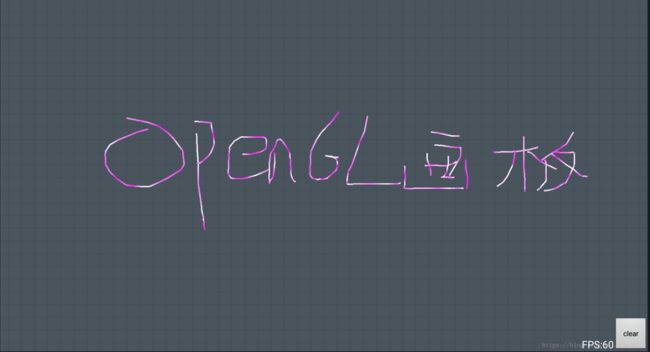使用GLSurfaceView实现涂鸦画板功能
首先需要实现一个画线工具,代码如下:
package com.project.testOpenGLWithAndroidUI;
import android.util.Log;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.ByteOrder;
import java.nio.FloatBuffer;
import javax.microedition.khronos.opengles.GL10;
/**
* Created by cjz on 2018/8/14.
*/
public class GLLine {
/**顶点字节数组**/
private ByteBuffer pointByteBuffer;
/**顶点RGBA字节数组**/
private ByteBuffer colorByteBuffer;
/**顶点坐标数组**/
private FloatBuffer pointBuffer = null;
/**顶点RGBA数组**/
private FloatBuffer colorBuffer = null;
/**正在写入第几个顶点float**/
private int pointBufferPos = 0;
/**正在写入第几个颜色float**/
private int colorBufferPos = 0;
/**初始化时的顶点数目**/
private int initVertexCount = 1 * 1024;
public void drawLine(float x, float y) {
//按初始化大小初始化顶点字节数组和顶点数组
if (pointBuffer == null) {
pointByteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(initVertexCount * 4); //顶点数 * sizeof(float)
pointByteBuffer.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
pointBuffer = pointByteBuffer.asFloatBuffer();
pointBuffer.position(0);
pointBufferPos = 0;
}
//按初始化大小初始化RGBA字节数组和RGBA数组
if (colorBuffer == null) {
colorByteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(initVertexCount * 4);
colorByteBuffer.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
colorBuffer = colorByteBuffer.asFloatBuffer();
colorBuffer.position(0);
colorBufferPos = 0;
}
//写入坐标值x,y,z
pointBuffer.put(pointBufferPos++, x);
pointBuffer.put(pointBufferPos++, y);
pointBuffer.put(pointBufferPos++, 0f);
//写入颜色值r,g,b,a
colorBuffer.put(colorBufferPos++, 1f);
colorBuffer.put(colorBufferPos++, (float) Math.random());
colorBuffer.put(colorBufferPos++, 1f);
colorBuffer.put(colorBufferPos++, 1f);
//如果写入的颜色数超过初始值,将顶点数和颜色数组容量翻倍
if (colorBufferPos * 4 >= initVertexCount) {
Log.i("GLLines", "扩容点数到:" + initVertexCount);
initVertexCount *= 2;
ByteBuffer qbb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(initVertexCount * 4); //顶点数 * sizeof(float) ;
qbb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
System.arraycopy(pointByteBuffer.array(), 0, qbb.array(), 0, (pointBufferPos) * 4); //顶点数 * sizeof(float)
pointByteBuffer = qbb;
pointBuffer = pointByteBuffer.asFloatBuffer();
ByteBuffer qbb2 = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(initVertexCount * 4); //顶点数 * sizeof(float) ;
qbb2.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
System.arraycopy(colorByteBuffer.array(), 0, qbb2.array(), 0, (colorBufferPos ) * 4); //sizeof(R,G,B,Alpha) * sizeof(float)
colorByteBuffer = qbb2;
colorBuffer = colorByteBuffer.asFloatBuffer();
}
}
public int getVertexCount(){
return pointBufferPos / 3;
}
public void drawTo(GL10 gl) {
if (pointBuffer != null && colorBuffer != null) {
pointBuffer.position(0);
colorBuffer.position(0);
gl.glVertexPointer(3, GL10.GL_FLOAT, 0, pointBuffer);
gl.glColorPointer(4, GL10.GL_FLOAT,0, colorBuffer);
gl.glLineWidth(3f);
gl.glDrawArrays(GL10.GL_LINE_STRIP,0, pointBufferPos / 3); //添加的point浮点数/3才是坐标数(因为一个坐标由x,y,z3个float构成,不能直接用), 第三个参数count如果超过实际点数就会不断有指向0的点在最后
// gl.glDrawElements(GL10.GL_LINE_STRIP,0, pointBufferPos / 3, null); //第一个参数是点的类型,第二个参数是点的个数,第三个是第四个参数的类型,第四个参数是点的存储绘制顺序。
}
}
}
其中drawLine函数可以根据传来的浮点值写入到NativeBuffer中,如果线太长就会自动通过System.arraycopy扩容。drawTo是传入gl上下文之后把数组里面的顶点和顶点颜色绘制到OpenGL画布上的。(在里面我留了一个彩蛋,绿色浓度(0f~1f)我用了随机数进行赋值,使得线条呈现出紫色和白色交替的特殊效果,这也是Canvas+path难以实现的一点)
然后是渲染器:
package com.project.testOpenGLWithAndroidUI;
import android.content.Context;
import android.opengl.GLSurfaceView.Renderer;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.microedition.khronos.egl.EGLConfig;
import javax.microedition.khronos.opengles.GL10;
public class MyGLRenderer implements Renderer {
Context context; // Application's context
private float x;
private float y;
private GLLine currentLines = null; //当前绘制的线
private List linesList = new ArrayList<>(); //当前绘制线的表
public long frameCount = 0; //共绘制了多少帧
private float ratio;
private int width;
private int height;
public MyGLRenderer(final Context context) {
this.context = context;
}
/**图形引擎回调产生绘图过程,每画完一帧又会调用这个函数画下一帧**/
@Override
public void onDrawFrame(GL10 gl) {
// 清除屏幕和深度缓存
gl.glClear(GL10.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL10.GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); //不加这个可以产生残影(模拟器可以)
// 重置当前的模型观察矩阵
gl.glLoadIdentity();
// 允许设置顶点
//GL10.GL_VERTEX_ARRAY顶点数组
gl.glEnableClientState(GL10.GL_VERTEX_ARRAY);
// 允许设置颜色
//GL10.GL_COLOR_ARRAY颜色数组
gl.glEnableClientState(GL10.GL_COLOR_ARRAY);
//反走样
gl.glEnable(GL10.GL_BLEND);
//线条抗锯齿
gl.glEnable(GL10.GL_LINE_SMOOTH);
//绘制模型
drawModel(gl);
// 取消颜色设置
gl.glDisableClientState(GL10.GL_COLOR_ARRAY);
// 取消顶点设置
gl.glDisableClientState(GL10.GL_VERTEX_ARRAY);
//绘制结束
gl.glFinish();
}
@Override
public void onSurfaceChanged(GL10 gl, int width, int height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
ratio = (float) width / height;
// 设置OpenGL场景的大小,(0,0)表示窗口内部视口的左下角,(w,h)指定了视口的大小
gl.glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
// 设置投影矩阵
gl.glMatrixMode(GL10.GL_PROJECTION);
// 重置投影矩阵
gl.glLoadIdentity();
// 设置视口的大小
gl.glFrustumf(-ratio, ratio, -1, 1, 1, 10);
//以下两句声明,以后所有的变换都是针对模型(即我们绘制的图形)
gl.glMatrixMode(GL10.GL_MODELVIEW);
gl.glLoadIdentity();
}
@Override
public void onSurfaceCreated(GL10 gl, EGLConfig config) {
// 设置透明色为清屏
gl.glClearColor(0, 0, 0, 0);
}
/**帧绘制**/
public void drawModel(GL10 gl) {
gl.glTranslatef(-2f * ratio, 2f, -2f); //必须有,z轴可以用于做缩放,按16比9来做,只要右下角象限
synchronized (linesList) {
for(GLLine line : linesList) {
line.drawTo(gl);
}
}
frameCount++;
}
public void clearAll() {
synchronized (linesList) {
linesList.clear();
}
}
public void setPointer(MotionEvent event) {
this.x = event.getX();
this.y = event.getY();
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
currentLines = new GLLine();
synchronized (linesList) {
linesList.add(currentLines);
}
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
Log.i("setPointer", String.format("x: %f, y: %f", x, y));
float realtiveX = x / height * 4f; //4个象限
float realtiveY = -y / height * 4f;
currentLines.drawLine(realtiveX, realtiveY);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
break;
}
}
} onDrawFrame每16ms间隔就会被调用一次,也就是绘制一帧,然后我们真正绘制线条的地方是drawModel函数,drawModel函数绘制一个List里面保存的GLLine线条对象。setPointer里面每一次接收到down事件就会创建一个GLLine线条,move的时候会纪录线条轨迹顶点。而我们这里是采用比例进行绘图的,也就是假设屏幕为1920*1080,那么(0.1,0.1)这个坐标在实际中代表的就是(192,108)坐标。
然后是我们自定义的GLSurfaceView:
package com.project.testOpenGLWithAndroidUI;
import android.content.Context;
import android.opengl.GLSurfaceView;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
/**
* Created by cjz on 2018/8/2.
*/
public class MyGLSurfaceView extends GLSurfaceView{
private MyGLRenderer renderer;
public MyGLSurfaceView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyGLSurfaceView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
@Override
public void setRenderer(Renderer renderer) {
super.setRenderer(renderer);
this.renderer = (MyGLRenderer) renderer;
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
renderer.setPointer(event);
return true;
}
}
其中onTouchEvent的事件将直接传递到我实现的renderer中进行处理。
最后载入到MainActivity中:
package com.project.testOpenGLWithAndroidUI;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.pm.ActivityInfo;
import android.graphics.PixelFormat;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.FrameLayout;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.TextView;
import com.project.testopengl.R;
/**
* Created by cjz on 2018/8/2.
*/
public class MainActivity extends Activity{
private FrameLayout ll_container;
private TextView tv_frame_rate;
private MyGLRenderer myGlRenderer;
private Button btn_clear;
Handler handler = new Handler();
private MyGLSurfaceView myGLSurfaceView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setTheme(android.R.style.Theme_Translucent_NoTitleBar);
//强制横屏:
setRequestedOrientation(ActivityInfo.SCREEN_ORIENTATION_LANDSCAPE);
getWindow().addFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_KEEP_SCREEN_ON);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main_3);
ll_container = findViewById(R.id.ll_container);
myGLSurfaceView = new MyGLSurfaceView(this);
myGLSurfaceView.setEGLConfigChooser(8, 8, 8, 8, 16, 0);
//设置背景透明:
myGLSurfaceView.getHolder().setFormat(PixelFormat.TRANSLUCENT);
myGLSurfaceView.setZOrderOnTop(true);
myGlRenderer = new MyGLRenderer(this);
myGLSurfaceView.setRenderer(myGlRenderer);
// myGLSurfaceView.setZOrderMediaOverlay(true);
ll_container.addView(myGLSurfaceView);
initView();
loopGetRate();
}
/**利用handler+递归轮询帧率**/
private void loopGetRate() {
handler.postDelayed(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
tv_frame_rate.setText("FPS:" + myGlRenderer.frameCount);
myGlRenderer.frameCount = 0;
if(!MainActivity.this.isFinishing()) {
loopGetRate();
}
}
}, 1000);
}
private void initView() {
tv_frame_rate = findViewById(R.id.tv_frame_rate); //帧率显示
//清屏:
btn_clear = findViewById(R.id.btn_clear);
btn_clear.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
myGlRenderer.clearAll();
}
});
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
if (myGLSurfaceView != null) {
myGLSurfaceView.onPause();
}
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
if (myGLSurfaceView != null) {
myGLSurfaceView.onResume();
}
}
}
我在onCreate处通过一些设置使得GLSurfaceView浮于App的最表面,并使得背景色透明,使得App其他地方可以通过绘制内容呈现。
最后是UI配置文件:
使用效果:
因时间有限暂时没来得及仔细讲解代码的一些细节,呆有空时将会对本文进行更新。