扫描dir目录函数之scandir()
scandir: 读取特定的目录数据头文件: dirent.h 函数定义: int scandir(const char *dir, struct dirent ***namelist, int (*select)(const struct dirent *), int (*compar)(const struct dirent**, const struct dirent**));
说明: scandir()会扫描参数dir指定的目录文件, 经由参数select指定的函数来挑选目录结构至参数 namelist数组中, 最后在调用参数compar指定的函数来排序namelist数组中的目录数据. 每次从目录文件中读取一个目录结构后便将此结构传给参数select所指的函数, select函数若不想要将此目录机构复制到 namelist数组就返回0, 若select为空指针则代表选择所有的目录结构. scandir()会调用qsort()来排序数据, 参数compar则为qsort()的参数, 若是要排列目录名称字母则可使用alphasort(). 结构dirent定义请参考readdir(). 成功则返回复制到namelist数组中的数据结构数目, 有错误发生则返回-1. ENOMEM表示核心内存不足.
其中 dirent原型为:
struct linux_dirent64 {
u64 d_ino;
s64 d_off;
unsigned short d_reclen;
unsigned char d_type;
char d_name[0];
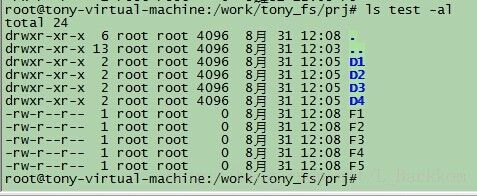
};测试一下该函数功能,新建一个文件夹“test”在里面建若干文件和文件夹 如图:
编写测试代码:
#include
int
main(void)
{
struct dirent **namelist;
int n;
n = scandir(".", &namelist, NULL, alphasort);
if (n < 0)
perror("scandir");
else {
while (n--) {
printf("%s:%d\n", namelist[n]->d_name,namelist[n]->d_type);
free(namelist[n]);
}
free(namelist);
}
} 运行发现:
F5:0
F4:0
F3:0
F2:0
F1:0
D4:0
D3:0
D2:0
D1:0
..:0
.:0
说明namelist[n]->d_type对文件类型支持还是不够的,需要用stat函数继续对其分析。
完整测试代码如下:
struct dirent **namelist;
struct stat tStat;
int n;
char strTmp[256];
n = scandir("/prj/test/", &namelist, NULL, alphasort);
if (n < 0)
perror("scandir");
else {
while (n--) {
snprintf(strTmp, 256, "%s/%s", "/prj/test/", namelist[n]->d_name);
strTmp[255] = '\0';
if ((stat(strTmp, &tStat) == 0))
{
if(S_ISDIR(tStat.st_mode))
{
printf("%s:is a dir\n", namelist[n]->d_name);
}
else if(S_ISREG(tStat.st_mode))
{
printf("%s:is a file\n", namelist[n]->d_name);
}
else
{
printf("%s:unknow2\n", namelist[n]->d_name);
}
}
free(namelist[n]);
}
free(namelist);
}
此时打印信息为:
F5:is a file
F4:is a file
F3:is a file
F2:is a file
F1:is a file
D4:is a dir
D3:is a dir
D2:is a dir
D1:is a dir
..:is a dir
.:is a dir
将该目录下的文件及目录都识别出来了