【Android Audio 入门 五】--- AudioSW介绍
【Android Audio 入门 五】--- AudioSW介绍
- 五、AudioSW介绍
- 5.1 Audio SW 的作用
- 5.2 正常Audio SW Architecture
- 5.3 通话Voice Audio SW Architecture
- 5.4 混音Audio Mixer
- 5.5 AFE 通路
- 5.6 Audio Policy Manager
- 5.7 如何获得当前支持的所有Audio 设备
- 5.8 音量控制 Volume Control
- 5.9 Code Path
五、AudioSW介绍
5.1 Audio SW 的作用
简单来说, Audio SW 只要做好两件事:
-
管理好整个数据链路上的输入模块和输入模块
包含直观意义上的输入设备和输出设备,比如说MIC,Speaker
还包括整个数据链路上的各个输入模块和输出模块,
比如说播放文件系统里面的mp3 文件,对于mp3 解码器来说,文件系统就是它的输入模块。 -
做好音频数据的处理
5.2 正常Audio SW Architecture
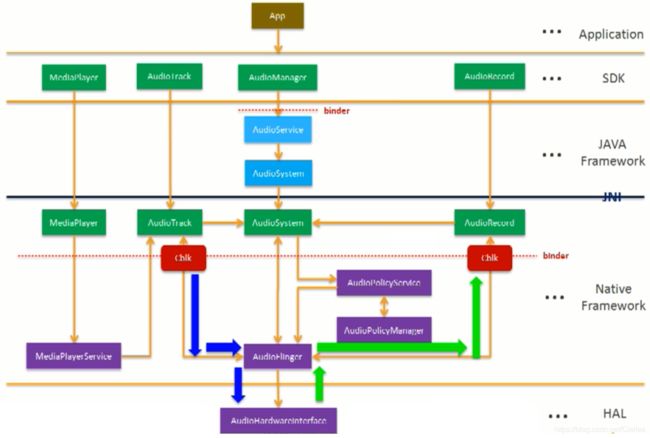
对于上层apk 来说,Audio 主要有两大功能: 播放 和 录音
-
播放
(1)上层可以通过 AudioTrack ,调用 Native 层的 AudioTrack ,然后将数据写到 AudioFlinger,最终将数据写到Audio Hardware。(2)上层还可以通过MediaPlayer的接口来控制播放的功能,通过Native 层的 MediaPlayer 将数据送到 MediaPlayerService 的解码器中,解析为 纯PCM的数据,最终还是通过AudioTrack - AudioFlinger 来发送播放数据。
(3)MediaPlayer 和 AudioTrack 的区别: AudioTrack 只能播放纯PCM 的数据 ;MediaPlayer 除了能写PCM数据外,还能够写MP3,wav 等经过压缩的音频数据格式
- 录音
从硬件拿到数据之后,AudioFlinger 会送到 Native 层的 AudioRecord 接口中,最终给到上层的AudioRecord 中。
- AudioManager
上层除了要控制播放和录音外,还要控制选择哪个播放的输入输出设备,音量多少等。
通过 AudioManager,调用AudioService --> AudioSystem ,通过 Native 层的AudioSystem ,调用AudioPolicyService,
由 AudioPolicyManager 来控制采用哪个设备,使用什么音量。
在Audio 的播放音乐上面,AudioTrack 最多可支持 32 个 Track,出就是说 Android 最多可支持 32 个声音同时播放。
这32 个声音是在 AudioFlinger 中被混合 Mixer 在一起的,Mixer 之后再送给硬件播放,因为硬件只有一个。
5.3 通话Voice Audio SW Architecture
如下图是除了播放录音功能外,还增加了打电话的框图。
-
如果不考虑打电话的功能的话
播放音乐时,AudioSystem 通过 AudioFlinger 在 HAL层通过Create Playback Handler ,把数据写到 ALSA Driver 。
录音时,ALSA Driver 通过 Capture Handler 把数据向上送到 AudioSystem 中,就 OK 了。
-
通话时候的播放和录音
在打电话时,Audio 的数据会走到 Modem 中,AP会控制Modem, 在Modem 中直接 和 MD Audio HW 进行沟通,然后将数据直接送到 AP Audio HW 进行播放。如果在打电话的时候要的播放音乐:
则 AudioSystem 会先在 Stream Manager 中创建 PlaybackHandler ,将数据送到 BGSPlayer, BGSPlayer 会将相关的音频数据送到Modem 中,在Modem 中会把打电话的声音 和 Audio 声音 Mixer 混合在一起,然后再送给 MD Audio HW ,通过 AP Audio HW 播放出来。如果在打电话的时候,还想录音:
此时,Modem 会把录音相关的数据通过 Create Capture Handler 往上送,这样, AP 应能拿到相关的数据。 录音时,可以选择,只录MIC的声音,只录对方的声音,还是所有声音都录进来,都可以。打电话时相关的Audio参数,AudioSystem会通过 AudioPolicyService,在AudioPolicyManager 中下发或者上传,
打电话时,会涉及到模拟增益和数字增益,会在Volume Control Driver 计算出来会,通过LAD 送到Modem中,在Modem 中调整相关的配置。
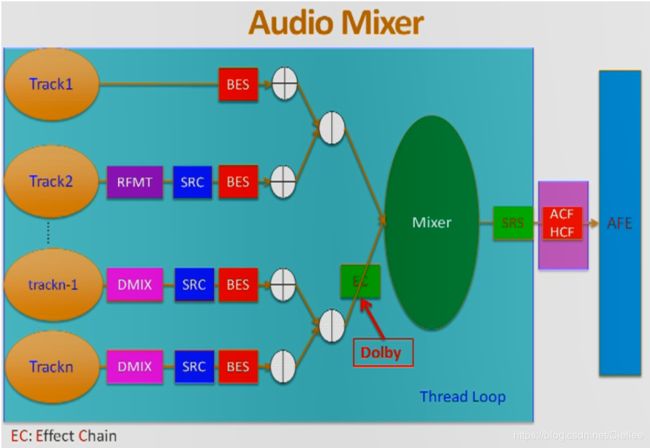
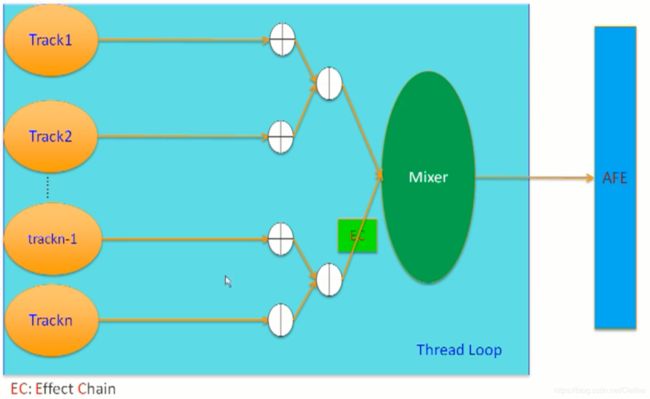
5.4 混音Audio Mixer
前面讲了,Anroid AudioTrack 最多支持 32 个声音同时Mixer 在一起,它们是如何工作的呢?
如下图中:
(1)假如 Track 1 和 Track2, 这两个Track 的软件和硬件参数是一样的,我们就可能直接将它俩Mixer 在一起,送到AFE中硬件 播放。
(2)有些Track 有音效的需求,比如假设 Track n-1 和 Track n ,这两个Track 有相同的音效的需求,我们会先把它俩 Mixer 在一起,然后再经过 EC (Effect Chain) 的音效处理后,再和 其他的Track Mixer 后,送到AFE硬件 中播放。
比如,第三方的音效 Dolby 就是通过 Effect Chain 的形式来写的。
有点晚了,该睡觉了,明天再来更新吧 ^_^
Date: 2019/09/19 - 23:22
-
RFMT (格式化)
假设 Track 1 正常的采样深度是16bit ,但 Track 2 的采样深度是32bit ,此时在Mixer 之前,Track 2 会做一个RFMT(格式化),从32bit 转成 16bit 格式数据,然后再Mixer. -
DMIX (声道转换)
假设 Track 1 和 Track 2 量正常的双声道,而Track n-1 和 Track n 是七声道的数据,此时,在Mixer 之前,Track n 和 Track n-1 会先做一个 DMIX ( 声道转换) ,转为双声道,然后再Mixer. -
SRC (重采样)
如果某个Track 的采样率和硬件的采样率不一样,则会经过SRC重采样到和硬件保持一致。
比如Track的采样率是48KHz,而硬件采样率支持16KHz,这样,在进入Mixer 之前,则会先经过 SRC(重采样),将48KHz 重采样为 16KHz,然后送进入Mixer再播放。 -
BES / ACF / HCF
MTK 平台特有的增加的音效处理。 -
SRS 第三方音效
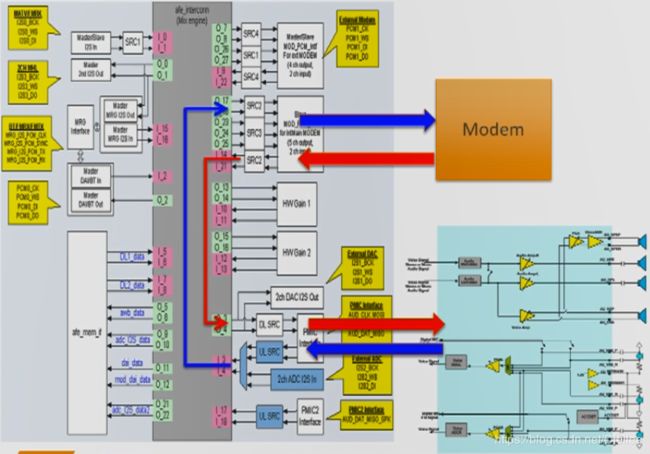
5.5 AFE 通路
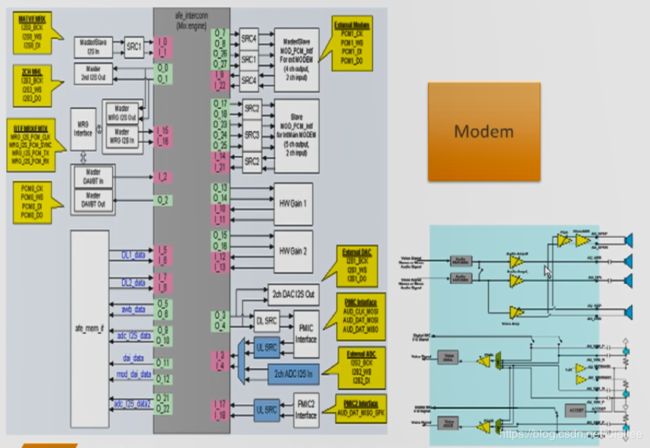
上图是一个AFE的模块图,上面有很多的输入和输出模块,不同的应用场景,我们会组合不同的 Input 和 Output 模块。
比如: 播放音乐时,Mixer 之后的数据会从 I5、I6 进来,然后将数据往 O3、O4送到 PMIC,PMIC 最终会从耳机或喇叭播放出来。
对于录音时,数据是反向的,录音数据从 I3、I4进入 送给 O9、O10 后,软件取到PCM数据后,再做相关编码的处理。
见下图:红色 和 蓝色箭头
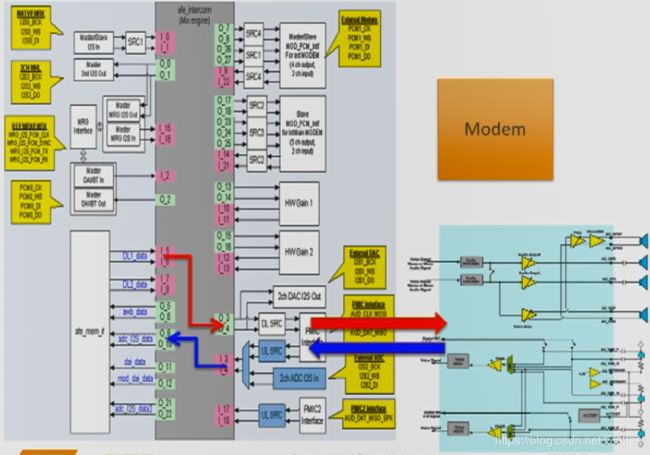
而打电话时,
下行数据的流向:
首先从 Modem 将数据送给 I14, 然后 把 I14 和 O3/O4 连接起来,再通过O3/O4将数据送给 PMIC ,最终PMIC 通过耳机或喇叭播放出来。
上行数据的流向:
从MIC 录音后,数据会从I3/I4 流入,然后 I3/I4 把数据 送到 O17/O18 进入Modem 中,在Modem进行编码,再通过网络送给对方。
5.6 Audio Policy Manager
前面讲了,分据链路怎么选择处理的,
现在我们主要介绍下在Android SW 中是如何选择输出设备的。
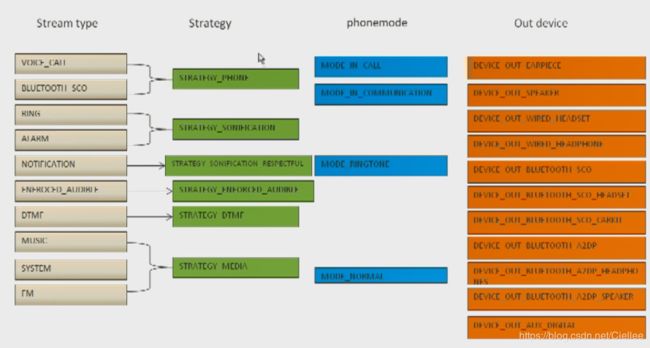
前面我们说了一共支持32个的Audio Track,每个Audio Track 有不同的Stream type。
在安卓中,支持 VOICE_CALL、BLUETOOTH SCO、RING 、ALARM、NOTIFICATION、DTMF、MUSIC、SYSTEM、FM 等Stream type。
@ \frameworks\base\QGAPI\src\com\qinggan\audiopolicy\AudioPolicyManager.java
public static String getStreamTypeString(int streamType){
switch (streamType){
case STREAM_MEDIA:
return "stream_media";
case STREAM_NAVI:
return "stream_navi";
case STREAM_TTS:
return "stream_tts";
case STREAM_RING:
return "stream_ring";
case STREAM_A2DP:
return "stream_a2dp";
case STREAM_NOTIFICATION:
return "stream_notification";
case STREAM_VOICE_CALL:
return "stream_voice_call";
case STREAM_VOIP:
return "stream_voip";
case STREAM_BLUETOOTH_SCO:
return "stream_bluetooth_sco";
case STREAM_RADIO:
return "stream_radio";
case STREAM_IVOKA:
return "stream_ivoka";
case STREAM_AUX:
return "stream_aux";
case STREAM_RECORD:
return "stream_record";
case STREAM_SYSTEM_ENFORCED:
return "stream_system_enforced";
case STREAM_SAFETY_TIP:
return "stream_safety_tip";
default:
return "unknown";
}
}
支持的输出设备有, DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER、DEVICE_OUT_EARPHONE、DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_SCO 听筒,喇叭,耳机等设备。
但问题来了,这么多声音,要从哪个设备输出呢?
谷歌定义了一个策略,把某些 StreamType 归类在一起,
如上图,
把 VOICE_CALL 和 BLUETOOTH_SCO 归类为 STRATEGY_PHONE。
把 Musice / System / FM 等归类为 STRATEGY_MEDIA
然后,对Device 的选择,还会取决于当前的模式。
比如: MODE_IN_CALL( GSM通话使用 )、MODE_IN_COMMUCATION( 4G通话使用 )、MODE_RINGTONE(来电铃声)、MODE_NORMAL(正常媒体)
详细有哪些 Stream 可以看 AudioPolicyManger::getStrategy() 函数。
在知道有哪些 StreamType 和 phonemode 后,分选择哪个Device,
可以看函数 AudioPolicyManger::getNewOutputDevice() 里面,这个函数会决定到底要从哪个输出设备输出声音。
在这个 函数中,能过 if – else 就能知道其 Device 的优先级。
代码如下:
@ \src\frameworks\av\services\audiopolicy\managerdefault\AudioPolicyManager.cpp
audio_devices_t AudioPolicyManager::getNewOutputDevice(const sp<AudioOutputDescriptor>& outputDesc, bool fromCache)
{
audio_devices_t device = AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE;
ssize_t index = mAudioPatches.indexOfKey(outputDesc->getPatchHandle());
if (index >= 0) {
sp<AudioPatch> patchDesc = mAudioPatches.valueAt(index);
if (patchDesc->mUid != mUidCached) {
ALOGV("getNewOutputDevice() device %08x forced by patch %d", outputDesc->device(), outputDesc->getPatchHandle());
return outputDesc->device();
}
}
// check the following by order of priority to request a routing change if necessary:
// 1: the strategy enforced audible is active and enforced on the output:
// use device for strategy enforced audible
// 2: we are in call or the strategy phone is active on the output:
// use device for strategy phone
// 3: the strategy sonification is active on the output:
// use device for strategy sonification
// 4: the strategy for enforced audible is active but not enforced on the output:
// use the device for strategy enforced audible
// 5: the strategy accessibility is active on the output:
// use device for strategy accessibility
// 6: the strategy "respectful" sonification is active on the output:
// use device for strategy "respectful" sonification
// 7: the strategy media is active on the output:
// use device for strategy media
// 8: the strategy DTMF is active on the output:
// use device for strategy DTMF
// 9: the strategy for beacon, a.k.a. "transmitted through speaker" is active on the output:
// use device for strategy t-t-s
if (isStrategyActive(outputDesc, STRATEGY_ENFORCED_AUDIBLE) &&
mEngine->getForceUse(AUDIO_POLICY_FORCE_FOR_SYSTEM) == AUDIO_POLICY_FORCE_SYSTEM_ENFORCED) {
device = getDeviceForStrategy(STRATEGY_ENFORCED_AUDIBLE, fromCache);
} else if (isInCall() || isStrategyActive(outputDesc, STRATEGY_PHONE)) {
device = getDeviceForStrategy(STRATEGY_PHONE, fromCache);
} else if (isStrategyActive(outputDesc, STRATEGY_SONIFICATION)) {
device = getDeviceForStrategy(STRATEGY_SONIFICATION, fromCache);
} else if (isStrategyActive(outputDesc, STRATEGY_ENFORCED_AUDIBLE)) {
device = getDeviceForStrategy(STRATEGY_ENFORCED_AUDIBLE, fromCache);
} else if (isStrategyActive(outputDesc, STRATEGY_ACCESSIBILITY)) {
device = getDeviceForStrategy(STRATEGY_ACCESSIBILITY, fromCache);
} else if (isStrategyActive(outputDesc, STRATEGY_SONIFICATION_RESPECTFUL)) {
device = getDeviceForStrategy(STRATEGY_SONIFICATION_RESPECTFUL, fromCache);
} else if (isStrategyActive(outputDesc, STRATEGY_MEDIA)) {
device = getDeviceForStrategy(STRATEGY_MEDIA, fromCache);
} else if (isStrategyActive(outputDesc, STRATEGY_DTMF)) {
device = getDeviceForStrategy(STRATEGY_DTMF, fromCache);
} else if (isStrategyActive(outputDesc, STRATEGY_TRANSMITTED_THROUGH_SPEAKER)) {
device = getDeviceForStrategy(STRATEGY_TRANSMITTED_THROUGH_SPEAKER, fromCache);
} else if (isStrategyActive(outputDesc, STRATEGY_REROUTING)) {
device = getDeviceForStrategy(STRATEGY_REROUTING, fromCache);
}
ALOGV("getNewOutputDevice() selected device %x", device);
return device;
}
前面说过了,决定我们的输出设备有三个决定性的因素:
- Stream Type
- Mode
- Force use — 上层会强制使用某个设备,比如打电话时要从听筒切到喇叭输出。
5.7 如何获得当前支持的所有Audio 设备
在 getDeviceForStrategy() 的log中,可以打印出来当前设备支持的所有音频设备。
audio_devices_t AudioPolicyManager::getDeviceForStrategy(routing_strategy strategy,
bool fromCache)
{
// Routing
// see if we have an explicit route
// scan the whole RouteMap, for each entry, convert the stream type to a strategy
// (getStrategy(stream)).
// if the strategy from the stream type in the RouteMap is the same as the argument above,
// and activity count is non-zero and the device in the route descriptor is available
// then select this device.
for (size_t routeIndex = 0; routeIndex < mOutputRoutes.size(); routeIndex++) {
sp<SessionRoute> route = mOutputRoutes.valueAt(routeIndex);
routing_strategy routeStrategy = getStrategy(route->mStreamType);
if ((routeStrategy == strategy) && route->isActive() &&
(mAvailableOutputDevices.indexOf(route->mDeviceDescriptor) >= 0)) {
return route->mDeviceDescriptor->type();
}
}
if (fromCache) {
ALOGVV("getDeviceForStrategy() from cache strategy %d, device %x",
strategy, mDeviceForStrategy[strategy]);
return mDeviceForStrategy[strategy];
}
return mEngine->getDeviceForStrategy(strategy);
}
问题分析:
如果,碰到输出设备不对的问题,
比如,播放音乐的时候,没有从喇叭出来,而从听筒出来了。
就可能根据 Stream Type、Mode、Force use 这三个方向来排查,如果都对,
可以从这个 log 看下当前设备到底支不支持该设备
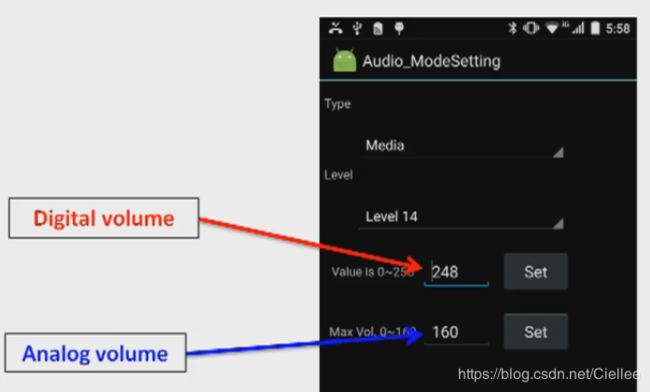
5.8 音量控制 Volume Control
在Audio SW 中,音量控制主要是对 数字增益 Digital Volume 和 模拟增益 Analog Volume 两个音量的控制。
-
数字增益 Digital Volume
不同的 Stream Type 使用不同的digital gain。 -
模拟增益 Analog Volume
因为使用同一台硬件,所有的 Stream 使用同一个 模拟增益 analog gain。
数字和模拟增益 使用场景如下:
5.9 Code Path
Kernel Audio 代码路径
/kernel/sound/soc/msm/
––– 包含平台 sdm660-common.c machine driver
/kernel/sound/soc/msm/qdsp6v2
––– 包含平台驱动代码platform drivers, 前端front end (FE),
and 后端back-end (BE) DAI driver, 骁龙DSP驱动
Hexagon DSP drivers for AFE, ADM, and ASM, voice driver, and so on.
/kernel/sound/soc/codecs/
––– 包含Audio Codec 驱动
/kernel/drivers/mfd/
––– 包含Codec相关代码 the codec driver-related files
/kernel/sound/soc/soc-*.c
––– audio接口代码,供framework使用,
All the SoC-*.c files provide information on the ALSA SoCs framework
/kernel/drivers/slimbus/ ––– Contains the source for the SLIMbus driver
/kernel/arch/arm/boot/dts ––– Audio DTS 配置
【音频客制化及调试指南】《80_na157_193_f_linux_android_audio_customization_a.pdf》
UserSpace Audio 代码
/hardware/qcom/audio/hal/msm8974 ––– Audio Hal 层代码
/external/tinyalsa/
–––tinymix, tinyplay, and tinycap 可执行程序代码
/hardware/qcom/audio/mm-audio
–––高通Audio编解码接口 QTI OMX components for the audio encoder and decoders
/frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/
––– Contains the source code of Stagefright implementation from Google.
/frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/
––– Contains the source code for AudioFlinger that manages audio streams from the user space
/vendor/qcom/proprietary/mm-audio/
––– Audio dts 解析,acdb 音频参数解析代码
/external/bluetooth/bluedroid/
––– A2DP 蓝牙Audio 相关代码
/hardware/libhardware/modules/usbaudio/
––– USB Audio的HAL 层代码
/system/core/include/system/
––– Contains audio.h and audio_policy.h that contain enum definitions
and inline functions used all over the code for audio in the user space
frameworks/base/media/java/android/media/ ––– java 层Audio 接口代码
Date: 2019/09/20 - 13:41