Ansible概述
Ansible基于Python开发,集合了众多优秀运维工具的特点,实现了批量运行命令、部署程序、配置系统等功能。默认通过SSH协议进行远程命令执行或下发配置,无需部署任何客户端代理软件,从而使得自动化环境部署变得更加简单。可同时支持多台主机并行管理,使得管理主机更加便捷。
Ansible核心组件
Ansible可以看作是一种基于模块进行工作的框架结构,批量部署能力就是由Ansible所运行的模块实现的。
Ansible基本架构有六个部分组成
- Ansible core核心引擎
- Host inventory主机清单:用来定义Ansible所管理的主机,默认是在Ansible的hosts配置文件中定义被管理主机,同时也支持自定义动态主机清单和指定其他配置文件的位置。
- Connection plugins连接插件:负责和被管理主机实现通信。
- Playbooks(yaml,jinja2)剧本:用来集中定义Ansible任务的配置文件,即将多个任务定义在一个剧本中由Ansible自动执行,可以由控制主机针对多台被管理主机同时运行多个任务。
- Core modules核心模块:是Ansible自带的模块,使用执行模块将资源分发到被管理主机,使其执行特定任务或匹配特定的状态。
- Custom modules自定义模块:用于完成模块功能的补充,可借助相关插件完成记录日志、发送邮件等功能。
安装部署Ansible服务
Ansible自动化运维环境由控制主机与被管理主机组成,由于Ansibble是基于SSH协议进行通信的,所以控制主机安装Ansible软件后不需要重启或运行任何程序,被管理主机也不需要安装和运行任何代理程序。
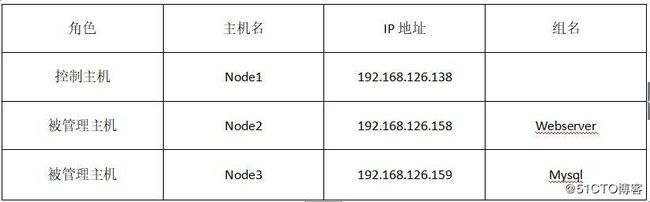
Ansible环境表
实验步骤
1.安装Ansible
1)通过YUM方式安装Ansible,需要依赖第三方的EPEL源,下面配置 epel源作为部署Ansible的yum源。
[root@localhost ~]# yum install epel-release -y2)使用yum命令安装ansible
[root@localhost ~]# yum install ansible -y
[root@localhost ~]# ansible --version #查看版本信息
ansible 2.6.2
config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
.....//省略3)使用树状结构展示文件夹
[root@localhost ~]# yum install tree -y
[root@localhost ~]# tree /etc/ansible/
/etc/ansible/
├── ansible.cfg #ansible的配置文件
├── hosts #ansible的主仓库,用于存储需要管理的远程主机的相关信息
└── roles #角色2.配置主机清单
Ansible通过读取默认主机清单/etc/ansible/hosts文件,修改主机与组配置后,可同时连接到多个被管理主机上执行任务。
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[webserver] #被管理主机node2的别名,可自定义。
192.168.126.158
[mysql] #被管理主机node3的别名,可自定义。
192.168.126.1593.设置SSH无密码登录
为了避免Ansible下发指令时输入被管理主机的密码,可以通过证书签名达到SSH无密码登录的效果,使用ssh-keygen产生一对密钥,使用ssh-copy-id来下发生成的公钥。
[root@localhost ~]# ssh-keygen -t rsa
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa): #Enter
/root/.ssh/id_rsa already exists.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): #输入密码
Enter same passphrase again: #确认密码
SHA256:RRrz8tRs6aW8YHDEVAp+Kfcn139TheaTAu0n8s4+AwU [email protected]
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| +o+.. |
| . OE* . . |
| * @.* + .|
| @ B.= o.|
| S =.X B o|
| ..+ O .o|
| .o .o|
| oo o|
| .+o |
+----[SHA256]-----+
[root@localhost ~]# ssh-copy-id [email protected]
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
[email protected]'s password: #被管理主机的root登录密码
[root@localhost ~]# ssh-copy-id [email protected]
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
[email protected]'s password: #被管理主机的root登录密码
免交互代理:
[root@localhost ~]# ssh-agent bash
[root@localhost ~]# ssh-add
Enter passphrase for /root/.ssh/id_rsa: #免交互的密码
Identity added: /root/.ssh/id_rsa (/root/.ssh/id_rsa)到此Ansible的环境部署完成
Ansible基础命令应用
1.command模块
Ansible管理工具使用-m选项来指定使用模块。默认使用command模块,即-m选项省略时会运行此模块,用于在被管理主机上运行命令。分别有三种执行命令的方式去管理写入之际清单中的主机。如下所示:
[root@localhost ~]# ansible all -m command -a 'date' #显示所有被管理主机的时间
192.168.126.159 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
2018年 08月 02日 星期四 06:41:55 CST
192.168.126.158 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
2018年 08月 02日 星期四 06:41:55 CST
[root@localhost ~]# ansible 192.168.126.158 -m command -a 'date' #指定ip执行date
192.168.126.158 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
2018年 08月 02日 星期四 06:44:46 CST
[root@localhost ~]# ansible webserver -m command -a 'date' #/指定分类执行date
192.168.126.158 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
2018年 08月 02日 星期四 06:45:45 CST
2.cron模块
cron模块用于定义任务计划。其中有两种状态(state):present表示添加(省略状态时使用默认),absent表示移除。
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -m cron -a 'minute="*/1" job="/bin/echo haha" name="test cron job"' #添加任务计划
192.168.126.159 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": [
"test cron job"
]
}
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -a 'crontab -l' #查看任务计划
192.168.126.159 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
#Ansible: test cron job
*/1 * * * * /bin/echo haha
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -m cron -a 'name="test cron job" state=absent' #移除计划任务,假如该计划任务没有取名字,name=None即可
192.168.126.159 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": []
}
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -a 'crontab -l'
192.168.126.159 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>3.user模块
user用于创建新的用户和更改、删除已存在的用户。其中name选项用来指明创建用户的名称。
[root@localhost ~]# ansible webserver -m user -a 'name=zhangsan' #创建用户
192.168.126.158 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"comment": "",
"create_home": true,
"group": 1001,
"home": "/home/zhangsan",
"name": "zhangsan",
"shell": "/bin/bash",
"state": "present",
"system": false,
"uid": 1001
}
被管理主机上查看是否有用户zhangsan:
[root@localhost ~]# id zhangsan #创建用户成功
uid=1001(zhangsan) gid=1001(zhangsan) 组=1001(zhangsan)
[root@localhost ~]# ansible webserver -m user -a 'name=zhangsan state=absent' #删除用户
192.168.126.158 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"force": false,
"name": "zhangsan",
"remove": false,
"state": "absent"
}
查看:
[root@localhost ~]# id zhangsan #删除成功
id: zhangsan: no such user4.group模块
group模块用于用户组进行管理
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -m group -a 'name=mysql gid=406 system=yes' #创建mysql组,将mysql用户添加到mysql组中。
192.168.126.159 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"gid": 406,
"name": "mysql",
"state": "present",
"system": true
}
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -a 'tail /etc/group'
192.168.126.159 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
slocate:x:21:
postdrop:x:90:
postfix:x:89:
stapusr:x:156:
stapsys:x:157:
stapdev:x:158:
tcpdump:x:72:
mysql:x:406: #添加成功
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -m user -a 'name=lisi uid=304 system=yes group=mysql' #把用户lisi添加到mysql组中
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -a 'id lisi' #查看用户李四信息
192.168.126.159 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
uid=304(lisi) gid=406(mysql) 组=406(mysql),10(wheel)5.copy模块
copy模块用于实现文件复制和批量下发文件。其中使用src来定义本地源文件路径,使用dest定义被管理主机的文件路径,使用content则是通过指定信息内容来生成目标文件。
1)将本地文件/etc/fstab复制到被管理主机上的/opt/fstab.back,将所有者设置为root,权限设置为604.
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -m copy -a 'src=/etc/fstab dest=/opt/fstab.back owner=root mode=640'
192.168.126.159 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "242f00a74b3d3b43a062c02d905cdbeb9300677d",
"dest": "/opt/fstab.back",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "742b16b5d70b86faa48211e3b92b1a07",
"mode": "0640",
"owner": "root",
"secontext": "system_u:object_r:usr_t:s0",
"size": 465,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1533165452.1-274964488903006/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -a 'ls -l /opt'
192.168.126.159 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 15 8月 1 21:22 fstab.link -> /opt/fstab.back
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -a 'cat /opt/fstab.back' #查看被管理主机/opt/目录下的fstab.back
#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Thu May 31 18:13:32 2018
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
/dev/mapper/centos-root / xfs defaults 0 0
UUID=1a66bd48-697c-4fca-9822-1f2ada9250e3 /boot xfs defaults 0 0
/dev/mapper/centos-swap swap swap defaults 0 02)将hello wangwu写入/opt/fstab.back
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -m copy -a 'content="hello wangwu!" dest=/opt/fstab.back'
.....//省略
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -a 'cat /opt/fstab.back'
192.168.126.159 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
hello wangwu! #写入成功注意:
如果出现报错,是因为被管理主机开启了SELinux,需要在被管理主机上安装libselinux-python软件包,才可以使用Ansible中与copy、file相关函数。6.file模块
设置文件属性,其中使用path指定文件路径,使用src定义源文件路径,使用name或dest来替换创建文件的符号链接。
1)设置文件/opt/fstab.back的属主和属组为mysql,权限为644.
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -m file -a 'owner=mysql group=mysql mode=644 path=/opt/fstab.back'
查看:
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l /opt/fstab.back
-rw-r--r--. 1 mysql mysql 465 8月 2 07:31 /opt/fstab.back2)设置文件/opt/fstab.link为/opt/fstab.back的链接文件
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -m file -a 'path=/opt/fstab.link src=/opt/fstab.back state=link' 3)文件的添加和删除
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -m file -a "path=/opt/test state=touch" #添加文件
查看被管理主机node3:
[root@localhost ~]# ls /opt/
apache-tomcat-8.5.16 fstab.back fstab.link jdk1.8.0_91 rh script.txt test
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -m file -a "path=/opt/fstab.back state=absent" #删除文件
[root@localhost ~]# ls /opt/
apache-tomcat-8.5.16 fstab.link jdk1.8.0_91 rh script.txt test7.ping模块检测指定主机的连通性
[root@localhost ~]# ansible all -m ping
192.168.126.159 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
192.168.126.158 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}8.yum模块
yum模块负责在被管理主机上安装与卸载软件包,但是需要提前在每个节点配置自己的YUM仓库。其中使用name指定要安装的软件包,还需要带上软件包的版本号,否则安装最新的软件包;使用state指定安装软件包的状态,present、latest用来表示安装,absent表示卸载。
1)安装httpd软件包
[root@localhost ~]# ansible webserver -m yum -a 'name=httpd'
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -q httpd
httpd-2.4.6-80.el7.centos.1.x86_642)卸载httpd服务
[root@localhost ~]# ansible webserver -m yum -a 'name=httpd state=absent'9.service模块
控制服务的运行状态,使用enable表示开机自启动,取值为true或false;使用name定义服务名称;使用state指定服务状态,取值分别为started、stoped、restarted。
1)查看被管理主机node3的httpd服务状态
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -a 'systemctl status httpd'
192.168.126.159 | FAILED | rc=3 >>
● httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: inactive (dead)
Docs: man:httpd(8)
man:apachectl(8)non-zero return code2)启动httpd服务并设置为开机自启动
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -m service -a 'enabled=true name=httpd state=started'
192.168.126.159 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"enabled": true,
"name": "httpd",
"state": "started",
.....//省略
node3:
[root@localhost ~]# netstat -ntap | grep 80
tcp 0 0 192.168.126.159:22 192.168.126.10:55807 ESTABLISHED 2613/sshd: root@pts
tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 6893/httpd 10.shell模块
shell模块可以在被管理主机上运行命令,并支持像管道符号等功能的复杂命令。
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -m shell -a 'echo abc123|passwd --stdin lisi' #无交互模式给用户设置密码
192.168.126.159 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
更改用户 lisi 的密码 。
passwd:所有的身份验证令牌已经成功更新。11.script模块
script模块可以将本地脚本复制到被管理主机上进行运行。需要注意的是,使用相对路径来指定脚本。
[root@localhost opt]# vim test.sh #编辑本地脚本
#!/bin/bash
echo "hello ansible from script" > /opt/script.txt
[root@localhost opt]# chmod +x test.sh
[root@localhost opt]# ansible webserver -m script -a 'test.sh' #复制到被管理主机上运行
192.168.126.158 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"rc": 0,
"stderr": "Shared connection to 192.168.126.158 closed.\r\n",
"stderr_lines": [
"Shared connection to 192.168.126.158 closed."
],
"stdout": "",
"stdout_lines": []
}
node3:
[root@localhost ~]# cat /opt/script.txt
hello ansible from script12.setup模块
setup模块收集、查看被管理主机的设备信息的一个功能。每个被管理主机在接收并运行管理命令之前,都会将自己的相关消息发送给控制主机。
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -m setup #输出信息太多,这里省略