内容:
1、linux系统启动排错及恢复(救援模式的使用)
2、自制linux系统
3、编译linux内核
一、系统启动排错及恢复(救援模式的使用)
1、bootloader损坏恢复
(1)进入救援模式
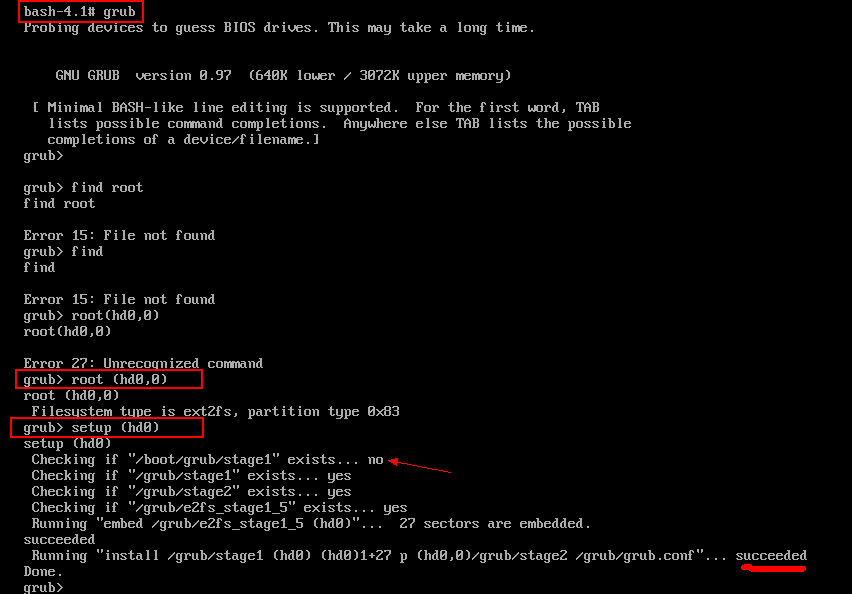
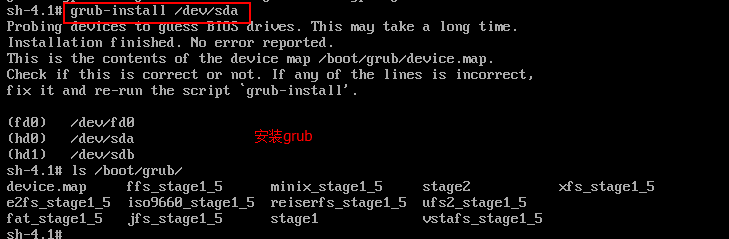
(2)在shell中运行grub程序
sh 3.1#grub grub>root (hdx,y) grub>setup (hd0) # setup (hd0)就是把GRUB写到硬盘的MBR上。 grub>quit
这里的X,如果是一个盘,就是0,如果你所安装的linux的根分区在第二个硬盘上,那X就是1了;Y,就是装有linux系统所在的根分区。
总结:在rescue模式下可以重装GRUB引导程序,修复MBR扇区。
[16:54 [email protected]~]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda bs=30 count=1 1+0 records in 1+0 records out 30 bytes (30 B) copied, 0.00292207 s, 10.3 kB/s [18:44 [email protected]~]# reboot now
成功修复:
2、vmlinux内核损坏恢复
(1)删除kernel做实验,要加上--nodeps:忽略依赖关系
(2)开机进入救援模式
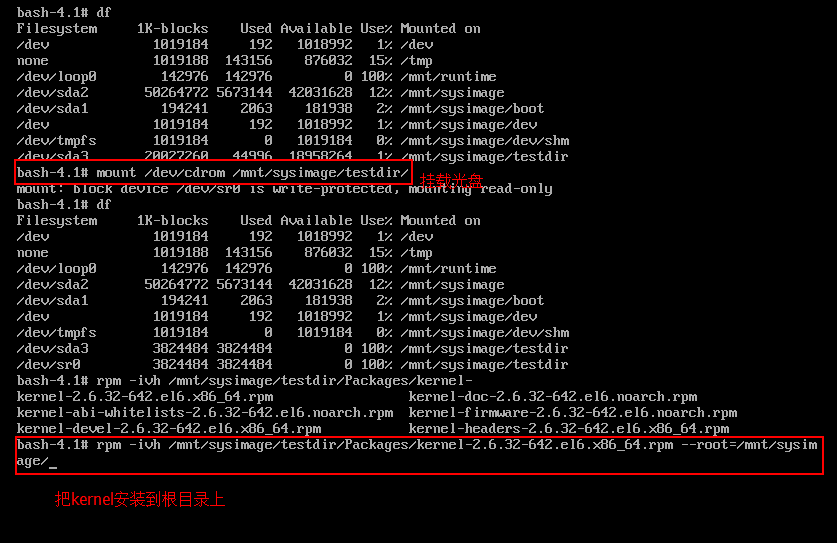
(3)把光盘挂载上(内核文件在光盘里),注意,不要把光盘直接挂载在/mnt下,会把真根系统给隐藏了
(4)rpm安装kernel包,注意,救援模式下的真正的根是在/mnt/sysp_w_picpath下,所以rpm要加上选项--root=/mnt/sysp_w_picpath(如果切换了根chroot,则不需要此参数)
(5)重启后恢复系统
[19:22 [email protected]~]# rpm -q kernel kernel-2.6.32-642.el6.x86_64 [19:31 [email protected]~]# rpm -e kernel error: Failed dependencies: kernel >= 2.6.30 is needed by (installed) pulseaudio-0.9.21-24.el6.x86_64 kernel >= 2.6.17 is needed by (installed) autofs-1:5.0.5-122.el6.x86_64 kernel >= 2.6.14 is needed by (installed) fuse-2.8.3-5.el6.x86_64 kernel >= 2.6.32-33.el6 is needed by (installed) xorg-x11-drv-intel-2.99.917-0.4.20151111.el6.x86_64 kernel >= 2.6.32-33.el6 is needed by (installed) xorg-x11-drv-ati-7.6.1-2.el6.x86_64 kernel >= 2.6.32-358.2.1 is needed by (installed) irqbalance-2:1.0.7-8.el6.x86_64 kernel >= 2.6.12-1.1411_FC5 is needed by (installed) pcmciautils-015-4.2.el6.x86_64 kernel-drm-nouveau = 16 is needed by (installed) xorg-x11-drv-nouveau-1:1.0.12-1.el6.x86_64 [19:31 [email protected]~]# rpm -e kernel --nodeps grubby fatal error: unable to find a suitable template grubby: doing this would leave no kernel entries. Not writing out new config. warning: erase unlink of /lib/modules/2.6.32-642.el6.x86_64/weak-updates failed: No such file or directory warning: erase unlink of /lib/modules/2.6.32-642.el6.x86_64/modules.order failed: No such file or directory warning: erase unlink of /lib/modules/2.6.32-642.el6.x86_64/modules.networking failed: No such file or directory warning: erase unlink of /lib/modules/2.6.32-642.el6.x86_64/modules.modesetting failed: No such file or directory warning: erase unlink of /lib/modules/2.6.32-642.el6.x86_64/modules.drm failed: No such file or directory warnin g: erase unlink of /lib/modules/2.6.32-642.el6.x86_64/modules.block failed: No such file or directory
无法进入系统:
进入救援模式:
安装kernel:
成功修复:
3、initramfs文件损坏恢复
(1)把initramfs文件删除,模拟initramfs文件损坏
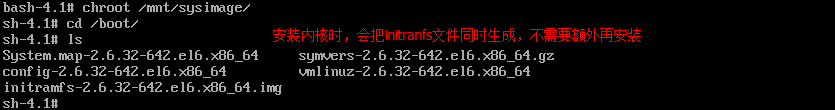
(2)进入救援模式,chroot=/mnt/sysp_w_picpath,再使用mkinitrd命令重新生成initramfs文件【注意,一定要在boot目录下使用该命令】
(3)重启即可
[19:58 [email protected]/boot]# rm -f initramfs-2.6.32-642.el6.x86_64.img [19:58 [email protected]/boot]# reboot Broadcast message from [email protected] (/dev/pts/0) at 19:58 ... The system is going down for reboot NOW! sh 3.1# mkinitrd /boot/initramfs-`uname -r`.img `uname -r`
4、/etc/fstab文件损坏恢复
(1)进入救援模式
(2)知道根在哪个分区就是直接把根挂载上,然后修改fstab文件,如果不知道根在哪个分区则需要逐一尝试挂载,直到找到根系统,然后修改fstab文件
(3)修改完后重启即可
[19:14 [email protected]~]# rm -f /etc/fstab [19:15 [email protected]~]# reboot Broadcast message from [email protected] (/dev/pts/0) at 19:15 ... The system is going down for reboot NOW!
5、/boot目录文件误删除恢复
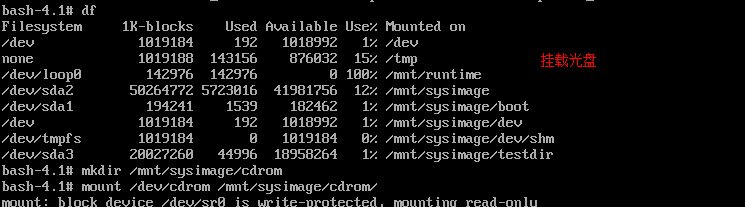
(1)挂载光盘
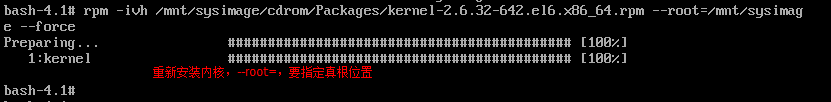
(2)安装kernel rpm -ivh --force(会同时生成initramfs)
(3)安装grub:grub-install (必须切换到真根目录运行该命令),但是没有grub.conf文件需要手动创建
总结:把boot分区删掉,实际是删除了kernel和grub,所以把kernel和grub安装上去即可,同时需要手工配置grub.conf文件
[19:22 [email protected]/]# rm -rf /boot/ rm: cannot remove `/boot': Device or resource busy [19:22 [email protected]/]# ls /boot/ [19:22 [email protected]/]# ls /boot/ [19:22 [email protected]/]# ll /boot/ total 0
挂载光盘:
安装kernel:
安装grub(需要切换到真根):
更多内容请关注我的博客。
二、自制linux系统
步骤概述:
1、新建一个硬盘
2、在该新硬盘上新建两个分区,一个当boot分区,一个当/分区
3、格式化并且挂载两个分区,注意,其中boot分区的挂载目录一定是boot名字的目录
4、在新硬盘安装grub(要使用--root-directory参数指定新硬盘的根分区),同时手动配置grub.conf配置文件
5、把kernel和initramfs文件放置boot分区
6、在根分区创建相应的目录
7、把一些常用命令拷贝至新硬盘的根分区,注意,同时要把二进制程序相应的库文件一并拷到新硬盘的lib文件夹(这里更加加深了二进制程序和库文件的关系,可以把库文件理解成二进制程序的函数)
8、把硬盘拆下,安装到新的虚拟机测试
步骤演示详解过程:
1、新建一个硬盘
2、在该新硬盘上新建两个分区,一个当boot分区,一个当/分区
[20:00 [email protected]~]# fdisk /dev/sdb WARNING: DOS-compatible mode is deprecated. It's strongly recommended to switch off the mode (command 'c') and change display units to sectors (command 'u'). Command (m for help): n Command action e extended p primary partition (1-4) p Partition number (1-4): 1 First cylinder (1-2610, default 1): Using default value 1 Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (1-2610, default 2610): +100M Command (m for help): n Command action e extended p primary partition (1-4) p Partition number (1-4): 2 First cylinder (15-2610, default 15): Using default value 15 Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (15-2610, default 2610): +1G Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes 255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk identifier: 0xefd94e53 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/sdb1 1 14 112423+ 83 Linux /dev/sdb2 15 146 1060290 83 Linux Command (m for help): w The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table. Syncing disks. [20:01 [email protected]~]# lsblk NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT sr0 11:0 1 3.7G 0 rom sda 8:0 0 200G 0 disk ├─sda1 8:1 0 200M 0 part /boot ├─sda2 8:2 0 48.8G 0 part / ├─sda3 8:3 0 19.5G 0 part /testdir ├─sda4 8:4 0 1K 0 part └─sda5 8:5 0 3.9G 0 part [SWAP] sdb 8:16 0 20G 0 disk ├─sdb1 8:17 0 109.8M 0 part └─sdb2 8:18 0 1G 0 part
3、格式化并且挂载两个分区,注意,其中boot分区的挂载目录一定是boot名字的目录
[20:04 [email protected]~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1 mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010) Filesystem label= OS type: Linux Block size=1024 (log=0) Fragment size=1024 (log=0) Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks 28112 inodes, 112420 blocks 5621 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user First data block=1 Maximum filesystem blocks=67371008 14 block groups 8192 blocks per group, 8192 fragments per group 2008 inodes per group Superblock backups stored on blocks: 8193, 24577, 40961, 57345, 73729 Writing inode tables: done Creating journal (4096 blocks): done Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done This filesystem will be automatically checked every 22 mounts or 180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override. [20:05 [email protected]~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb2 mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010) Filesystem label= OS type: Linux Block size=4096 (log=2) Fragment size=4096 (log=2) Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks 66384 inodes, 265072 blocks 13253 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user First data block=0 Maximum filesystem blocks=272629760 9 block groups 32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group 7376 inodes per group Superblock backups stored on blocks: 32768, 98304, 163840, 229376 Writing inode tables: done Creating journal (8192 blocks): done Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done This filesystem will be automatically checked every 27 mounts or 180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override. [20:05 [email protected]~]# mkdir /mnt/boot [20:05 [email protected]~]# mkdir /mnt/root [20:05 [email protected]~]# mount /dev//sdb1 /mnt/boot/ [20:05 [email protected]~]# mount /dev//sdb2 /mnt/root/ [20:05 [email protected]~]# df Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on /dev/sda2 50264772 5723488 41981284 12% / tmpfs 1019184 0 1019184 0% /dev/shm /dev/sda1 194241 33869 150132 19% /boot /dev/sda3 20027260 44996 18958264 1% /testdir /dev/sdb1 104769 1550 97598 2% /mnt/boot /dev/sdb2 1010812 1304 956496 1% /mnt/root
4、在新硬盘安装grub,同时手动配置grub.conf配置文件
[20:08 [email protected]/mnt/boot]# ls lost+found [20:08 [email protected]/mnt/boot]# ll total 12 drwx------. 2 root root 12288 Sep 9 20:05 lost+found [20:09 [email protected]/mnt/boot]# grub-install --root-directory=/mnt /dev/sdb Probing devices to guess BIOS drives. This may take a long time. Installation finished. No error reported. This is the contents of the device map /mnt/boot/grub/device.map. Check if this is correct or not. If any of the lines is incorrect, fix it and re-run the script `grub-install'. (fd0)/dev/fd0 (hd0)/dev/sda (hd1)/dev/sdb [20:10 [email protected]/mnt/boot]# ll total 14 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 1024 Sep 9 20:10 grub drwx------. 2 root root 12288 Sep 9 20:05 lost+found [20:34 [email protected]/mnt/root/lib]# cat !$ cat /mnt/boot/grub/grub.conf default=0 timeout=5 title YOUR LINUX root(hd0,0) kernel /initramfs-2.6.32-642.el6.x86_64.img root=/dev/sda2 init=/bin/bash initrd /vmlinuz-2.6.32-642.el6.x86_64
5、把kernel和initramfs文件放置boot分区
[20:10 [email protected]/mnt/boot]# cp /boot/vmlinuz-2.6.32-642.el6.x86_64 /boot/initramfs-2.6.32-642.el6.x86_64.img . [20:17 [email protected]/mnt/boot]# ls grub initramfs-2.6.32-642.el6.x86_64.img lost+found vmlinuz-2.6.32-642.el6.x86_64
6、在根分区创建相应的目录
[20:17 [email protected]/mnt/boot]# cd /mnt/root/ [20:18 [email protected]/mnt/root]# ls lost+found [20:18 [email protected]/mnt/root]# mkdir {etc,home,lib,lib64,usr,proc,sys,mnt,media,var,root,bin,sbin,tmp,dev} [20:20 [email protected]/mnt/root]# ls bin dev etc home lib lib64 lost+found media mnt proc root sbin sys tmp usr var
7、把一些常用命令拷贝至新硬盘的根分区,注意,同时要把二进制程序相应的库文件一并拷到新硬盘的lib文件夹(这里更加加深了二进制程序和库文件的关系,可以把库文件理解成二进制程序的函数)
这里写了一个脚本来进行复制:
#!/bin/bash
ch_root="/mnt/root"
[ ! -d $ch_root ] && mkdir $ch_root
bincopy() {
if which $1 &>/dev/null; then
local cmd_path=`which --skip-alias $1`
local bin_dir=`dirname $cmd_path`
[ -d ${ch_root}${bin_dir} ] || mkdir -p ${ch_root}${bin_dir}
[ -f ${ch_root}${cmd_path} ] || cp $cmd_path ${ch_root}${bin_dir}
return 0
else
echo "Command not found."
return 1
fi
}
libcopy() {
local lib_list=$(ldd `which --skip-alias $1` | grep -Eo '/[^[:space:]]+')
for loop in $lib_list;do
local lib_dir=`dirname $loop`
[ -d ${ch_root}${lib_dir} ] || mkdir -p ${ch_root}${lib_dir}
[ -f ${ch_root}${loop} ] || cp $loop ${ch_root}${lib_dir}
done
}
read -p "Please input a command or quit: " command
while [ "$command" != "quit" ];do
if bincopy $command ;then
libcopy $command
fi
read -p "Please input a command or quit: " command
done
[20:44 [email protected]/mnt/root/etc]# tree /mnt/root/ /mnt/root/ ├── bin │ ├── bash │ ├── df │ ├── echo │ ├── ls │ ├── lsblk │ └── mount ├── dev ├── etc │ └── fstab ├── home ├── lib │ ├── ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 │ ├── libacl.so.1 │ ├── libattr.so.1 │ ├── libblkid.so.1 │ ├── libcap.so.2 │ ├── libc.so.6 │ ├── libdl.so.2 │ ├── libpthread.so.0 │ ├── librt.so.1 │ ├── libselinux.so.1 │ ├── libsepol.so.1 │ ├── libtinfo.so.5 │ └── libuuid.so.1 ├── lib64 ├── lost+found ├── media ├── mnt ├── proc ├── root ├── sbin ├── sys ├── tmp ├── usr └── var
8、把硬盘拆下,安装到新的虚拟机测试
三、编译linux内核
1、为什么需要编译内核
编译内核可能是出于某种需求,比如对内核大小有要求,去掉内核中某些用不到的部分,或者添加一些自己需要的部分,如ntfs文件系统,或者自己修改了某部分内核代码,需要编译后验证功能。
2、编译内核步骤
(1)到kernel.org下载需要编译的版本的内核源码包
(2)准备相应的开发编译环境:包组(CentOS 6):
Server Platform Development
Development Tools
(2)把kernel拷贝到/usr/src目录下,并且解压放在linux的目录(一般编译会再/usr/src/linux目录进行,放在其他目录也可以)
[12:16 [email protected]/usr/src]# ll total 71504 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 Sep 23 2011 debug drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 4096 Aug 26 19:03 kernels drwxrwxr-x. 23 root root 4096 Aug 29 21:50 linux -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 73207156 Aug 30 2013 linux-3.10.10.tar.xz
(3)进入/usr/src/linux目录,注意,一定要进入该目录,运行字符界面的模块选择界面命令make menuconfig,然后按需要选择需要的功能即可
[12:19 [email protected]/usr/src/linux]# make menuconfig .config - Linux/x86 3.10.10 Kernel Configuration qqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqq lqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqq Linux/x86 3.10.10 Kernel Configuration qqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqk x Arrow keys navigate the menu.selects submenus --->. Highlighted letters are hotkeys. Pressing includes, x x excludes, modularizes features. Press to exit, for Help, for Search. Legend: [*] built-in [ ] x x excluded module < > module capable x x x x lqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqk x x x [*] 64-bit kernel x x x x General setup ---> x x x x [*] Enable loadable module support ---> x x x x -*- Enable the block layer ---> x x x x Processor type and features ---> x x x x Power management and ACPI options ---> x x x x Bus options (PCI etc.) ---> x x x x Executable file formats / Emulations ---> x x x x -*- Networking support ---> x x x x Device Drivers ---> x x x x Firmware Drivers ---> x x x x File systems ---> x x x x Kernel hacking ---> x x x x Security options ---> x x x x -*- Cryptographic API ---> x x x x [*] Virtualization ---> x x x x Library routines ---> x x x mqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqj x tqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqu x
(4)保存好编译模块后,就可以进行内核的编译了(注意,请预留至少10G的空间,在编译的过程中会产生很多临时文件,同时编译时间长短根据机器性能决定)
make [-j #] :#表示多少个CPU进行编译
make modules_install:安装模块
make install :安装内核相关文件
重启
重启系统后即可看见编译的内核
OK,更多内容请关注我的博客。