Solution[i][j]))")# 输出解阵列
self.button.SetLabel("Clear")
# 清除
elif Label == "Clear":
for i in range(0, 9):
for j in range(0, 9):
Map_i_j = "self.Map_" + "%d" %i + "_" +"%d" %j# self.Map_0_0...Map_i_j...Map_8_8
exec(Map_i_j + ".SetValue('0')")# 清除数独阵列
self.button.SetLabel("Solve")
# 建立菜单
def setupMenuBar(self):
self.CreateStatusBar()# 创建
Menu = wx.MenuBar()# 总菜单
programMenu = wx.Menu()# 程序菜单
# 将关于加入程序菜单
menuabout = programMenu.Append(wx.ID_ABOUT, "&About", "About this program")
# 将退出加入程序菜单
menuexit = programMenu.Append(wx.ID_EXIT, "&Exit", "Exit program")
Menu.Append(programMenu, "&Menu")# 将程序菜单加入总菜单
# 事件绑定
self.Bind(wx.EVT_MENU, self.onAbout, menuabout)# 关于事件
self.Bind(wx.EVT_MENU, self.onExit, menuexit)# 退出事件
self.SetMenuBar(Menu)
# 点击关于的事件响应
def onAbout(self, evt):
dlg = wx.MessageDialog(self, "An Easy Sudoku Solver\n'0' represents blank\n\nAuthor: Alex_Pan @UCAS", "About this program", wx.OK)
dlg.ShowModal()
dlg.Destroy()
# 点击退出的事件响应
def onExit(self, evt):
self.Close(True)
"""#################主函数#################"""
def main():
app = App()
app.MainLoop()# 将app作为主事件消息循环
"""#################main#################"""
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()4、【示例求解过程】
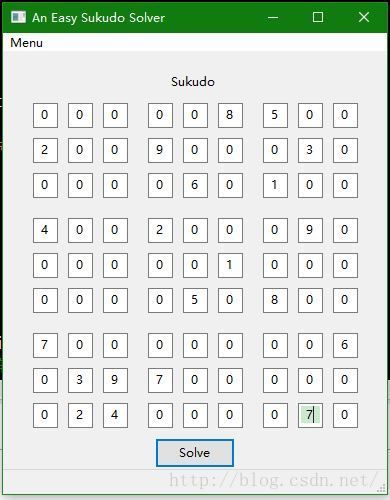
输入待求解数独:
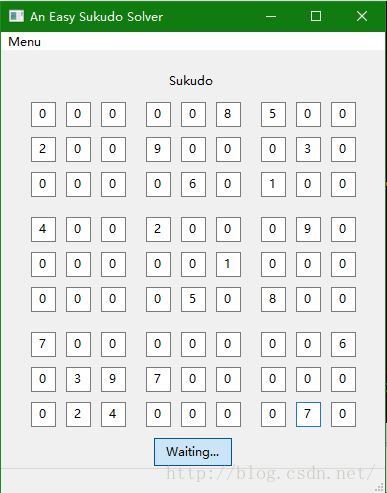
求解中:
求解结果:
清空:
希望能够对大家有所帮助和启发~