Java 注解编程
一、注解介绍
注解(Annotation) 是 jdk1.5 版本以后引入的一个新特性,注解可以说是类反射的延伸,在一些需要配置文件的应用中,可以使用注解替代配置文件,从而提高应用的灵活。比如 常见的 @Autowired,@Controller 等。
下面是 Java 底层内置的几个注解
@Override: 只适用于方法,表示重写父类中的方法
@Deprecated: 表示某各类或方法已过时,比如 Date 类中的 toLocaleString() 方法
@SuppressWarnings: 抑制编译器的警告
二、元注解
元注解用于修饰注解,用于约束注解的作用范围,注解级别等,下面是 Java 提供的 4 种元注解
@Target:指定注解使用的位置,@Target 中有一个 ElementType 数组,因此被 @Target 注解修饰的注解可以在多个位置上使用。下面是 ElementType 枚举中的一些属性(只列举一些常用的属性)
TYPE:能在类、接口(包含注解类型)和枚举类型上使用FIELD:只能在属性上使用METHOD:只能在方法上使用- ……
@Retention:用于表示该注解可以保留的作用域,@Retention 注解包含一个 RetentionPolicy 属性,通过这个属性来设置注解的保留域。RetentionPolicy 是一个枚举,其中有 3 个属性,如下
SOURCE:只在源代码中显示,在编译成 .class 文件的时候会被丢弃CLASS:编译器会把注解记录在 .class 文件中,当程序运行时,虚拟机不会保留该注解RUNTIME:当程序运行时,也会被保留,因此可以通过反射技术获取该类型注解中的一些信息
@Documented:被该注解修饰的类可以使用 javadoc 工具生成文档,这里就不演示了
Inherited:如果子类继承了被 Inherited 修饰的注解,则子类也自动拥有父类中的注解
下面我们通过个例子来加深下理解,下面是 @Deprecated 注解的底层实现
/**
* 表示可以被生成文档
* 在程序运行时也会被保留
* 可以使用在构造器,属性,方法,类或接口,包上等
*/
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(value={CONSTRUCTOR, FIELD, LOCAL_VARIABLE, METHOD, PACKAGE, PARAMETER, TYPE})
public @interface Deprecated {
}三、反射注解
jdk1.5 在 java.lang.refelect 包下新增了 AnnotatedElement 接口,该接口中提供了一些用于反射注解的方法,如下
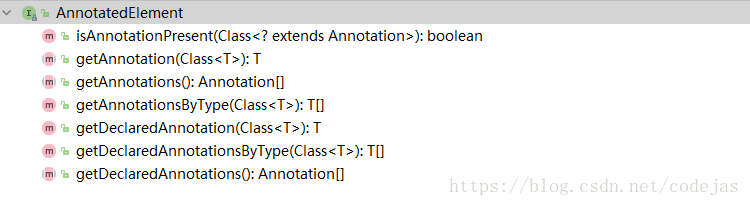
下面通过一个例子来解析注解
自定义 @MyAnno 注解
/**
* @Target 约束该注解只能作用于类接口或枚举上
* @Retention 表示这是一个运行时注解,可以通过反射技术获取注解中的信息
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnno {
String username();
int age() default 18;
}Person 类,使用 @MyAnno 注解标识
@MyAnno(username = "张三")
public class Person { }MainDriver 测试类
public class MainDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 通过反射获得 Person 类的 class 对象
Class clazz = Person.class;
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnno.class)) {
// 通过 class 对象获取 MyAnno 注解对象
MyAnno anno = clazz.getAnnotation(MyAnno.class);
// 获取注解中的属性值
String username = anno.username();
int age = anno.age();
System.out.println(username + " " + age);
} else {
System.out.println("该类上没有注解");
}
}
} 四、注解与反射的综合应用
这里我们模拟一下 Spring Data JPA 中有关注解的实现,使用注解与反射技术拼接查询的 SQL 语句
自定义 @Table 注解
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Table {
String value();
}自定义 @Column 注解
@Target({ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Column {
String value();
}与数据库映射的实体 Student 类
/**
* 当注解中只有一个 value 属性时,可以直接定义注解属性值
*/
@Table("student")
public class Student {
@Column("id")
private int id;
@Column("user_name")
private String username;
@Column("age")
private int age;
@Column("city")
private String city;
@Column("phone")
private String phone;
// 省略 get 与 set 方法
}注解解析 MainDriver 类
public class MainDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Student student1 = new Student();
student1.setUsername("张三");
student1.setAge(18);
student1.setCity("hangzhou");
String s1 = query(student1);
System.out.println(s1);
Student student2 = new Student();
student2.setUsername("李四");
student2.setPhone("12345678977");
String s2 = query(student2);
System.out.println(s2);
}
public static String query(Student student) throws Exception {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Class clazz = student.getClass();
boolean tableAnnoExits = clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Table.class);
// 判断 class 对象上是否有 @Table 注解
if (!tableAnnoExits) {
return null;
}
// 获取 @Table 注解中的表名,拼接 SQl
Table table = clazz.getAnnotation(Table.class);
String tableName = table.value();
sb.append("SELECT * FROM " + tableName + " WHERE 1 = 1");
// 获取 class 对象中的所有字段并遍历
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
boolean fieldAnnoExits = field.isAnnotationPresent(Column.class);
// 判断字段上是否含有 @Column 注解
if (!fieldAnnoExits) {
continue;
}
// 获取注解中的字段名
Column column = field.getAnnotation(Column.class);
String columnName = column.value();
// 通过 get() 方法获取传入的字段值
String fieldName = field.getName();
String getMethodName = "get" + fieldName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase()
+ fieldName.substring(1);
Method method = clazz.getMethod(getMethodName);
Object fieldValue = method.invoke(student);
if (fieldValue == null
|| (fieldValue instanceof Integer && (Integer)fieldValue == 0)) {
continue;
}
// 接着拼接 SQL 语句
sb.append(" AND ").append(columnName).append(" = ");
if (fieldValue instanceof String) {
sb.append("'").append(fieldValue).append("'");
} else if (fieldValue instanceof Integer) {
sb.append(fieldValue);
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
}GitHub 代码地址,点我前往~