机器学习——exercise2
Programming Exercise 2: Logistic Regression:
已给脚本:
ex2.m - Octave/MATLAB 第一部分练习题
ex2 reg.m - Octave/MATLAB 第二部分练习题
ex2data1.txt - 第一部分练习的训练集
ex2data2.txt - 第二部分的训练集
mapFeature.m - 生成多项式特征的函数
plotDecisionBoundary.m - 绘制决策边界的函数
编写脚本:
plotData.m - 绘制可视化数据的函数
sigmoid.m - Sigmoid Function
costFunction.m - Logistic 回归损失函数
predict.m - Logistic 回归预测函数
costFunctionReg.m - 正则化后的 Logistic 回归损失函数
1 Logistic 回归:
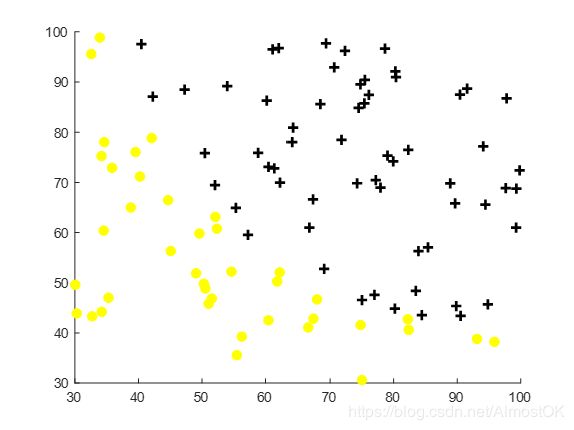
构建Logistic回归模型来预测学生通过两门考试中的成绩是否可以进入大学,现给训练集是以前申请人的历史数据,包括一百个样本,每个样本有两个成绩以及录取结果(0 or 1)。
需要建立分类模型,根据两个考试的成绩来估算测试集的概率
1.1 plotDdata.m 数据的可视化
function plotData(X, y)
%PLOTDATA Plots the data points X and y into a new figure
% PLOTDATA(x,y) plots the data points with + for the positive examples
% and o for the negative examples. X is assumed to be a Mx2 matrix.% Create New Figure
figure; hold on;% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Plot the positive and negative examples on a
% 2D plot, using the option 'k+' for the positive
% examples and 'ko' for the negative examples.
pos = find(y == 1);
neg = find(y == 0);
plot(X(pos,1), X(pos,2), 'k+', 'LineWidth', 2, 'MarkerSize', 7);
plot(X(neg,1), X(neg,2), 'ko', 'MarkerFaceColor', 'y', 'MarkerSize', 7);% =========================================================================
hold off;
end
1.2 CostFunction.m 损失函数:
function [J, grad] = costFunction(theta, X, y)
%COSTFUNCTION Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression
% J = COSTFUNCTION(theta, X, y) computes the cost of using theta as the
% parameter for logistic regression and the gradient of the cost
% w.r.t. to the parameters.% Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta));% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta
%
% Note: grad should have the same dimensions as theta
%
h = zeros(size(y'));
z = theta' * X';
h = ones(size(z)) ./ (ones(size(z))+exp(-z));
grad = (((h-y')*X) / m)';
J = ((-y)'*log(h') - (ones(size(y))-y)'*log(ones(size(h))-h)') / m;
% theta = theta - LearnRate * grad;% Normal Equation:
% z = theta' * X';
% h = ones(size(z)) ./ (ones(size(z))+exp(-z));
% theta = inv(X'*X) * X' * y;
% J = ((-y)'*log(h') - (ones(size(y))-y)'*log(ones(size(h))-h)') / m;% =============================================================
end
在特征较少的情况下用正规方程要比梯度下降简单,而且不需要选取学习率α,不需要进行迭代。但如果特征数量大于10000,考虑用梯度下降。
1.3 sigmoid.m:
function g = sigmoid(z)
%SIGMOID Compute sigmoid functoon
% J = SIGMOID(z) computes the sigmoid of z.g = 1.0 ./ (1.0 + exp(-z));
end
z与g的维数一致
1.4 predict.m 预测
function p = predict(theta, X)
%PREDICT Predict whether the label is 0 or 1 using learned logistic
%regression parameters theta
% p = PREDICT(theta, X) computes the predictions for X using a
% threshold at 0.5 (i.e., if sigmoid(theta'*x) >= 0.5, predict 1)m = size(X, 1); % Number of training examples
% You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(m, 1);% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
% your learned logistic regression parameters.
% You should set p to a vector of 0's and 1's
%
z = theta' * X';
h = ones(size(z')) ./ (ones(size(z')) + exp(-z'));
for isample = 1:size(h,1)
if h(isample) > 0.5
p(isample) = 1;
end
if h(isample) < 0.5
p(isample) = 0;
end
end% =========================================================================
end
在进行预测之前先使用fminunc函数进行迭代求取theta:
% Set options for fminunc
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 400); %MaxIter 400 为最大迭代次数400% Run fminunc to obtain the optimal theta
% This function will return theta and the cost
[theta, cost] = ...
fminunc(@(t)(costFunction(t, X, y)), initial_theta, options);
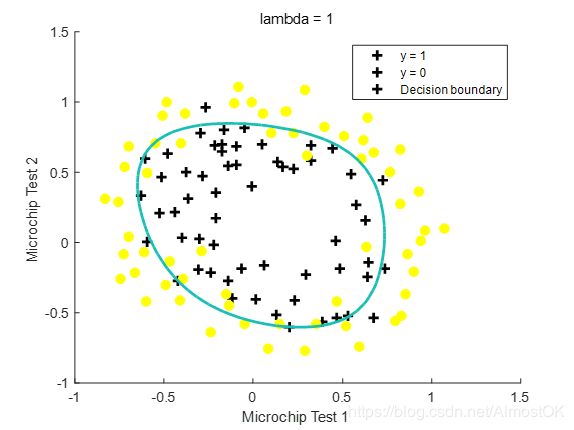
2 正则化 logistic 回归:
若数据集具有过多的特征,但是只有较少的训练数据,容易发生过拟合。过拟合 = 高方差
解决过拟合的方法有两种:
- 减少特征的数量
- 正则化(相应的缩小特征的值,减少无关重要的特征所带来的波动)
注意:正则化引入的惩罚项只对theta0之后的参数进行惩罚,theta0 还是为1
2.1 costFunctionReg.m 引入惩罚项的损失函数:
function [J, grad] = costFunctionReg(theta, X, y, lambda)
%COSTFUNCTIONREG Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression with regularization
% J = COSTFUNCTIONREG(theta, X, y, lambda) computes the cost of using
% theta as the parameter for regularized logistic regression and the
% gradient of the cost w.r.t. to the parameters.% Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta));% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta
z = theta' * X';
h = ones(size(z')) ./ (ones(size(z')) + exp(-z'));
J = ((-y')*log(h) - (ones(size(y))-y)'*log(ones(size(h))-h)) / m + lambda / (2*m) * (theta'*theta);
grad = (ones(size(y'))*((h - y) .* X) + lambda*theta') / m; %为行向量
% 将结果和实际的误差与每个样本的每个特征各乘一次% =============================================================
end
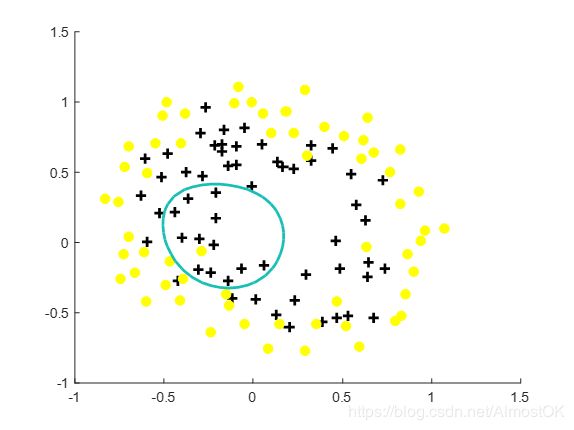
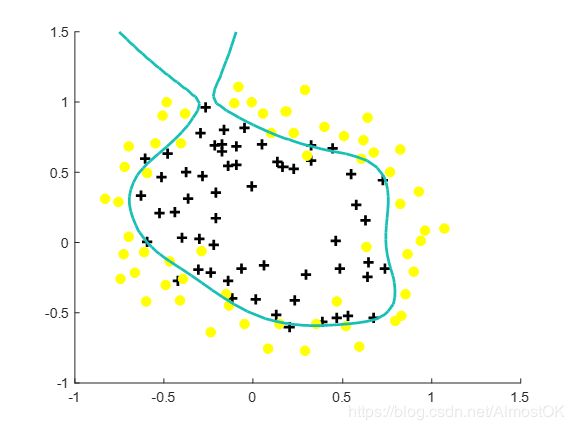
正则化后的损失函数和标准的损失函数相比只是多了一个正则化参数λ,随着λ的增加,决策边界会欠拟合;λ减小,决策边界会过拟合。