现在很多安全类的软件,比如360手机助手,百度手机助手等等,都有一个悬浮窗,可以飘浮在桌面上,方便用户使用一些常用的操作。
今天这篇文章,就是介绍如何实现桌面悬浮窗效果的。
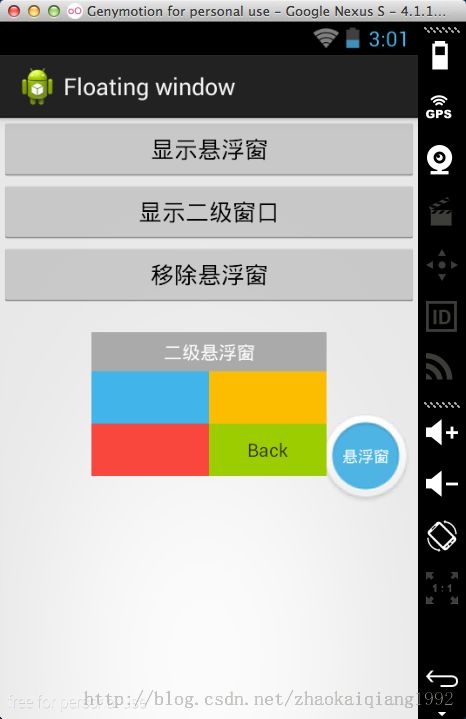
首先,看一下效果图。
悬浮窗一共分为两个部分,一个是平常显示的小窗口,另外一个是点击小窗口显示出来的二级悬浮窗口。
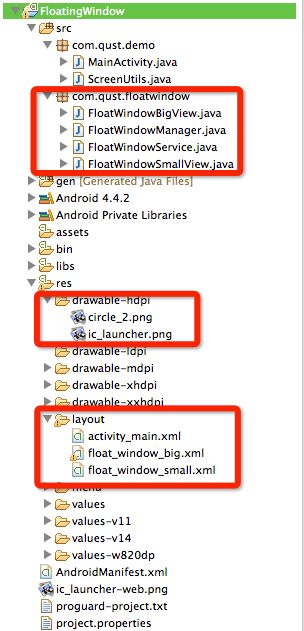
首先,先看一下这个项目的目录结构。
最关键的就是红框内的四个类。
首先,FloatWindowService是一个后台的服务类,主要负责在后台不断的刷新桌面上的小悬浮窗口,否则会导致更换界面之后,悬浮窗口也会随之消失,因此需要不断的刷新。下面是实现代码。
package com.qust.floatwindow;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.IBinder;
/**
* 悬浮窗后台服务
*
* @author zhaokaiqiang
*
*/
public class FloatWindowService extends Service {
public static final String LAYOUT_RES_ID = "layoutResId";
public static final String ROOT_LAYOUT_ID = "rootLayoutId";
// 用于在线程中创建/移除/更新悬浮窗
private Handler handler = new Handler();
private Context context;
private Timer timer;
// 小窗口布局资源id
private int layoutResId;
// 布局根布局id
private int rootLayoutId;
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
context = this;
layoutResId = intent.getIntExtra(LAYOUT_RES_ID, 0);
rootLayoutId = intent.getIntExtra(ROOT_LAYOUT_ID, 0);
if (layoutResId == 0 || rootLayoutId == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"layoutResId or rootLayoutId is illegal");
}
if (timer == null) {
timer = new Timer();
// 每500毫秒就执行一次刷新任务
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new RefreshTask(), 0, 500);
}
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
// Service被终止的同时也停止定时器继续运行
timer.cancel();
timer = null;
}
private class RefreshTask extends TimerTask {
@Override
public void run() {
// 当前界面没有悬浮窗显示,则创建悬浮
if (!FloatWindowManager.getInstance(context).isWindowShowing()) {
handler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
FloatWindowManager.getInstance(context)
.createSmallWindow(context, layoutResId,
rootLayoutId);
}
});
}
}
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return null;
}
}
除了后台服务之外,我们还需要两个自定义的布局,分别是FloatWindowSmallView和FloatWindowBigView,这两个自定义的布局,主要负责悬浮窗的前台显示,我们分别看一下代码实现。
首先是FloatWindowSmallView类的实现。
package com.qust.floatwindow;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.PixelFormat;
import android.view.Gravity;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.TextView;
import com.qust.demo.ScreenUtils;
import com.qust.floatingwindow.R;
/**
* 小悬浮窗,用于初始显示
*
* @author zhaokaiqiang
*
*/
public class FloatWindowSmallView extends LinearLayout {
// 小悬浮窗的宽
public int viewWidth;
// 小悬浮窗的高
public int viewHeight;
// 系统状态栏的高度
private static int statusBarHeight;
// 用于更新小悬浮窗的位置
private WindowManager windowManager;
// 小悬浮窗的布局参数
public WindowManager.LayoutParams smallWindowParams;
// 记录当前手指位置在屏幕上的横坐标
private float xInScreen;
// 记录当前手指位置在屏幕上的纵坐标
private float yInScreen;
// 记录手指按下时在屏幕上的横坐标,用来判断单击事件
private float xDownInScreen;
// 记录手指按下时在屏幕上的纵坐标,用来判断单击事件
private float yDownInScreen;
// 记录手指按下时在小悬浮窗的View上的横坐标
private float xInView;
// 记录手指按下时在小悬浮窗的View上的纵坐标
private float yInView;
// 单击接口
private OnClickListener listener;
/**
* 构造函数
*
* @param context
* 上下文对象
* @param layoutResId
* 布局资源id
* @param rootLayoutId
* 根布局id
*/
public FloatWindowSmallView(Context context, int layoutResId,
int rootLayoutId) {
super(context);
windowManager = (WindowManager) context
.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(layoutResId, this);
View view = findViewById(rootLayoutId);
viewWidth = view.getLayoutParams().width;
viewHeight = view.getLayoutParams().height;
statusBarHeight = getStatusBarHeight();
TextView percentView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.percent);
percentView.setText("悬浮窗");
smallWindowParams = new WindowManager.LayoutParams();
// 设置显示类型为phone
smallWindowParams.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_PHONE;
// 显示图片格式
smallWindowParams.format = PixelFormat.RGBA_8888;
// 设置交互模式
smallWindowParams.flags = WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_TOUCH_MODAL
| WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE;
// 设置对齐方式为左上
smallWindowParams.gravity = Gravity.LEFT | Gravity.TOP;
smallWindowParams.width = viewWidth;
smallWindowParams.height = viewHeight;
smallWindowParams.x = ScreenUtils.getScreenWidth(context);
smallWindowParams.y = ScreenUtils.getScreenHeight(context) / 2;
}
@SuppressLint("ClickableViewAccessibility")
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
switch (event.getAction()) {
// 手指按下时记录必要的数据,纵坐标的值都减去状态栏的高度
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
// 获取相对与小悬浮窗的坐标
xInView = event.getX();
yInView = event.getY();
// 按下时的坐标位置,只记录一次
xDownInScreen = event.getRawX();
yDownInScreen = event.getRawY() - statusBarHeight;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
// 时时的更新当前手指在屏幕上的位置
xInScreen = event.getRawX();
yInScreen = event.getRawY() - statusBarHeight;
// 手指移动的时候更新小悬浮窗的位置
updateViewPosition();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
// 如果手指离开屏幕时,按下坐标与当前坐标相等,则视为触发了单击事件
if (xDownInScreen == event.getRawX()
&& yDownInScreen == (event.getRawY() - getStatusBarHeight())) {
if (listener != null) {
listener.click();
}
}
break;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 设置单击事件的回调接口
*/
public void setOnClickListener(OnClickListener listener) {
this.listener = listener;
}
/**
* 更新小悬浮窗在屏幕中的位置
*/
private void updateViewPosition() {
smallWindowParams.x = (int) (xInScreen - xInView);
smallWindowParams.y = (int) (yInScreen - yInView);
windowManager.updateViewLayout(this, smallWindowParams);
}
/**
* 获取状态栏的高度
*
* @return
*/
private int getStatusBarHeight() {
try {
Class c = Class.forName("com.android.internal.R$dimen");
Object o = c.newInstance();
Field field = c.getField("status_bar_height");
int x = (Integer) field.get(o);
return getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(x);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 0;
}
/**
* 单击接口
*
* @author zhaokaiqiang
*
*/
public interface OnClickListener {
public void click();
}
}
在这个类里面,主要的工作是实现悬浮窗口在桌面前端的实现,还有就是位置的移动和单击事件的判断以及处理。这里使用的是主要是WindowManager类的一些方法和属性,下一篇会详细说明,这篇只说实现。
除了小悬浮窗之外,点击之后弹出的二级悬浮窗也是类似的方式添加到桌面上,下面是二级悬浮窗的代码。
package com.qust.floatwindow;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.PixelFormat;
import android.view.Gravity;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.TextView;
import com.qust.demo.ScreenUtils;
import com.qust.floatingwindow.R;
public class FloatWindowBigView extends LinearLayout {
// 记录大悬浮窗的宽
public int viewWidth;
// 记录大悬浮窗的高
public int viewHeight;
public WindowManager.LayoutParams bigWindowParams;
private Context context;
public FloatWindowBigView(Context context) {
super(context);
this.context = context;
LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.float_window_big, this);
View view = findViewById(R.id.big_window_layout);
viewWidth = view.getLayoutParams().width;
viewHeight = view.getLayoutParams().height;
bigWindowParams = new WindowManager.LayoutParams();
// 设置显示的位置,默认的是屏幕中心
bigWindowParams.x = ScreenUtils.getScreenWidth(context) / 2 - viewWidth
/ 2;
bigWindowParams.y = ScreenUtils.getScreenHeight(context) / 2
- viewHeight / 2;
bigWindowParams.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_PHONE;
bigWindowParams.format = PixelFormat.RGBA_8888;
// 设置交互模式
bigWindowParams.flags = WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_TOUCH_MODAL
| WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE;
bigWindowParams.gravity = Gravity.LEFT | Gravity.TOP;
bigWindowParams.width = viewWidth;
bigWindowParams.height = viewHeight;
initView();
}
private void initView() {
TextView tv_back = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_back);
tv_back.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
FloatWindowManager.getInstance(context).removeBigWindow();
}
});
}
}
这些基本的类建立起来之后,剩下的就是最重要的类FloatWindowManager的实现。这个类实现的就是对悬浮窗的操作。
package com.qust.floatwindow;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.view.WindowManager;
/**
* 悬浮窗管理器
*
* @author zhaokaiqiang
*
*/
public class FloatWindowManager {
// 小悬浮窗对象
private FloatWindowSmallView smallWindow;
// 大悬浮窗对象
private FloatWindowBigView bigWindow;
// 用于控制在屏幕上添加或移除悬浮窗
private WindowManager mWindowManager;
// FloatWindowManager的单例
private static FloatWindowManager floatWindowManager;
// 上下文对象
private Context context;
private FloatWindowManager(Context context) {
this.context = context;
}
public static FloatWindowManager getInstance(Context context) {
if (floatWindowManager == null) {
floatWindowManager = new FloatWindowManager(context);
}
return floatWindowManager;
}
/**
* 创建小悬浮窗
*
* @param context
* 必须为应用程序的Context.
*/
public void createSmallWindow(Context context, int layoutResId,
int rootLayoutId) {
WindowManager windowManager = getWindowManager();
if (smallWindow == null) {
smallWindow = new FloatWindowSmallView(context, layoutResId,
rootLayoutId);
windowManager.addView(smallWindow, smallWindow.smallWindowParams);
}
}
/**
* 将小悬浮窗从屏幕上移除
*
* @param context
*/
public void removeSmallWindow() {
if (smallWindow != null) {
WindowManager windowManager = getWindowManager();
windowManager.removeView(smallWindow);
smallWindow = null;
}
}
public void setOnClickListener(FloatWindowSmallView.OnClickListener listener) {
if (smallWindow != null) {
smallWindow.setOnClickListener(listener);
}
}
/**
* 创建大悬浮窗
*
* @param context
* 必须为应用程序的Context.
*/
public void createBigWindow(Context context) {
WindowManager windowManager = getWindowManager();
if (bigWindow == null) {
bigWindow = new FloatWindowBigView(context);
windowManager.addView(bigWindow, bigWindow.bigWindowParams);
}
}
/**
* 将大悬浮窗从屏幕上移除
*
* @param context
*/
public void removeBigWindow() {
if (bigWindow != null) {
WindowManager windowManager = getWindowManager();
windowManager.removeView(bigWindow);
bigWindow = null;
}
}
public void removeAll() {
context.stopService(new Intent(context, FloatWindowService.class));
removeSmallWindow();
removeBigWindow();
}
/**
* 是否有悬浮窗显示(包括小悬浮窗和大悬浮)
*
* @return 有悬浮窗显示在桌面上返回true,没有的话返回false
*/
public boolean isWindowShowing() {
return smallWindow != null || bigWindow != null;
}
/**
* 如果WindowManager还未创建,则创建新的WindowManager返回。否则返回当前已创建的WindowManager
*
* @param context
* @return
*/
private WindowManager getWindowManager() {
if (mWindowManager == null) {
mWindowManager = (WindowManager) context
.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
}
return mWindowManager;
}
}
还有个获取屏幕宽高的帮助类。
package com.qust.demo;
import android.content.Context;
import android.view.WindowManager;
/**
* 屏幕帮助类
*
* @author zhaokaiqiang
*
*/
public class ScreenUtils {
/**
* 获取屏幕宽度
*
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public static int getScreenWidth(Context context) {
return ((WindowManager) context
.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE)).getDefaultDisplay()
.getWidth();
}
/**
* 获取屏幕宽度
*
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public static int getScreenHeight(Context context) {
return ((WindowManager) context
.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE)).getDefaultDisplay()
.getHeight();
}
}
完成这些,我们就可以直接用了。
package com.qust.demo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.KeyEvent;
import android.view.View;
import com.qust.floatingwindow.R;
import com.qust.floatwindow.FloatWindowManager;
import com.qust.floatwindow.FloatWindowService;
import com.qust.floatwindow.FloatWindowSmallView.OnClickListener;
/**
* 示例
*
* @ClassName: com.qust.demo.MainActivity
* @Description:
* @author zhaokaiqiang
* @date 2014-10-23 下午11:30:13
*
*/
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private FloatWindowManager floatWindowManager;
private Context context;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
context = this;
floatWindowManager = FloatWindowManager.getInstance(context);
}
/**
* 显示小窗口
*
* @param view
*/
public void show(View view) {
// 需要传递小悬浮窗布局,以及根布局的id,启动后台服务
Intent intent = new Intent(context, FloatWindowService.class);
intent.putExtra(FloatWindowService.LAYOUT_RES_ID,
R.layout.float_window_small);
intent.putExtra(FloatWindowService.ROOT_LAYOUT_ID,
R.id.small_window_layout);
startService(intent);
}
/**
* 显示二级悬浮窗
*
* @param view
*/
public void showBig(View view) {
// 设置小悬浮窗的单击事件
floatWindowManager.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void click() {
floatWindowManager.createBigWindow(context);
}
});
}
/**
* 移除所有的悬浮窗
*
* @param view
*/
public void remove(View view) {
floatWindowManager.removeAll();
}
@Override
public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
// 返回键移除二级悬浮窗
if (keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK
&& event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
floatWindowManager.removeBigWindow();
return true;
}
return super.onKeyDown(keyCode, event);
}
}
项目下载地址:https://github.com/ZhaoKaiQiang/FloatWindow
在上面文章中,我们介绍了如何实现桌面悬浮窗口,在这个效果的实现过程中,最重要的一个类就是WindowManager,今天这篇文章,将对WindowManager的使用进行介绍,并且实现一个使用WindowManager来实现用户打开APP,显示首次使用教学蒙板的效果。
WindowManager类实现了ViewManager接口,ViewManager接口允许我们在Activity上添加或者是移除view,因此WindowManager也允许我们在Activity上进行View的添加和移除操作。
我们可以通过下面的方法获取一个WindowManager对象
Context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE)
在Activity之中,我们可以直接通过getWindowManager()获取到一个WindowManager对象。
每一个WindowManager实例都被绑定到一个独有的Display对象上面,如果我们想获取不同Display的WindowManager对象,我们可以通过createDisplayContext(Display)获取到这个Display的Context对象,然后使用上面的方法,也可以获取到一个WindowManager对象。
我们在使用WindowManager类的时候,通常使用下面的几个方法:
windowManager.addView(View,WindowManager.LayoutParam); windowManager.removeView(); windowManager.getDefaultDisplay();
windowManager.addView()方法用来向当前的窗口上添加View对象,需要接受两个参数,View是要添加到窗口的View对象,而WindowManager.LayoutParam则是添加的窗口的参数,在上一篇添加悬浮窗的操作的时候,需要对LayoutParam设置很多参数,下面我们看一下常用的设置
// 设置LayoutParams参数 LayoutParams params = new WindowManager.LayoutParams(); //设置显示的类型,TYPE_PHONE指的是来电话的时候会被覆盖,其他时候会在最前端,显示位置在stateBar下面,其他更多的值请查阅文档 params.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_PHONE; //设置显示格式 params.format = PixelFormat.RGBA_8888; //设置对齐方式 params.gravity = Gravity.LEFT | Gravity.TOP; //设置宽高 params.width = ScreenUtils.getScreenWidth(this); params.height = ScreenUtils.getScreenHeight(this); //设置显示的位置 params.x; params.y;
设置好LayoutParam之后,我们就可以通过windowManager.addView(View,WindowManager.LayoutParam)将View添加到窗口之上,不过,我们需要申明权限
添加完成之后,我们就可以在窗口上看到我们添加的View对象了。如果我们想将添加的View移除,我们只需要调用windowManager.removeView()即可,参数就是我们前面使用的View对象,使用很简单。除了这个方法,还有个windowManager.removeViewImmediate(),也可以将View移除,但是文档中说,这个方法并不是给一般程序调用的,因此需要小心使用,我们开发的都属于一般程序,建议不要使用这个方法。
除了这两个方法之外,我们最常用的另外一个方法就是windowManager.getDefaultDisplay(),通过这个方法,我们可以获取到当前界面的Display的一个对象,然后我们就可以获取到当前屏幕的一些参数,比如说宽高。
下面是我常用的一个工具类。
package com.qust.teachmask;
import android.content.Context;
import android.view.WindowManager;
/**
* 屏幕帮助类
*
* @author zhaokaiqiang
*
*/
public class ScreenUtils {
/**
* 获取屏幕宽度
*
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public static int getScreenWidth(Context context) {
return ((WindowManager) context
.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE)).getDefaultDisplay()
.getWidth();
}
/**
* 获取屏幕宽度
*
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public static int getScreenHeight(Context context) {
return ((WindowManager) context
.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE)).getDefaultDisplay()
.getHeight();
}
}
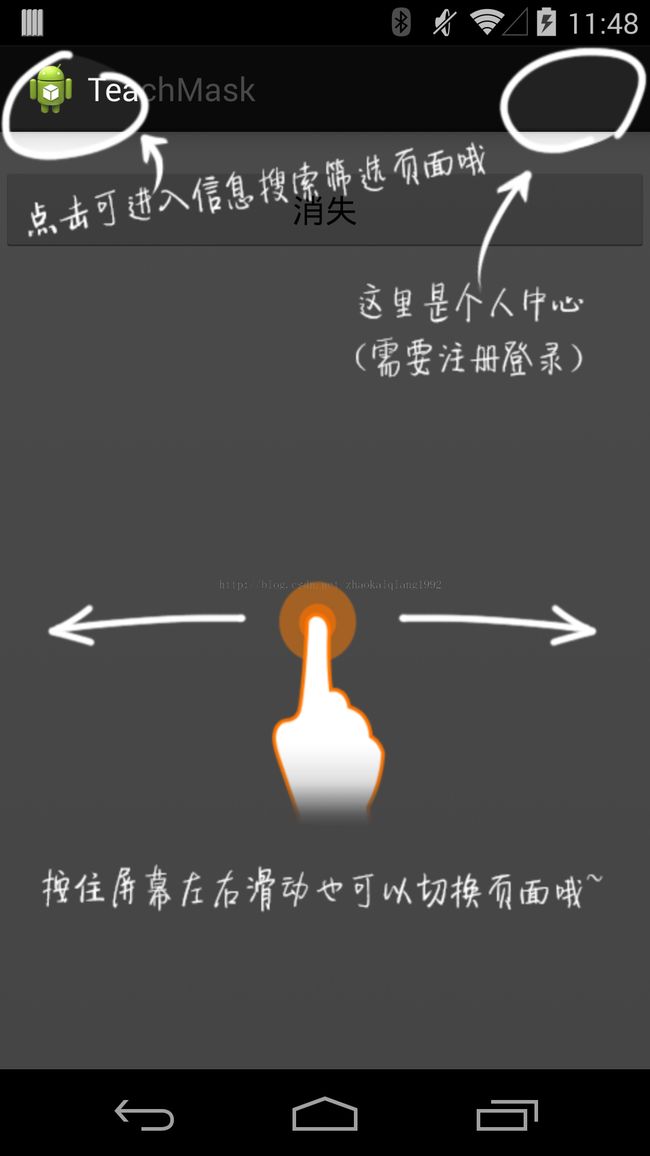
知道上面这些之后,我们就可以实现教学模板效果了,首先看效果图。
下面是代码实现
package com.qust.teachmask;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.PixelFormat;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Gravity;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import android.view.WindowManager.LayoutParams;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.ImageView.ScaleType;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private ImageView img;
private WindowManager windowManager;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
windowManager = getWindowManager();
// 动态初始化图层
img = new ImageView(this);
img.setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(
android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,
android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT));
img.setScaleType(ScaleType.FIT_XY);
img.setImageResource(R.drawable.guide);
// 设置LayoutParams参数
LayoutParams params = new WindowManager.LayoutParams();
// 设置显示的类型,TYPE_PHONE指的是来电话的时候会被覆盖,其他时候会在最前端,显示位置在stateBar下面,其他更多的值请查阅文档
params.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_PHONE;
// 设置显示格式
params.format = PixelFormat.RGBA_8888;
// 设置对齐方式
params.gravity = Gravity.LEFT | Gravity.TOP;
// 设置宽高
params.width = ScreenUtils.getScreenWidth(this);
params.height = ScreenUtils.getScreenHeight(this);
// 添加到当前的窗口上
windowManager.addView(img, params);
// 点击图层之后,将图层移除
img.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
windowManager.removeView(img);
}
});
}
}
本文非原创,转载于:http://blog.csdn.net/zhaokaiqiang1992
以上所述是小编给大家介绍的Android实现桌面悬浮窗、蒙板效果实例代码,希望对大家有所帮助!