集合
集合
.NET框架基类库提供了集合的正式定义:System.Collections.ICollection接口。
ICollection接口从Ienumerable接口继承而不来,Icollection接口定义了一个CopyTo方法和三个只读属性IsSynchronized、SyncRoot 和 Count。
1.在System.Collection命名间中定义了各种对象的集合,以及这些集合应该具备的功能:
下图是System.Collection中的接口:
在这些接口中的关系继承如下:
System.Collection命名空间的类:
2.集合与数组的比较:
1) 数组是固定大小的,集合是可变长的。
2)数组要声明元素的类型,集合元素的类型却是Object。
3)数组可读可写,不能声明可读数组,尽管数组有IsReadOnly属性,但是这个属性是制度的,不能进行设置,集合类可以提供ReadOnly方法以只读方式使用集合。
3.集合中的类型转换(装箱与拆箱):
在集合中允许操作的数据类型是Object。因此,当向集合中添加元素时,需将对象转换为Object类型(隐式转换,不必声明);在获取元素时,需将Object类型转换为所需要的类型。
1) 当数据类型为值类型时,需进行装箱或拆箱。
2) 当数据类型为引用类型时,需要在基类(Object)到子类之间进行转换。
4.简单的例子:
以系统自定义Hashtable类为例子,写一个存储客户姓名和联系方式的,和对客户信息简单的操作。
先介绍一下Hashtable集合类的用法
哈希表实现一种按键(key)/值(value)方式存储内部元素的数据结构,每个元素都存储在一个叫做DictionaryEntry对象中。Key不能为null且唯一,值可以。
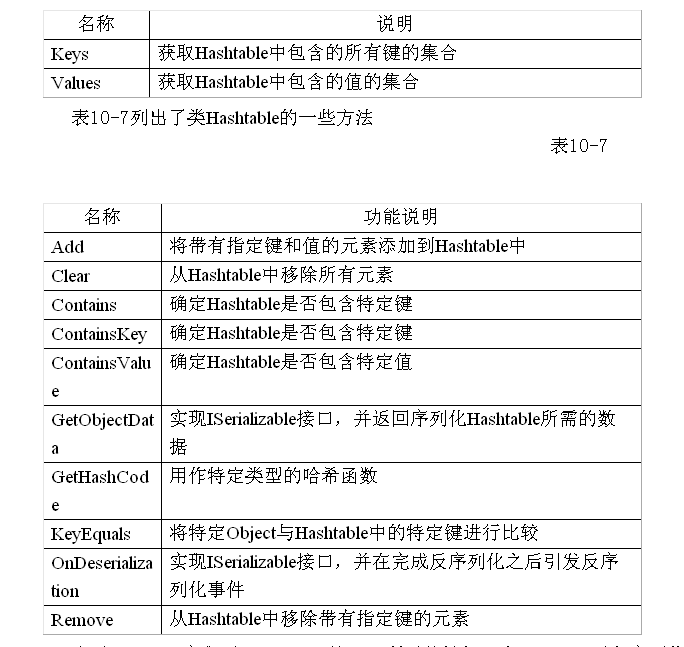
Hashtable属性:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Collections;
using System.IO; //文件的读写
using System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary; //序列化
namespace HashtableTest
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//生成哈希表,用存储客户姓名,联系电话
//姓名为键,联系方式为值
Hashtable ht = new Hashtable();
//添加客户
ht.Add("黎明", "13578962145");
ht.Add("张学友", "12457896325");
ht.Add("刘德华","13589632145");
ht.Add("郭富城","13596214587");
//遍历哈希表中客户的信息
Console.WriteLine("遍历哈希表中客户信息(按任意键继续):");
print1(ht);
//序列化哈希表(以二进制方式存储客户信息)
serialize(ht);
//反序列化哈希表(从文件中读取到哈希表)
Hashtable ht2 = deserialize();
Console.WriteLine("遍历反序列化后的哈希表中客户的信息(按任意键继续)");
print2(ht2);//遍历反序列化的合希表表中客户的信息
//判断特定客户是否在表中,若存在,则将其联系方式改为***********,
//若不存在,则添加新客户,联系方式也为***********
Console.WriteLine("判断特定客户是否在表中,若存在,则将其联系方式改为***********," +
"若不存在,则添加新客户,联系方式也为***********");
Console.WriteLine("请输入客户的名称(如:黎明):");
String key = Console.ReadLine(); //接收输入的客户
if (ht.ContainsKey(key)) //判断输入的客户是否存在
{
ht[key] = "***********";//如果此键不存在,则会自动创建新元素。
Console.WriteLine("此客户存在表中,其联系方式已修改为{0}",ht[key]);
}
else
{
ht[key] = "***********";//如果此键不存在,则会自动创建新元素。
Console.WriteLine("已新添加一名客户:{0}:{1}", key, ht[key]);
}
Console.WriteLine("更新后的哈希表中的客户为(按任意键继续):");
print1(ht);
Console.ReadKey();
}
///
/// 用于遍历哈希表
///
/// 所要遍历的哈希表
static void print1(Hashtable ht)
{
Console.ReadKey();
foreach (DictionaryEntry p in ht)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}:{1},其哈希代码是:0x{2:X0}",
p.Key, p.Value, p.Key.GetHashCode());
}
}
///
/// 用于遍历哈希表
///
/// 所要遍历的哈希表
static void print2(Hashtable ht)
{
Console.ReadKey();
IDictionaryEnumerator enumerator = ht.GetEnumerator();
while (enumerator.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}:{1},其哈希代码是:0x{2:X0}",
enumerator.Key, enumerator.Value, enumerator.Key.GetHashCode());
}
}
///
/// 序列化哈希表
///
/// 所要序列化的哈希表
static void serialize(Hashtable ht)
{
BinaryFormatter binfor = new BinaryFormatter();
try
{
FileStream fs = new FileStream("HashTable.xml", FileMode.OpenOrCreate);
binfor.Serialize(fs, ht);
fs.Close();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message.ToString());
}
}
///
/// 反序列化
///
/// 反序列化后的哈希表
static Hashtable deserialize()
{
Hashtable ht = new Hashtable();
BinaryFormatter binfor = new BinaryFormatter();
try
{
FileStream fs = new FileStream("HashTable.xml", FileMode.OpenOrCreate);
ht= (Hashtable)binfor.Deserialize(fs);
fs.Close();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message.ToString());
}
return ht;
}
}
}
运行结果:
5.集合的缺点:
由于集合中的元素为Oject类型,因此在使用过程中经常需要进行,装箱/拆箱,类型转换,这样严重影响性能,更何况类型转换是隐式转换,这样在编译阶段可以说是没有进行类型检查,类型一旦出错,会相当麻烦。
例如:在上面例子,添加一客户信息:
ht.Add(4.56,789); //客户的名字为4.56
person p=new person();
ht.Add(p,456); //客户名字为一个对象
这样的在编译中也是没问题的。因此在System.Collections命名空间中提供三个抽象基类,确保类型的安全。
6.强类型集合基类:
在System.Collection的三个强类型集合基类为:CollectionBase,OnlyReadCollectionBase,DictionaryBase它们都提供创建强类型的功能,我们可根据需要对它们进行扩展。
下面以DictionaryBase 为例,同样实现上面的例子:
先看看DictionaryBase的功能
1)其定义:public abstract class DictionaryBase : IDictionary, ICollection, Ienumerable
2)其属性:
3) 已经显示实现的接口:
在DictionaryBase中有一些比较特殊的保护方法,这些方法都是以On开头,这些方法的功能是在执行某个操作之前或者之后能够被自动调用的方法,在这些方法中可以添加一些代码,以达到对数据操作的验证或者纠错功能。比如,方法OnInsert就是在向DictionaryBase实例中插入新元素之前被自动执行。而方法OnInsertComplete在向DictionaryBase实例中插入新元素之后被执行。一般不使用DictionaryBase中InnerHashtable来获得列表,就是因为使用InnerHashtable获得的列表在执行增加,插入等操作的同时,不能够触发这些以On开头的方法。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Collections;
namespace DictionaryBaseTest
{
class MyDictionaryBase: DictionaryBase
{
///
/// 通过Key获取或设置值的功能(设置客户的联系方式)
///
/// String类型
///
public String this[String key]
{
get
{
return ((String)Dictionary[key]);
}
set
{
try
{
Dictionary[key] = value;
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message.ToString());
}
}
}
///
/// 获取字典中键的集合(获取所有客户的姓名)
///
public ICollection Keys
{
get
{
return Dictionary.Keys;
}
}
///
/// 获取字典中值的集合(获取所有客户的联系方式)
///
public ICollection Values
{
get
{
return Dictionary.Values;
}
}
///
/// 向字典添加新项(添加新客户)
///
/// 键:String类型
/// 值:String类型
public void Add(String key, String value)
{
try
{
Dictionary.Add(key, value);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message.ToString());
}
}
///
/// 判断特定键是否在字典中(判断客户是否在字典中)
///
/// 键:String类型
///
public Boolean Contains(String key)
{
return Dictionary.Contains(key);
}
///
/// 在字典中移除带有指定键的元素(删除指定客户)
///
/// String:类型
public void Remove(String key)
{
Dictionary.Remove(key);
}
///
/// 插入之前进行检查(在添加客户之前,对客户信息的检查)
///
///
///
protected override void OnInsert(object key, object value)
{
if (key.GetType() != typeof(System.String))
{
throw new ArgumentException("姓名不是String类型",key.ToString());
}
else
{
String strkey = (String)key;
if (strkey.Length > 6)
throw new ArgumentException("姓名的长度不能超过6个符", key.ToString());
}
if (value.GetType() != typeof(System.String))
{
throw new ArgumentException("联系方式不是String类型", value.ToString());
}
else
{
String strvalue = (String)value;
if (strvalue.Length > 11)
throw new ArgumentException("联系方式的长度不要超过11个字符", value.ToString());
}
}
///
/// 设置值前进行检查(在设置客户联系方式之前对客户信息进行检查)
///
///
///
///
protected override void OnSet(object key, object oldValue, object newValue)
{
if (key.GetType() != typeof(System.String))
{
throw new ArgumentException("联系方式不是String类型", key.ToString());
}
else
{
String strkey = (String)key;
if (strkey.Length > 6)
throw new ArgumentException("姓名的长度不能超过6个字符", key.ToString());
}
if (newValue.GetType() != typeof(System.String))
{
throw new ArgumentException("联系方式不是String类型", newValue.ToString());
}
else
{
String strnewvalue = (String)newValue;
if (strnewvalue.Length > 11)
throw new ArgumentException("联系方式的长度不能超过11个字符", newValue.ToString());
}
}
}
}
主类:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Collections;
namespace DictionaryBaseTest
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyDictionaryBase mydb = new MyDictionaryBase();
mydb.Add("黎明", "13756487036");
mydb.Add("郭富城", "13546897412");
mydb.Add("刘德华", "14578963254");
mydb.Add("张学友", "14562897412");
mydb.Add("李自成", "14562897412963");//联系方式的长度超过11个字符
mydb.Add("abcdefg", "13589451269"); //名字长度超过6个字符
mydb["黎明"] = "12345678911111"; //重新设置的联系方式长度超过11个字符
Console.WriteLine("字典中的客户的信息(按任意键继续):");
print1(mydb);
Console.ReadKey();
}
//遍历的方法:
static void print1(MyDictionaryBase mydb)
{
Console.ReadKey();
foreach (DictionaryEntry p in mydb)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}: {1}", p.Key, p.Value);
}
}
}
}
运行结果:
从上面的例子:可以看出强类型集合基类实质上是对集合的一种封装机制(DictionaryBase是对Hashtable的封装),通过各种方式验证类型,以确保运行时类型的安全。但这样也很麻烦,因为每需要一种类型,就必须派生一个,这些派生的功能非常相似。而且它也没有解决频繁的类型转换和装箱/拆箱问题。因此C#提供了泛型以解决此问题。
7.泛型集合:
泛型:即通过参数化类型来实现在同一份代码上操作多种数据类型。泛型编程是一种编程范式,它利用“参数化类型”将类型抽象化,从而实现更为灵活的复用。
在System.Collections命名空间提供的集合都有相应的泛型版本,这些泛型集合类是在System.Collections.Generic命名空间中。例如:Hashtable的泛型版本是Dictionary
简单的例子(还是客户的姓名和联系方式):
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace GenericTest
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Dictionary<String, String> Mydic = new Dictionary<String, String>();
Mydic.Add("郭富城", "13756984512");
Mydic.Add("黎明", "13564784512");
Mydic.Add("刘德华", "13695874512");
Mydic.Add("张学友", "13569854123");
Console.WriteLine("遍历客户的信息(按任意键继续)");
print(Mydic); //遍历字典
//获取键的集合
Dictionary<String, String>.KeyCollection keycoll = Mydic.Keys;
//查询黎明的联系方式
Console.WriteLine("查询黎明的联系方式(按任意键继续)");
Console.ReadKey();
String value="";
Mydic.TryGetValue("黎明", out value);
Console.WriteLine("黎明的联系方式为:{0}",value);
Console.ReadKey();
}
///
/// 遍历的方法
///
static void print(Dictionary<String,String> Mydic)
{
//遍历泛型字典
Console.ReadKey();
foreach (KeyValuePair<String, String> p in Mydic)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}:{1}", p.Key, p.Value);
}
}
}
}
运行结果:
在上面的3个例子中,它们遍历集合的方法:
Hashtable,DictionaryBase
foreach (DictionaryEntry p in mydb)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}: {1}", p.Key, p.Value);
}
Dictionary
foreach (KeyValuePair<String, String> p in Mydic)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}:{1}", p.Key, p.Value);
}
不难看出非泛型集合Hashtable,Dictionary元素的键/值是存储在DictionaryEntry对象中:
// 定义可设置或检索的字典键/值对。
[Serializable]
[ComVisible(true)]
public struct DictionaryEntry
{
public DictionaryEntry(object key, object value);
public object Key { get; set; }
public object Value { get; set; }
}
键/值为Object类型,使用过程中需要频繁类型转换或装箱/拆箱。
而Dictionary
// 摘要:
// 定义可设置或检索的键/值对。
//
[Serializable]
public struct KeyValuePair
{
public KeyValuePair(TKey key, TValue value);
public TKey Key { get; }
public TValue Value { get; }
public override string ToString();
}
在使用过程中参数Tkey,Tvalue会被实际类型替代例如:String,因此它是类型安全和可以减少装箱、拆箱。