黑马程序员之网络编程
------http://www.itheima.com" target="blank">Java培训、Android培训、iOS培训、.Net培训、期待与您交流! -------
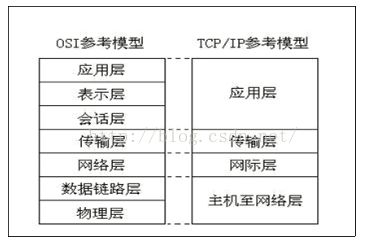
一、OSI七层模型
在网络通讯的过程中,数据有上而下的打包,并发送出去, 当收到数据,则是由下而上的解析数据。为了方便参考TCP/IP参考模则简化为四层。
二、通信协议
为了在不同系统,不同的硬件上进行通信而提供支持,这就是通信协议。常见的通信协议有:TCP/IP传输控制协议、HTTP超文本传输协议、POP邮件协议、WAP无线应用协议、UDP用户数据报协议等等。在JAVA中TCP和UDP协议应用很多,广泛。在这个两个协议中的优缺点。
TCP协议:1.需要建立连接形成传输数据的通道
2.在连接中可进行大量的数据传输
3.需要三次握手才能建立连接,是一种可靠的协议
4.在通信过程中,必须要建立连接,略微降低效率
UDP协议:1.将数据封装在数据包中,不需要建立连接
2.每个数据包的大小限制在64k以内
3.因不需要建立连接,是不可靠的协议
4.不需要建立连接,速度快
在通信的过程中除了需要通信的协议,还需要两个重要的要素:1.网络地址也就是IP地址 2.端口号。IP地址在网络中就是用来标识网络中的设备的,而端口号则是用来标识该设备中的程序具体用哪个端口来收发数据的。
三、JAVA中UDP通信示例
/**
* @author
*
* 通过UDP的方式, 将一段文字数据发送出去.
*
* 1.建立UDPSocket服务
* 2.封装数据到数据报包中
* 3.通过Socket服务的发送功能将数据发送出去
* 4.关闭资源
*
*/
class UDPSend{
public static void send() throws IOException{
//1.创建UDP服务, 通过DatagramSocket对象
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(8888); //指定数据从哪个端口出去
//2.确定数据, 并封装成数据包
byte[] buf = "hello UDP .".getBytes();
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length,
InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"),10000);
//3.通过Socket服务将已有的数据包发送出去
ds.send(dp);
//4.关闭资源
ds.close();
}
}
/**
* @author
*
* 定义一个应用程序, 用于接收UDP协议传输的数据并处理
*
* 1.建立UDPSocket服务. 通常会监听一个端口, 其实就是给这个网络程序一个数字标识, 明确哪些数据过来应该这个程序处理
* 2.定义数据包, 用于存储接收到的字节数据
* 3.通过Socket服务的receive()方法接收数据并存入已定义好的数据包中
* 4.通过数据包的特有功能解析数据
* 5.关闭资源
*
*/
class UDPRece{
public static void receive() throws IOException {
//1.创建UDP的Socket服务, 建立端点
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(10000);
//2.定义数据包, 用于存储数据
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf,buf.length);
//3.通过服务的receive()方法将数据存入数据包中
ds.receive(dp);
//4.通过数据包的方法获取数据
String ip = dp.getAddress().toString();
int port = dp.getPort();
String data = new String(dp.getData(),0,dp.getLength());
System.out.println("IP : " + ip + "port : " + port + "data : " + data);
//5.关闭资源
ds.close();
}
}
四、TCP通信示例
/**
* 客服端
* 1.创建Socket链接, 并制定要链接的主机和端口
*/
class TCPClient{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.创建Socket链接, 并制定要链接的主机和端口
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1",10003);
//为了发送数据, 获取Socket中的输出流
OutputStream out = socket.getOutputStream();
out.write("hello TCP.".getBytes());
socket.close();
}
}
/**
*
* 服务端
* 1.建立服务端的Socket服务, ServerSocket
* 2.获取链接过来的客服端对象, 通过ServerSocket的accept()方法, 没有链接就会等, 所以这个方法是诸塞式的
* 3.客服端如果发过来数据, 服务端要使用对应的客服端对象, 并获取客服端对象的读取流对象来读取发过来的数据
* 4.关闭服务端
*
*/
class TCPServer{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//建立服务端的Socket对象, 并监听一个端口
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10003);
//获取链接过来的客服端对象
Socket s = ss.accept();
//获取客服端发送过来的数据, 那么要使用客服端对象的读取流来读取数据
InputStream is = s.getInputStream();
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while(-1 != (len = is.read(buf))){
sb.append(new String(buf,0,len));
}
String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
System.out.println(ip + " : " + sb.toString());
s.close(); //关闭客服端
ss.close();
}
}
使用TCP复制一个文件, 在复制最后一定要加上结束标记, 不然客户端和服务端都陷入阻塞状态。示例:
class TextClient{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Socket s = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 10006);
//定义时间戳, 为结束标记
// long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
// DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(s.getOutputStream());
// dos.writeLong(time);
BufferedReader bufr = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:/FaceProv.log"));
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(s.getOutputStream(),true);
String line = null;
while(null != (line = bufr.readLine())){
// System.out.println(line);
out.println(line);
}
// out.println("over");
// out.println(Long.toString(time));
s.shutdownOutput(); //关闭客户端输出流, 相当于在流的末尾加入结束标记-1.
BufferedReader bufin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
String str = bufin.readLine();
System.out.println(str);
bufr.close();
s.close();
}
}
class TextServer{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10006);
Socket s = ss.accept();
//读取时间戳
// DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(s.getInputStream());
// long time = dis.readLong();
BufferedWriter bufw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("d:/1.txt"));
BufferedReader bufin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
String line = null;
while(null != (line = bufin.readLine())){
// if("over".equals(line)) break;
// if(Long.toString(time).equals(line)) break;
bufw.write(line);
bufw.newLine();
bufw.flush();
}
BufferedWriter bufout = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(s.getOutputStream()));
bufout.write("success ");
bufout.newLine();
bufout.flush();
bufw.close();
s.close();
ss.close();
}
}
使用TCP和多线程上传文件,以下示例将展示上传图片
class PicClient{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1",10007);
BufferedInputStream bufr = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:/149.png"));
OutputStream out = socket.getOutputStream();
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while(-1 != (len = bufr.read(buf))){
out.write(buf, 0, len);
}
//告诉服务端数据已写完
socket.shutdownOutput();
InputStream in = socket.getInputStream();
buf = new byte[1024];
int num = in.read(buf);
String str = new String(buf, 0, num);
System.out.println(str);
bufr.close();
socket.close();
}
}
/**
* @author
*
* 当多个客户端访问服务端的时候, 必须要等待上一个客户端访问完成, 下一个客户端才可以访问, 所以这样是不好的.
* 为了可以让多个客户端同时并发访问服务端, 服务端最好将每个客户端封装到一个单独的线程中, 这样就可以同时处理多个客户端请求.
*
* 如何定义线程?
* 只要明确每个客户端要在服务端执行的代码就好, 将该代码放在run()方法中即可.
*
*
*/
class PicThread implements Runnable{
private Socket socket;
public PicThread(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int count = 1;
String ip = socket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
try {
System.out.println(ip + " : connected !");
File file = new File(ip + "(" + count + ").png");
while(file.exists())
file = new File(ip + "(" + (count++) + ").png");
InputStream in = socket.getInputStream();
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while(-1 != (len = in.read(buf))){
bos.write(buf, 0, len);
bos.flush();
}
OutputStream out = socket.getOutputStream();
out.write("success !".getBytes());
bos.close();
socket.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(ip + " : 上传失败 !");
}
}
}
class PicServer{
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10007);
while(true){
Socket socket = ss.accept();
new Thread(new PicThread(socket)).start();
}
// ss.close();
}
}