1.前言
关于redux的基本概念和工作流如何进行的这里就不进行过多概述了,可以查看相关文档去了解。
流程图链接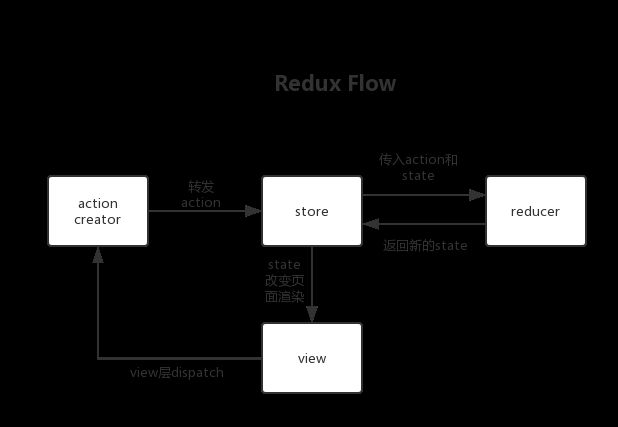
2.redux源码结构
以下是redux的源码结构图,主要的就是以下几个文件组成,我们接下来按顺序进行介绍其中原理和实现过程。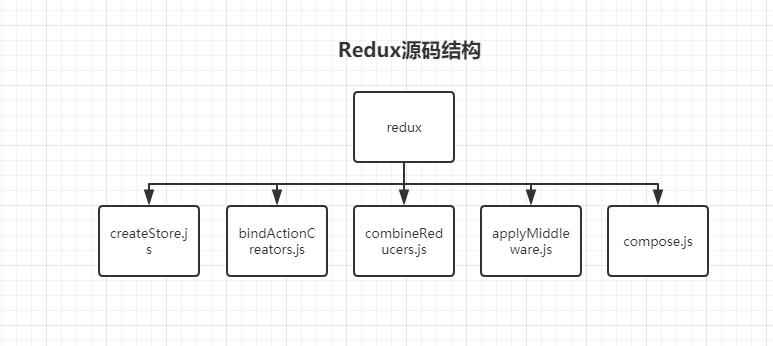
3.createStore.js
首先了解下createStore.js。通过调用createStore创建唯一的store,store中暴露出getState,dispatch,subscribe,replaceReducer这几个方法。通常我们用到的主要是前三个方法,这里作为主要介绍内容。如下是createStore的主要内容:
export function createStore(reducer, preloadedState, enhancer) {
/**
* 以下的判断都是对传入的参数进行验证
*/
if(
(typeof preloadedState === 'function' && typeof enhancer === 'function') ||
(typeof enhancer === 'function' && typeof arguments[3] === 'function')
) {
throw new Error('只能传递一个enhancer到createStore()中')
}
if(typeof preloadedState === 'function' && typeof enhancer === 'undefined') {
enhancer = preloadedState
preloadedState = undefined
}
if(typeof enhancer !== 'undefined') {
if(typeof enhancer !== 'function') {
throw new Error('enhancer应该为一个函数')
}
return enhancer(createStore)(reducer, preloadedState)
}
if(typeof reducer !== 'function') {
throw new Error('reducer应该为一个函数')
}
/**
* 初始化参数
*/
let currentReducer = reducer //初始化reducer
let currentState = preloadedState //初始化state
let currentListeners = [] //初始化subscribe监听函数数组
let nextListeners = currentListeners
let isDispatching = false
/**
* 复制一份currentListeners,为了防止在dispatch的时候
* 调用subscribe和unsubscribe时候发生错误
*/
function ensureCanMutateNextListeners() {
if(nextListeners === currentListeners) {
nextListeners = currentListeners.slice()
}
}
/**
* 获取当前的state
*/
function getState() {
if(isDispatching) {
throw new Error('不可以在isDispatching的时候调用getState')
}
return currentState
}
/**
* 订阅监听事件,触发dispatch后执行
*/
function subscribe(listener) {
if(typeof listener != 'function') {
throw new Error('Expected the listener to be a function.')
}
if(isDispatching) {
throw new Error('isDispatching的时候无法调用')
}
let isSubscribed = true
ensureCanMutateNextListeners()
nextListeners.push(listener)
return function unsubscribe() {
if(!isSubscribed) { //正在解除监听事件的时候不向下执行
return
}
if(isDispatching) {
throw new Error('正在dispatch的时候不给执行')
}
isSubscribed = false
ensureCanMutateNextListeners()
const index = nextListeners.indexOf(listener)
nextListeners.splice(index)
}
}
/**
* 执行好dispatch循环调用每个subscribe的函数
*/
function dispatch() {
//关于验证的代码就不写了
const listeners = (currentListeners = nextListeners)
for(let i=0; i4. combineReducers.js
combineReducers,它接收多个reducer函数,并整合,归一化成一个rootReducer。其返回值rootReducer将会成为createStore的参数,完成store的创建。
combineReducers只接收一个参数,这个参数阐述了不同reducer函数和页面状态数据树不同部分的映射匹配关系。
const combineReducers = (reducers) => {
return (state={}, action) => {
Object.keys(reducers).reduce((nextState, key) => {
nextState[key] = reducers[key](state[key], action)
return nextState
}, {})
}
}5. applyMiddleware.js
可以通过此方法给redux在触发action到reducer的过程中增加一个中间环节。applyMiddleware返回的内容我们称为enhancer。这个是createStore方法的最后一个参数,并且是可选的。
在redux源码中涉及中间件的脚本有applyMiddleware.js、createStore.js、compose.js。那么applyMiddleware(...middlewares)中会发生什么事情。
在createStore.js中有一段源码如下:
export default function createStore(reducer, preloadedState, enhancer) {
//...
return enhancer(createStore)(reducer, preloadedState)
//...
}顾名思义,applyMiddleware就是对各个需要的中间件进行糅合,并作为createStore的第二个或者第三个参数传入。用于增强store。源码如下:
const combineReducers = (reducers) => {
return (state = {}, action) => {
return Object.keys(reducers).reduce((nextState, key) => {
nextState[key] = reducers[key](state[key], action)
return nextState
}, {})
}
}
export default function applyMiddleware(...middlewares) {
return (next) => {
return (reducer, initialState) => {
var store = next(reducer, initialState)
var dispatch = store.dispatch
var chain = []
//包装一下store的getState和dispatch方法
//是第三方中间件需要使用的参数
var middlewareAPI = {
getState: store.getState,
dispatch: (action) => dispatch(action)
}
//每个中间件也是一个高度柯里化的函数,它接收middlewareAPI参数后的第一次返回结果并存储到chain数组中
//chain数组中每一项都是对dispatch的增强,并进行控制权转移。
chain = middlewares.map(middleware => middleware(middlewareAPI))
//这里的dispatch函数就是增强后的dispatch,因此compose方法接收了chain数组和原始dispatch方法。
dispatch = compose(...chain, store.dispatch)
return {
...store,
dispatch
}
}
}
}
export default function compose(...funcs) {
if(funcs.length === 0) {
return arg => arg
}
if(funcs.length === 1) {
return funcs[0]
}
return funcs.reduce((a, b) => (...args) => a(b(...args)))
}6. compose.js
这个方法在applymiddleware中介绍了,可以在上面看到。
7.bindActionCreators.js
这个模块涉及的内容较少,我们直接去看源码:
function bindActionCreator(actionCreator, dispatch) {
//这个函数主要作用就是返回一个函数,当我们调用返回的这个函数的时候
//会自动的dispatch对应的action
return function() {
return dispatch(actionCreator.apply(this, args))
}
}/**
参数说明:
actionCreators: action create函数,可以是一个单函数,也可以是一个对象,这个对象的所有元素都是action create函数
dispatch: store.dispatch方法
*/
export default function bindActionCreators(actionCreators, dispatch) {
// 如果actionCreators是一个函数的话,就调用bindActionCreator方法对action create函数和dispatch进行绑定
if (typeof actionCreators === 'function') {
return bindActionCreator(actionCreators, dispatch)
}
// actionCreators必须是函数或者对象中的一种,且不能是null
if (typeof actionCreators !== 'object' || actionCreators === null) {
throw new Error(
`bindActionCreators expected an object or a function, instead received ${actionCreators === null ? 'null' : typeof actionCreators}. ` +
`Did you write "import ActionCreators from" instead of "import * as ActionCreators from"?`
)
}
// 获取所有action create函数的名字
const keys = Object.keys(actionCreators)
// 保存dispatch和action create函数进行绑定之后的集合
const boundActionCreators = {}
for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
const key = keys[i]
const actionCreator = actionCreators[key]
// 排除值不是函数的action create
if (typeof actionCreator === 'function') {
// 进行绑定
boundActionCreators[key] = bindActionCreator(actionCreator, dispatch)
}
}
// 返回绑定之后的对象
/**
boundActionCreators的基本形式就是
{
actionCreator: function() {dispatch(actionCreator.apply(this, arguments))}
}
*/
return boundActionCreators
}