记录我的爬虫之路1--爬虫起步的urlib.request Python写一个不用Scrapy框架的裸奔小幼儿爬爬
这几天得知保研失败了….刚好卡在保研名额外一名…虽然最近写什么东西都忍不住碎碎念叨这一句话
=。=,但是好像也觉得能找到喜欢的东西了~比如现在打算认真学的爬虫了~今天刚把小甲鱼入门python的爬虫部分学完,利用scrapy框架能顺利地爬出dmoztools的一点小东西了,所以先做个回顾,具体的写一些最近学习的知识,便于下一阶段的学习!
不管怎么样,希望能快快找到实习~新生活还是得开始的嘛!
突然想到学python之前我还跟猪文豪嚷嚷着我这辈子就走jsp html css 的网页全栈之路或者java写android APP的路….结果入门python以后…..真香!
1. 爬虫代码第一个问题: python 怎么联网?
还好我们的python自带电池: url+lib → urllib
↓
url的一般格式: protocol://hostname[:port]/path/[;parameters][?query]#fragment
protocol协议:http https ftp file(本地磁盘) ed2k电驴的专用链接
hostname:域名; port:端口号;http默认端口号80; path:路径 目录或者文件名
urllib事实上是一个包 ,包括几个模块:
1. urllib.request 打开并且读取urls
2. urllib.error 包含了由urllib.request 抛出的异常
3. urllib.parse for parsing(回避挡开) urls
4. urllib.robotparse for parsing(robots.txt) files
使用urllib写小爬虫之前需要导入包里面的request模块
import urllib.request
import urllib.parse
import json
↓
一个方法: urlopen用于打开一个对象,会返回一个response对象
urlopen(url,data=None,[timeout,]*,cafile=None,capath=None,cadefault=False)
让我们来写第一个小爬爬来解释urlopen函数吧:
↓
【例一】:爬取百度网页http://www.baidu.com的html内容
response = urllib.request.urlopen('http://www.baidu.com')
#urlopen的url参数可以是一个request对象,也是一个网址的字符串;
html = response.read() #读取
html = html.decode("utf-8") #解码
# decode:把其他编码形式变成unicode形式
# encode:把unicode形式变成其他形式
print(html) #解码后将会打印出网页文本编写的形式
urlopen函数会返回一个response对象,这里赋值给response变量 → 然后利用read方法读取字节型(bytes)数据,赋值给html变量 → html利用utf-8的格式解码以后 → 将会打印出网页文本编写的形式
效果:

【例二】:带参数爬取有道翻译的结果:
想当初我为了在APP里调用有道翻译API还费了老大劲呢咳咳…今天就用有道翻译来试试爬虫吧~
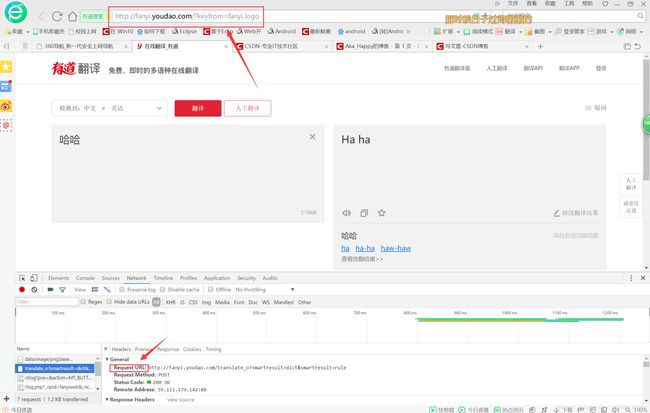
打开有道翻译的网址:有道翻译
右键点开审查元素→network→找到General:
可以看到这里有两个地址,网页搜索栏有一个地址,而General里Request好像又有一个地址,那我们到底该选哪个作为urlopen的入口参数呢?
答案是Request的网址;因为网址栏显示的地址只是当前输入页面的地址,而非真正翻译的地址;
写过网页的同学大概清楚这个流程(仅仅是大概,不做具体解释):
当用户在当前界面输入词汇,点击提交以后 → 词汇会作为参数跳转到真正处理参数的功能页面(这个页面通常是不显示出来的)→ 当功能页面处理完毕参数以后,就会返回相应的结果给当前这个页面→ 结果由当前页面显示出来。
而我们由于爬虫是直接提交参数,需要获取结果,所以我们的目标界面应该就是真正的功能页面,也即是这个request的页面:http://fanyi.youdao.com/translate_o?smartresult=dict&smartresult=rule
url="http://fanyi.youdao.com/translate_o?smartresult=dict&smartresult=rule"然后我们的输入参数怎么办呢?我们接着在审查元素里面搜寻有关的信息:

发现这个Data参数里的 i 竟然就是我们提交的参数!
于是可以着手编写了:
urlopen(url,data=None,[timeout,]*,cafile=None,capath=None,cadefault=False)
url已经有了,现在开始填充data参数(注意:data参数必须打包成 字典 输入!!)
data必须是x-www-form-urlencoded格式。
data={} #data是一个字典
data['from'] = 'AUTO'
data['to'] = 'AUTO'
data['i'] = input #input由用户自己输入字符串
data['smartresult'] = 'dict'
data['client'] = 'fanyideskweb'
data['salt'] = '1536844484730'
data['sign'] = 'c7be4ae1792e4c04dad0f42533387259'
data['doctype'] = 'json'
data['version']= '2.1'
data['keyfrom'] = 'fanyi.web'
data['action']= 'FY_BY_CLICKBUTTION'
data['typoResult']= 'false'
data = urllib.parse.urlencode(data).encode('utf-8')
#data必须是x-www-form-urlencoded格式。所以需要用这个函数来编码成url↓
现在url和data都准备好了,我们可以写一个urlopen来试试啦~
def Translation(input):
input = str(input)
url="http://fanyi.youdao.com/translate_o?smartresult=dict&smartresult=rule"
data={} #data是一个字典
data['from'] = 'AUTO'
data['to'] = 'AUTO'
data['i'] = input
data['smartresult'] = 'dict'
data['client'] = 'fanyideskweb'
data['salt'] = '1536844484730'
data['sign'] = 'c7be4ae1792e4c04dad0f42533387259'
data['doctype'] = 'json'
data['version']= '2.1'
data['keyfrom'] = 'fanyi.web'
data['action']= 'FY_BY_CLICKBUTTION'
data['typoResult']= 'false'
data = urllib.parse.urlencode(data).encode('utf-8')
#data必须是x-www-form-urlencoded格式。所以需要用这个函数来编码成url
response = urllib.request.urlopen(url, data)
response = response.read().decode('utf-8')
# decode:把其他编码形式变成unicode形式
# encode:把unicode形式变成其他形式
print(response)
# 以下为调用
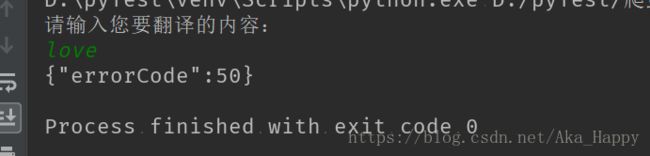
UserIn = str(input('请输入您要翻译的内容:\n'))
Translation(UserIn)↓
errorcode是50:有道有反爬虫机制 去掉url的_o就可以
url="http://fanyi.youdao.com/translate?smartresult=dict&smartresult=rule"↓
可以看到返回的结果里隐约有我们需要的翻译结果,但是整个形式是一个json格式的数据:
json结构的字符串 – json:一种轻量级的数据交换格式
所以我们来解析以下json字符串,得到我们需要的结果就好啦
#json 解析 -- 事先导入json模块
response= json.loads(response) #loads的s表示字符串,载入字符串变成字典↓
解析字典,提取需要的值:
#现在解析字典:
print('---------------\n')
print(response['translateResult']) #得到两层列表
print(response['translateResult'][0]) #得到一层列表
print(response['translateResult'][0][0]) #得到一个字典
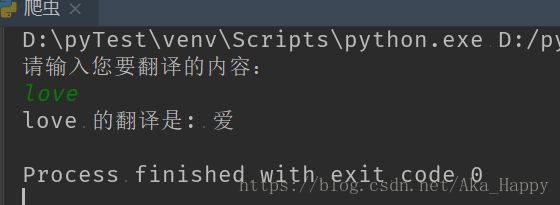
print(response['translateResult'][0][0]['tgt']) #目标结果result = str(response['translateResult'][0][0]['tgt'])
print(input, '的翻译是:', result)