Java访问Ceph数据的相关细节
Ceph很多公司内部已经进行了部署,当然也有很多公司使用阿里的OSS或者亚马逊的S3。在现在硬件廉价的大环境下,更多的公司愿意把自己的数据内容自我保管,实现企业私有云。下面我们来看一下如何使用Java技术栈来访问Ceph。
1. 部署LIBRADOS环境
客户端应用程序需要librados才能连接到Ceph存储集群。
1.1 安装jna.jar
Debian/Ubuntu环境下执行以下命令
sudo apt-get install libjna-java
CentOS/RHEL环境下执行以下命令
sudo yum install jna
JAR文件位于/usr/share/java.
1.2 克隆rados-java代码库
git clone --recursive https://github.com/ceph/rados-java.git
1.3 编译rados-java代码:
cd rados-java
ant
JAR文件位于rados-java/target目录下
1.4 关联路径
复制该JAR文件到公共目录 (例如 /usr/share/java) ,并且确认该文件和JNA JAR在你的JVM’s classpath目录中. 举个例子,你可以按照以下的方法来关联路径:
sudo cp target/rados-0.1.3.jar /usr/share/java/rados-0.1.3.jar
sudo ln -s /usr/share/java/jna-3.2.7.jar /usr/lib/jvm/default-java/jre/lib/ext/jna-3.2.7.jar
sudo ln -s /usr/share/java/rados-0.1.3.jar /usr/lib/jvm/default-java/jre/lib/ext/rados-0.1.3.jar
编译文档可执行以下的命令:
ant docs
2. 配置群集句柄
一个Ceph的客户端通过librados,直接与交互的OSD来存储和检索数据。要与OSD交互,客户端应用程序必须调用 librados 并连接到Ceph Monitor。连接后,librados从Ceph Monitor中检索 Cluster Map。当客户端应用程序想要读取或写入数据时,它会创建I/O上下文并绑定到池。该池具有关联的规则集,该规则集定义了如何将数据放入存储群集中。通过I/O上下文,客户端向librados提供对象名称,它获取对象名称和集群映射(即集群的拓扑)并计算用于定位数据的放置组和OSD。然后客户端应用程序可以读取或写入数据。客户端应用程序无需直接了解群集的拓扑。
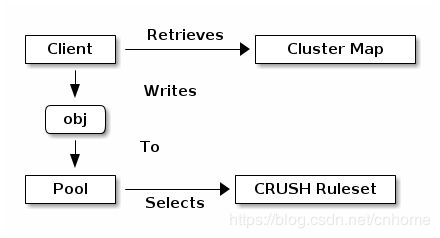
Ceph存储集群句柄封装了客户端配置,包括:
- 使用用户ID的rados_create() 或使用用户名称的rados_create2() (推荐使用此方法).
- cephx认证密钥
- 监视器ID和IP地址
- 记录级别
- 调试级别
因此,从您的应用程序使用群集的第一步是:1)创建应用程序将用于连接到存储群集的群集句柄,然后2)使用该句柄进行连接。要连接到群集,应用程序必须提供监视器地址,用户名和身份验证密钥(默认情况下启用cephx)。
注意 与不同的Ceph存储集群 - 或与不同用户的同一集群 - 交互需要不同的集群句柄。
RADOS提供了多种设置所需值的方法。对于监视器和加密密钥设置,一种处理它们的简单方法是确保您的Ceph配置文件包含密钥环文件的密钥环路径和至少一个监视器地址(例如,mon 主机)。例如:
[global]
mon host = 192.168.1.1
keyring = /etc/ceph/ceph.client.admin.keyring
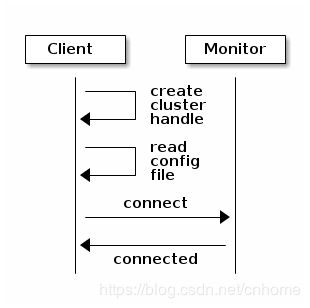
创建句柄后,可以读取Ceph配置文件以配置句柄。还可以将参数传递给您的应用程序,并使用函数解析它们以解析命令行参数(例如,rados_conf_parse_argv()),或解析Ceph环境变量(例如,rados_conf_parse_env())。某些包装器无法实现便捷方法,因此需要实现这些功能。下图提供了初始连接的高级流程。
连接后,应用程序可以仅使用群集句柄调用影响整个群集的功能。例如,一旦有了集群句柄,您就可以:
- 获取群集统计信息
- 使用池操作(存在,创建,列表,删除)
- 获取并设置配置
Ceph的一个强大功能是能够绑定到不同的池。每个池可能具有不同数量的放置组,对象副本和复制策略。例如,可以将池设置为“热”池,其将SSD用于常用对象或使用擦除编码的“冷”池。
Java要求你指定用户ID(admin)或用户名(client.admin),并使用默认的ceph cluster name。Java绑定将基于C ++的错误转换为异常。
import com.ceph.rados.Rados;
import com.ceph.rados.RadosException;
import java.io.File;
public class CephClient {
public static void main (String args[]){
try {
Rados cluster = new Rados("admin");
System.out.println("Created cluster handle.");
File f = new File("/etc/ceph/ceph.conf");
cluster.confReadFile(f);
System.out.println("Read the configuration file.");
cluster.connect();
System.out.println("Connected to the cluster.");
} catch (RadosException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage() + ": " + e.getReturnValue());
}
}
}
编译源代码; 然后,运行。如果你已经把连接Ceph的JAR文件复制到/usr/share/java并软连接到扩展路径, 就无需设置classpath. 如下运行:
javac CephClient.java
java CephClient
3. 创建I/O上下文
一旦应用程序具有集群句柄和与Ceph存储集群的连接,就可以创建I/O上下文并开始读取和写入数据。I/O上下文将连接绑定到特定池。用户必须具有适当的 CAPS权限才能访问指定的池。例如,具有读访问权但不具有写访问权的用户将只能读取数据。I/O上下文功能包括:
- 写/读数据和扩展属性
- 列出并迭代对象和扩展属性
- 快照池,列表快照等
RADOS使应用程序可以同步和异步交互。一旦应用程序具有I/O上下文,读/写操作只需要知道object / xattr名称。封装在librados中的CRUSH算法使用群集映射来识别适当的OSD。OSD守护程序处理复制,如Smart Daemons启用超大规模中所述。所述librados库也映射对象来展示位置组,如在 计算PG的ID。
以下示例使用默认数据池。但是,也可以使用API列出池,确保它们存在,或者创建和删除池。对于写操作,这些示例说明了如何使用同步模式。对于读取操作,这些示例说明了如何使用异步模式。
注意 使用此API删除池时请小心。如果删除池,池中的池和所有数据将丢失。
3.1 写入数据代码
import com.ceph.rados.Rados;
import com.ceph.rados.RadosException;
import java.io.File;
import com.ceph.rados.IoCTX;
public class CephClient {
public static void main (String args[]){
try {
Rados cluster = new Rados("admin");
System.out.println("Created cluster handle.");
//利用配置文件连接ceph
File f = new File("/etc/ceph/ceph.conf");
cluster.confReadFile(f);
System.out.println("Read the configuration file.");
cluster.connect();
System.out.println("Connected to the cluster.");
IoCTX io = cluster.ioCtxCreate("data");
String oidone = "hw";
String contentone = "Hello World!";
io.write(oidone, contentone);
String oidtwo = "bm";
String contenttwo = "Bonjour tout le monde!";
io.write(oidtwo, contenttwo);
String[] objects = io.listObjects();
for (String object: objects)
System.out.println(object);
io.remove(oidone);
io.remove(oidtwo);
cluster.ioCtxDestroy(io);
} catch (RadosException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage() + ": " + e.getReturnValue());
}
}
}
3.2 一些基本操作
package com.ceph.rbd;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import com.ceph.rados.IoCTX;
import com.ceph.rados.Rados;
import com.ceph.rados.exceptions.RadosException;
import com.ceph.rbd.jna.RbdImageInfo;
import com.ceph.rbd.jna.RbdSnapInfo;
public class RbdDao {
private static Rados rados;
private static IoCTX ioctx;
private static Rbd rbd;
/**
* 连接上ceph环境
*/
public static void connectCeph(){
try {
//利用参数连接Ceph
rados = new Rados("admin");
rados.confSet("mon_host", "172.16.60.41");
rados.confSet("key", "AQCdP9pYGI4jBBAAc96J8/OconCkVKWPBNU2vg==");
rados.connect();
ioctx = rados.ioCtxCreate("rbd");
rbd = new Rbd(ioctx);
System.out.println("successs connetc");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
/**
* 返回所有的image,并展示其详细信息
* @return
*/
public static List<String> imageList(){
List<String> imageList=null;
try {
imageList = Arrays.asList(rbd.list());
for(String s:imageList){
showDetailOfImage(s);
}
} catch (RbdException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return imageList;
}
/**
* 显示image的详细信息
* @param imageName
*/
public static void showDetailOfImage(String imageName){
RbdImage image;
try {
image = rbd.open(imageName);
RbdImageInfo info = image.stat();
System.out.println("=================================================================");
System.out.println("imageName: "+imageName);
System.out.println("imageSize: "+info.size);
System.out.println("order: "+info.order);
rbd.close(image);
} catch (RbdException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 以格式1创建image
* @param imageName 名称
* @param imageSize 大小
*/
public static void createRbd_format1(String imageName, long imageSize){
try {
rbd.create(imageName, imageSize);
RbdImage image = rbd.open(imageName);
boolean oldFormat = image.isOldFormat();
System.out.println("imageFormat:==========================="+oldFormat);
rbd.close(image);
} catch (RbdException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage() + ": " + e.getReturnValue());
}
}
/**
* 以格式2创建image,ceph 仅支持克隆 format 2 映像(即用 rbd create –format 2 创建的),而且内核 rbd 模块还不支持。
所以现在你 只能用 QEMU/KVM 或 librbd直接访问克隆品
* @param imageName 名称
* @param imageSize 大小
*/
public static void createRbd_format2(String imageName, long imageSize){
try {
int features = (1<<0);
System.out.println("features=============="+features);
rbd.create(imageName, imageSize,features, 0);
RbdImage image = rbd.open(imageName);
boolean oldFormat = image.isOldFormat();
System.out.println("imageFormat:==========================="+oldFormat);
rbd.close(image);
image.flatten();
} catch (RbdException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage() + ": " + e.getReturnValue());
}
}
/**
* 方法创建一个image并对重设置大小为初始化大小的2倍
* @param imageName
*/
public static void resizeImage(String imageName){
long initialSize = 10485760;
long newSize = initialSize * 2;
try {
int features = (1<<0);
System.out.println("features=============="+features);
rbd.create(imageName, initialSize,features, 0);
RbdImage image = rbd.open(imageName);
image.resize(newSize);
rbd.close(image);
} catch (RbdException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage() + ": " + e.getReturnValue());
}
}
/**
* 创建映像的快照
* @param imageName 映像名称
* @param snapName 快照名称
*/
public static void createSnap(String imageName,String snapName){
try {
RbdImage image = rbd.open(imageName);
//创建快照
image.snapCreate(snapName);
//保护快照可以防止快照被删除
image.snapProtect(snapName);
//返回一个image的所有快照
List<RbdSnapInfo> snaps = image.snapList();
for(RbdSnapInfo rbds:snaps){
System.out.println("快照名称:"+rbds.name);
System.out.println("快照大小:"+rbds.size);
}
} catch (RbdException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 通过快照克隆出新的image
* @param parentImageName 快照对应的image名称
* @param snapName 快照的名称
* @param newImageName 生成的新的image的名称
*/
public static void copySnapToNewImage(String parentImageName,String snapName,String newImageName){
int features = (1<<0);
try {
rbd.clone(parentImageName, snapName, ioctx, newImageName, features, 0);
} catch (RbdException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 删除某个image的名叫 snapName的快照,需要注意的是要删除快照,必须保证快照没有copy的子image,否则会删除失败。
* @param imageName
* @param snapName
*/
public static void deleteSnap(String imageName,String snapName){
try {
RbdImage image = rbd.open(imageName);
image.snapUnprotect(snapName);
image.snapRemove(snapName);
} catch (RbdException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 删除某一个image
* @param r
* @param io
* @param imageName
* @throws RadosException
* @throws RbdException
*/
public static void cleanupImage(Rados r, IoCTX io, String imageName) {
try {
if (r != null) {
if (io != null) {
Rbd rbd = new Rbd(ioctx);
RbdImage image = rbd.open(imageName);
rbd.close(image);
rbd.remove(imageName);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
connectCeph();
//createRbd_format1("mysql-hzb-2",10737418240l);
//createRbd_format2("imageformat2",10485760);
//cleanupImage(rados,ioctx,"mysql-hzb");
//resizeImage("mysql-hzb");
// createSnap("imageformat3","imageformat3-snap");
//copySnapToNewImage("imageformat3","imageformat3-snap","imageformat3-copy");
//deleteSnap("imageformat3","imageformat3-snap");
imageList();
}
}
3.3 IoCTX源代码
/*
* RADOS Java - Java bindings for librados
*
* Copyright (C) 2013 Wido den Hollander
* Copyright (C) 2014 1&1 - Behar Veliqi
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
* software distributed under the License is distributed on
* an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND,
* either express or implied. See the License for the specific
* language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
*/
package com.ceph.rados;
import static com.ceph.rados.Library.rados;
import java.io.Closeable;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import com.ceph.rados.exceptions.RadosException;
import com.ceph.rados.jna.RadosObjectInfo;
import com.ceph.rados.jna.RadosPoolInfo;
import com.sun.jna.Memory;
import com.sun.jna.Native;
import com.sun.jna.Pointer;
import com.sun.jna.ptr.IntByReference;
import com.sun.jna.ptr.LongByReference;
import com.sun.jna.ptr.PointerByReference;
public class IoCTX extends RadosBase implements Closeable {
private static final int EXT_ATTR_MAX_LEN = 4096;
private Pointer ioCtxPtr;
/**
* Create a new IO Context object
*
* This constructor should never be called, IO Context
* objects are created by the RADOS class and returned
* when creating a IO Context there
*/
public IoCTX(Pointer p) {
this.ioCtxPtr = p;
}
/**
* Return the pointer to the IO Context
*
* This method is used internally and by the RADOS class
* to destroy a IO Context
*
* @return Pointer
*/
public Pointer getPointer() {
return this.ioCtxPtr.getPointer(0);
}
/**
* Set the namespace for objects within an IO context.
*
* The namespace specification further refines a pool into different domains. The mapping of objects to PGs is also based on this value.
*
* @param namespace The name to use as the namespace, or NULL use the default namespace.
*/
public void setNamespace(String namespace) {
rados.rados_ioctx_set_namespace(getPointer(), namespace);
}
/**
* Get the pool ID of this context
*
* @return long
*/
public long getId() {
return rados.rados_ioctx_get_id(this.getPointer());
}
/**
* Set the associated auid owner of the current pool
*
* @param auid
* The new auid
* @throws RadosException
*/
public void setAuid(final long auid) throws RadosException {
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_ioctx_pool_set_auid(getPointer(), auid);
}
}, "Failed to set the auid to %s", auid);
}
/**
* Get the associated auid owner of the current pool
*
* @return long
* @throws RadosException
*/
public long getAuid() throws RadosException {
final LongByReference auid = new LongByReference();
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_ioctx_pool_get_auid(getPointer(), auid);
}
}, "Failed to get the auid");
return auid.getValue();
}
/**
* Get the pool name of the context
*
* @return String
* @throws RadosException
*/
public String getPoolName() throws RadosException {
final byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_ioctx_get_pool_name(getPointer(), buf, buf.length);
}
}, "Failed to get the pool name");
return Native.toString(buf);
}
/**
* Set the locator key
*
* @param key
* The new locator key or NULL to remove a previous one
*/
public void locatorSetKey(String key) {
rados.rados_ioctx_locator_set_key(this.getPointer(), key);
}
/**
* List all objects in a pool
*
* @return String[]
* @throws RadosException
*/
public String[] listObjects() throws RadosException {
Pointer entry = new Memory(Pointer.SIZE);
List<String> objects = new ArrayList<String>();
final Pointer list = new Memory(Pointer.SIZE);
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_nobjects_list_open(getPointer(), list);
}
}, "Failed starting to list all objects");
while (rados.rados_nobjects_list_next(list.getPointer(0), entry, null, null) == 0) {
objects.add(entry.getPointer(0).getString(0));
}
rados.rados_nobjects_list_close(list.getPointer(0));
return objects.toArray(new String[objects.size()]);
}
/**
* List all objects in a pool by piece. Useful if a lot of objects are in the pool and do not
* fit in memory through listObjects() method
* @param limit
* @return a ListCtx from which nextObjects()/nextObjects(skip) and getObjects() could be called
* @throws RadosException
*/
public ListCtx listObjectsPartial(int limit) throws RadosException {
Pointer list = new Memory(Pointer.SIZE);
int r = rados.rados_nobjects_list_open(this.getPointer(), list);
if (r < 0) {
throw new RadosException("Failed listing all objects", r);
}
return new ListCtx(limit, list);
}
/**
* Write to an object
*
* @param oid
* The object to write to
* @param buf
* The content to write
* @param offset
* The offset when writing
* @throws RadosException
*/
public void write(final String oid, final byte[] buf, final long offset) throws RadosException, IllegalArgumentException {
if (offset < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Offset shouldn't be a negative value");
}
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_write(getPointer(), oid, buf, buf.length, offset);
}
}, "Failed writing %s bytes with offset %s to %s", buf.length, offset, oid);
}
/**
* Write to an object without an offset
*
* @param oid
* The object to write to
* @param buf
* The content to write
* @throws RadosException
*/
public void write(String oid, byte[] buf) throws RadosException {
this.writeFull(oid, buf, buf.length);
}
/**
* Write an entire object
* The object is filled with the provided data. If the object exists, it is atomically truncated and then written.
*
* @param oid
* The object to write to
* @param buf
* The content to write
* @param len
* The length of the data to write
* @throws RadosException
*/
public void writeFull(final String oid, final byte[] buf, final int len) throws RadosException {
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_write_full(getPointer(), oid, buf, len);
}
}, "Failed to write %s bytes to %s", len, oid);
}
/**
* Write to an object without an offset
*
* @param oid
* The object to write to
* @param buf
* The content to write
* @param offset
* The offset when writing
* @throws RadosException
*/
public void write(String oid, String buf, long offset) throws RadosException {
this.write(oid, buf.getBytes(), offset);
}
/**
* Write to an object without an offset
*
* @param oid
* The object to write to
* @param buf
* The content to write
* @throws RadosException
*/
public void write(String oid, String buf) throws RadosException {
this.write(oid, buf.getBytes());
}
/**
* Asynchronously write to an object
*
* @param oid
* The object to write to
* @param completion
* The completion instructions
* @param buf
* The content to write
* @param offset
* The offset when writing
* @throws RadosException
*/
public void aioWrite(final String oid, final Completion completion, final byte[] buf, final long offset) throws RadosException, IllegalArgumentException {
if (offset < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Offset shouldn't be a negative value");
}
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_aio_write(getPointer(), oid, completion.getPointer(), buf, buf.length, offset);
}
}, "Failed AIO writing %s bytes with offset %s to %s", buf.length, offset, oid);
}
/**
* Asynchronously write to an object without an offset
*
* @param oid
* The object to write to
* @param completion
* The completion instructions
* @param buf
* The content to write
* @throws RadosException
*/
public void aioWrite(String oid, final Completion completion, byte[] buf) throws RadosException {
this.aioWriteFull(oid, completion, buf, buf.length);
}
/**
* Asynchronously write an entire object
* The object is filled with the provided data. If the object exists, it is atomically truncated and then written.
*
* @param oid
* The object to write to
* @param completion
* The completion instructions
* @param buf
* The content to write
* @param len
* The length of the data to write
* @throws RadosException
*/
public void aioWriteFull(final String oid, final Completion completion, final byte[] buf, final int len) throws RadosException {
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_aio_write_full(getPointer(), oid, completion.getPointer(), buf, len);
}
}, "Failed to AIO write %s bytes to %s", len, oid);
}
/**
* Asynchronously write to an object without an offset
*
* @param oid
* The object to write to
* @param completion
* The completion instructions
* @param buf
* The content to write
* @param offset
* The offset when writing
* @throws RadosException
*/
public void aioWrite(String oid, final Completion completion, String buf, long offset) throws RadosException {
this.aioWrite(oid, completion, buf.getBytes(), offset);
}
/**
* Asynchronously write to an object without an offset
*
* @param oid
* The object to write to
* @param completion
* The completion instructions
* @param buf
* The content to write
* @throws RadosException
*/
public void aioWrite(String oid, final Completion completion, String buf) throws RadosException {
this.aioWrite(oid, completion, buf.getBytes());
}
/**
* Block until all pending writes in an io context are safe.
*
* This is not equivalent to calling rados_aio_wait_for_safe() on all write completions, since this waits for the associated callbacks to complete as well.
* @throws RadosException
*/
public void aioFlush() throws RadosException {
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_aio_flush(getPointer());
}
}, "Failed to AIO flush");
}
/**
* Remove an object
*
* @param oid
* The object to remove
* @throws RadosException
*/
public void remove(final String oid) throws RadosException {
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_remove(getPointer(), oid);
}
}, "Failed removing object %s", oid);
}
/**
* Read data from an object
*
* @param oid
* The object's name
* @param length
* Amount of bytes to read
* @param offset
* The offset where to start reading
* @param buf
* The buffer to store the result
* @return Number of bytes read or negative on error
* @throws RadosException
*/
public int read(final String oid, final int length, final long offset, final byte[] buf)
throws RadosException {
if (length < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Length shouldn't be a negative value");
}
if (offset < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Offset shouldn't be a negative value");
}
return handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_read(getPointer(), oid, buf, length, offset);
}
}, "Failed to read object %s using offset %s and length %s", oid, offset, length);
}
/**
* Resize an object
*
* @param oid
* The object to resize
* @param size
* The new length of the object. If this enlarges the object,
* the new area is logically filled with
* zeroes. If this shrinks the object, the excess data is removed.
* @throws RadosException
*/
public void truncate(final String oid, final long size) throws RadosException {
if (size < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Size shouldn't be a negative value");
}
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_trunc(getPointer(), oid, size);
}
}, "Failed resizing objects %s to %s bytes", oid, size);
}
/**
* Append data to an object
*
* @param oid
* The name to append to
* @param buf
* The data to append
* @throws RadosException
*/
public void append(String oid, byte[] buf) throws RadosException {
this.append(oid, buf, buf.length);
}
/**
*
* @param oid
* The name to append to
* @param buf
* The data to append
* @param len
* The number of bytes to write from buf
* @throws RadosException
*/
public void append(final String oid, final byte[] buf, final int len) throws RadosException {
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_append(getPointer(), oid, buf, len);
}
}, "Failed appending %s bytes to object %s", len, oid);
}
/**
* Append data to an object
*
* @param oid
* The name to append to
* @param buf
* The data to append
* @throws RadosException
*/
public void append(String oid, String buf) throws RadosException {
this.append(oid, buf.getBytes());
}
/**
* Efficiently copy a portion of one object to another
*
* If the underlying filesystem on the OSD supports it, this will be a
* copy-on-write clone.
*
* The src and dest objects must be in the same pg. To ensure this,
* the io context should have a locator key set (see IoCTX.locatorSetKey()).
*
* @param dst
* The destination object
* @param dst_off
* The offset at the destination object
* @param src
* The source object
* @param src_off
* The offset at the source object
* @param len
* The amount of bytes to copy
* @throws RadosException
*/
public void clone(final String dst, final long dst_off, final String src, final long src_off, final long len) throws RadosException {
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_clone_range(getPointer(), dst, dst_off, src, src_off, len);
}
}, "Failed to copy %s bytes from %s to %s", len, src, dst);
}
/**
* Stat an object
*
* @param oid
* The name of the object
* @return RadosObjectInfo
* The size and mtime of the object
* @throws RadosException
*/
public RadosObjectInfo stat(final String oid) throws RadosException {
final LongByReference size = new LongByReference();
final LongByReference mtime = new LongByReference();
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_stat(getPointer(), oid, size, mtime);
}
}, "Failed performing a stat on object %s", oid);
return new RadosObjectInfo(oid, size.getValue(), mtime.getValue());
}
/**
* Stat the currently open pool
*
* @return RadosPoolInfo
* @throws RadosException
*/
public RadosPoolInfo poolStat() throws RadosException {
final RadosPoolInfo result = new RadosPoolInfo();
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_ioctx_pool_stat(getPointer(), result);
}
}, "Failed retrieving the pool stats");
return result;
}
/**
* Create a snapshot
*
* @param snapname
* The name of the snapshot
* @throws RadosException
*/
public void snapCreate(final String snapname) throws RadosException {
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_ioctx_snap_create(getPointer(), snapname);
}
}, "Failed to create snapshot %s", snapname);
}
/**
* Remove a snapshot
*
* @param snapname
* The name of the snapshot
* @throws RadosException
*/
public void snapRemove(final String snapname) throws RadosException {
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_ioctx_snap_remove(getPointer(), snapname);
}
}, "Failed to remove snapshot %s", snapname);
}
/**
* Get the ID of a snapshot
*
* @param snapname
* The name of the snapshot
* @return long
* @throws RadosException
*/
public long snapLookup(final String snapname) throws RadosException {
final LongByReference id = new LongByReference();
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_ioctx_snap_lookup(getPointer(), snapname, id);
}
}, "Failed to lookup the ID of snapshot %s", snapname);
return id.getValue();
}
/**
* Get the name of a snapshot by it's ID
*
* @param id
* The ID of the snapshot
* @return String
* @throws RadosException
*/
public String snapGetName(final long id) throws RadosException {
final byte[] buf = new byte[512];
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_ioctx_snap_get_name(getPointer(), id, buf, buf.length);
}
}, "Failed to lookup the name of snapshot %s", id);
return new String(buf).trim();
}
/**
* Get the timestamp of a snapshot
*
* @param id
* The ID of the snapshot
* @return long
* @throws RadosException
*/
public long snapGetStamp(final long id) throws RadosException {
final LongByReference time = new LongByReference();
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_ioctx_snap_get_stamp(getPointer(), id, time);
}
}, "Failed to retrieve the timestamp of snapshot %s", id);
return time.getValue();
}
/**
* List all snapshots
*
* @return Long[]
* @throws RadosException
*/
public Long[] snapList() throws RadosException {
final byte[] buf = new byte[512];
final Integer result = handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_ioctx_snap_list(getPointer(), buf, buf.length);
}
}, "Failed to list all snapshots");
Long[] snaps = new Long[result];
for (int i = 0; i < result; i++) {
snaps[i] = (long) buf[i];
}
return snaps;
}
public ReadOp readOpCreate() {
return new ReadOp(getPointer(), rados.rados_create_read_op());
}
/**
* Instead of releasing the read operation directly, better use ReadOp.close
*/
@Deprecated
public void readOpRelease(ReadOp read_op) {
rados.rados_release_read_op(read_op.getPointer());
}
/**
* Get the value of an extended attribute on an object.
*
* @param oid
* The name of the object
* @param xattrName
* The name of the extended attribute
* @return
* The value of the extended attribute
* @throws RadosException
* on failure -- common error codes:
* -34 (ERANGE) : value exceeds buffer
* -61 (ENODATA) : no such attribute
*/
public String getExtendedAttribute(final String oid, final String xattrName) throws RadosException {
final byte[] buf = new byte[EXT_ATTR_MAX_LEN];
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_getxattr(getPointer(), oid, xattrName, buf, buf.length);
}
}, "Failed to get extended attribute %s on %s", xattrName, oid);
// else...
return Native.toString(buf);
}
/**
* Set an extended attribute on an object.
*
* @param oid
* The name of the object
* @param xattrName
* The name of the extended attribute
* @param val
* The value of the extended attribute
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* attribute value is too long
* @throws RadosException
* on failure
*/
public void setExtendedAttribute(final String oid, final String xattrName, String val) throws IllegalArgumentException, RadosException {
final byte[] buf = Native.toByteArray(val);
if (buf.length > EXT_ATTR_MAX_LEN) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Length of attribute value must not exceed " + EXT_ATTR_MAX_LEN);
}
// else...
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_setxattr(getPointer(), oid, xattrName, buf, buf.length);
}
}, "Failed to set extended attribute %s on %s", xattrName, oid);
}
/**
* Delete an extended attribute from an object.
*
* @param oid
* The name of the object
* @param xattrName
* The name of the extended attribute
* @throws RadosException
* on failure
*/
public void removeExtendedAttribute(final String oid, final String xattrName) throws RadosException {
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_rmxattr(getPointer(), oid, xattrName);
}
}, "Failed to remove extended attribute %s from %s", xattrName, oid);
}
/**
* Get all extended attributes on an object.
*
* @param oid
* The name of the object
* @return
* The map of the extended attributes
* @throws RadosException
* on failure
*/
public Map<String, String> getExtendedAttributes(final String oid) throws RadosException {
Map<String, String> attr_map = new HashMap<>();
final Pointer iterator = new Memory(Pointer.SIZE);
final PointerByReference attr_name = new PointerByReference();
final PointerByReference attr_value = new PointerByReference();
final IntByReference attr_value_len = new IntByReference();
handleReturnCode(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return rados.rados_getxattrs(getPointer(), oid, iterator);
}
}, "Failed starting to list all extended attributes");
while (rados.rados_getxattrs_next(iterator.getPointer(0), attr_name, attr_value, attr_value_len) == 0
&& attr_value_len.getValue() > 0) {
int length = attr_value_len.getValue();
String name = (attr_name.getValue() == null ? null : new String(attr_name.getValue().getString(0)));
String value = (attr_value.getValue() == null ? null : new String(attr_value.getValue().getString(0)));
if (length > 0 && name != null && value != null) {
attr_map.put(name, value);
}
}
rados.rados_getxattrs_end(iterator.getPointer(0));
return attr_map;
}
@Override
public void close() throws IOException {
rados.rados_ioctx_destroy(getPointer());
}
}
至此,大家应该对Java访问Ceph有了彻底的认识了。
参考资料
- INTRODUCTION TO LIBRADOS
- java操作ceph之rbd基本操作
- Ceph API微服务开发–存储集群API调用