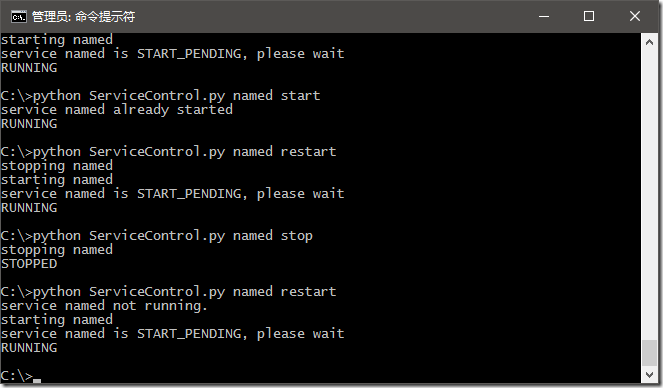
Windows服务常用的功能就是启动服务,关闭服务,重启服务和查询服务运行状态,其中查询服务运行状态是其他三种操作的基础。
本文中提到的使用Python脚本管理Windows服务实际上是调用win32serviceutil模块,此模块来自pywin32包,此模块本身有管理服务的功能,有兴趣的可以去阅读它的部分源码。
本脚本存在的目的是为了熟练Python的语法和基本操作,Windows下有更好的命令行工具来管理服务,如sc、Powershell等。通常命令行工具的执行速度要比services.msc工具要快得多。
本脚本实现的功能:
1.利用docopt解析命令行参数,-h和--help查看使用帮助,允许服务名和动作这个两个参数互换,如service mysql start和service start mysql具有同等作用
2.Windows平台下启动服务,关闭服务,重启服务和查询服务运行状态
脚本内容如下:
#!/usr/bin/python
# encoding: utf-8
# -*- coding: utf8 -*-
"""
Created by PyCharm.
File: LinuxBashShellScriptForOps:ServiceControl.py
User: Guodong
Create Date: 2016/10/14
Create Time: 17:57
Example of program with many options using docopt, control system service.
Usage:
ServiceControl.py SERVICE_NAME SERVICE_ACTION
ServiceControl.py SERVICE_ACTION SERVICE_NAME
ServiceControl.py --version | -v
ServiceControl.py --help | -h
Arguments:
SERVICE_NAME service name
SERVICE_ACTION service action in ["start", "stop", "restart", "status"]
Options:
-h --help show this help message and exit
-v --version show version and exit
"""
import sys
import codecs
import locale
import psutil
import win32serviceutil
import time
from collections import OrderedDict
from docopt import docopt
UNKNOWN = 0
STOPPED = 1
START_PENDING = 2
STOP_PENDING = 3
RUNNING = 4
status_code = {
0: "UNKNOWN",
1: "STOPPED",
2: "START_PENDING",
3: "STOP_PENDING",
4: "RUNNING"
}
def get_system_encoding():
"""
The encoding of the default system locale but falls back to the given
fallback encoding if the encoding is unsupported by python or could
not be determined. See tickets #10335 and #5846
"""
try:
encoding = locale.getdefaultlocale()[1] or 'ascii'
codecs.lookup(encoding)
except Exception:
encoding = 'ascii'
return encoding
DEFAULT_LOCALE_ENCODING = get_system_encoding()
# try:
# result = result.decode(DEFAULT_LOCALE_ENCODING)
# except UnicodeDecodeError:
# # UnicodeDecodeError - preventive treatment for non-latin Windows.
# return ''
def is_iterable(source):
if source is not None:
try:
iter(source)
except TypeError:
return False
return True
else:
raise RuntimeError("argument cannot be None")
def status_service(service_name):
try:
result = win32serviceutil.QueryServiceStatus(service_name)[1]
if result == START_PENDING:
print "service %s is %s, please wait" % (service_name, status_code[result])
time.sleep(2)
return RUNNING
elif result == STOP_PENDING:
print "service %s is %s, please wait" % (service_name, status_code[result])
time.sleep(2)
return STOPPED
else:
return result if result is not None else 0
except Exception as e:
if e.message:
raise RuntimeError(e.message)
elif e.args:
# print e.args
args = list()
for arg in e.args:
if is_iterable(arg):
args.append(unicode(eval(repr(arg)), 'gbk'))
else:
args.append(arg)
print "Error:", args[-1], tuple(args)
raise RuntimeError
else:
raise RuntimeError("Uncaught exception, maybe it is a 'Access Denied'") # will not reach here
def start_service(service_name):
status = status_service(service_name)
if status == STOPPED:
pass
elif status == RUNNING:
print "service %s already started" % service_name
return status
try:
print "starting %s" % service_name
win32serviceutil.StartService(service_name)
except Exception as e:
if e.message:
raise RuntimeError(e.message)
elif e.args:
# print e.args
args = list()
for arg in e.args:
if is_iterable(arg):
args.append(unicode(eval(repr(arg)), 'gbk'))
else:
args.append(arg)
print "Error:", args[-1], tuple(args)
raise RuntimeError
else:
raise RuntimeError("Uncaught exception, maybe it is a 'Access Denied'") # will not reach here
return status_service(service_name)
def stop_service(service_name):
status = status_service(service_name)
if status == STOPPED:
print "service %s already stopped" % service_name
return status
elif status == RUNNING:
pass
else:
return status
try:
print "stopping %s" % service_name
win32serviceutil.StopService(service_name)
except Exception as e:
if e.message:
print e.message
elif e.args:
# print e.args
args = list()
for arg in e.args:
if is_iterable(arg):
args.append(unicode(eval(repr(arg)), 'gbk'))
else:
args.append(arg)
print "Error:", args[-1], tuple(args)
raise RuntimeError
else:
raise RuntimeError("Uncaught exception, maybe it is a 'Access Denied'") # will not reach here
return status_service(service_name)
def restart_service(service_name):
status = status_service(service_name)
if status == START_PENDING or status == RUNNING:
if status == START_PENDING:
time.sleep(2)
stop_service(service_name)
status = status_service(service_name)
if status == STOPPED or status == STOP_PENDING:
if status == STOP_PENDING:
time.sleep(2)
return start_service(service_name)
elif status == STOPPED or status == STOP_PENDING:
print "service %s not running." % service_name
return start_service(service_name)
else:
return status_service(service_name)
def do_service(service_name, service_action):
# https://docs.python.org/2/faq/design.html#why-isn-t-there-a-switch-or-case-statement-in-python
# http://python.jobbole.com/82008/
valid_action = ["start", "stop", "restart", "status"]
maps = {
"start": "start_service(service_name)",
"stop": "stop_service(service_name)",
"restart": "restart_service(service_name)",
"status": "status_service(service_name)",
}
if service_name == "" or service_action == "":
raise RuntimeError("service_name and service_action cannot be empty.")
if service_action in valid_action:
return eval(maps[service_action])
else:
raise RuntimeError("bad service_action '%s', valid action is %s" % (service_action, valid_action))
def list_service():
service_dict = OrderedDict()
for service in psutil.win_service_iter():
service_dict[service.name()] = service.display_name()
return service_dict
def is_valid_service_name(service_name):
if service_name.lower() in [name.lower() for name, display_name in list_service().items()]:
return True
else:
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
SERVICE_ACTION = ["start", "stop", "restart", "status"]
arguments = docopt(__doc__, version='1.0.0rc2')
if arguments['SERVICE_NAME'] != "" and arguments['SERVICE_ACTION'] != "":
if arguments['SERVICE_ACTION'] in SERVICE_ACTION:
pass
elif arguments['SERVICE_NAME'] in SERVICE_ACTION:
tmp = arguments['SERVICE_ACTION']
arguments['SERVICE_ACTION'] = arguments['SERVICE_NAME']
arguments['SERVICE_NAME'] = tmp
else:
print __doc__
sys.exit(1)
if is_valid_service_name(arguments['SERVICE_NAME']):
pass
else:
raise RuntimeError("server '%s' not exist" % arguments['SERVICE_NAME'])
return_code = do_service(arguments['SERVICE_NAME'], arguments['SERVICE_ACTION'])
try:
print status_code[return_code]
except KeyError:
print "return_code is %s." % return_code
else:
print __doc__
sys.exit(1)
# TODO(Guodong Ding) run a command as administrator with administrative privilege, use 'runas' command?
state_command = "C:\WINDOWS\System32\sc.exe query MySQL56"
start_command = "C:\WINDOWS\System32\sc.exe start MySQL56"
stop_command = "C:\WINDOWS\System32\sc.exe stop MySQL56"
注:脚本内容可以从GitHub上找到:https://github.com/DingGuodong/LinuxBashShellScriptForOps/blob/master/projects/WindowsSystemOps/Services/ServiceControl.py
运行效果如下:
注意:利用Python脚本管理Windows服务有一个难以规避的问题就是管理员权限问题,因此运行此类Python脚本时应该以管理员权限运行,特别是Windows7以及更高版本的用户。
tag:Python管理Windows服务,Python Windows服务,Python 启动停止服务
--end--