Redis内存节省策略
Redis作为一款缓存软件,在Redis的源码中,处处体现着节省内存的思想,下面先从3个方面对Redis的内存节省策略做一个分享。(以下代码为Redis 3.0.5版本)
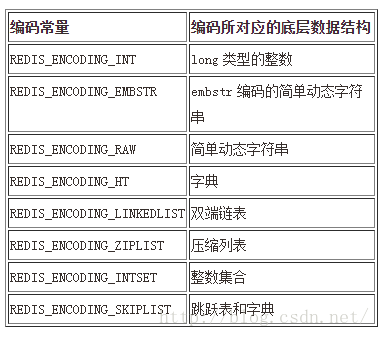
1.redisObject 是Redis中最常见的一个数据结构,Redis存储的所有的键和值都是一个redisObject, 因此必须尽肯能节省redisObject的大小。由于Redis 数据类型只有我们所常见的5种,而Redis的数据编码类型总共8种,所以Redis中分别采用4Bit来表示,两者相加正好1个字节。

typedef struct redisObject {
unsigned type:4;
unsigned encoding:4;
unsigned lru:REDIS_LRU_BITS; /* lru time (relative to server.lruclock) */
int refcount;
void *ptr;
} robj;
struct sharedObjectsStruct {
robj *crlf, *ok, *err, *emptybulk, *czero, *cone, *cnegone, *pong, *space,
*colon, *nullbulk, *nullmultibulk, *queued,
*emptymultibulk, *wrongtypeerr, *nokeyerr, *syntaxerr, *sameobjecterr,
*outofrangeerr, *noscripterr, *loadingerr, *slowscripterr, *bgsaveerr,
*masterdownerr, *roslaveerr, *execaborterr, *noautherr, *noreplicaserr,
*busykeyerr, *oomerr, *plus, *messagebulk, *pmessagebulk, *subscribebulk,
*unsubscribebulk, *psubscribebulk, *punsubscribebulk, *del, *rpop, *lpop,
*lpush, *emptyscan, *minstring, *maxstring,
*select[REDIS_SHARED_SELECT_CMDS],
*integers[REDIS_SHARED_INTEGERS],
*mbulkhdr[REDIS_SHARED_BULKHDR_LEN], /* "*\r\n" */
*bulkhdr[REDIS_SHARED_BULKHDR_LEN]; /* "$\r\n" */
}; 3.Redis的8种编码类型,REDIS_ENCODING_INT, REDIS_ENCODING_EMBSTR, REDIS_ENCODING_RAW是基础,对于其他几种编码类型,除REDIS_ENCODING_INTSET外,其所对应对象存储的信息对象均是以前三种编码类型为基础,生成一个个具体的对象。如Redis链表中,每个节点存储的对象,其编码类型可以为REDIS_ENCODING_INT, REDIS_ENCODING_EMBSTR, REDIS_ENCODING_RAW 中的任意一种。
/* Try to encode a string object in order to save space */
robj *tryObjectEncoding(robj *o) {
long value;
sds s = o->ptr;
size_t len;
/* Make sure this is a string object, the only type we encode
* in this function. Other types use encoded memory efficient
* representations but are handled by the commands implementing
* the type. */
redisAssertWithInfo(NULL,o,o->type == REDIS_STRING);
/* We try some specialized encoding only for objects that are
* RAW or EMBSTR encoded, in other words objects that are still
* in represented by an actually array of chars. */
if (!sdsEncodedObject(o)) return o;
/* It's not safe to encode shared objects: shared objects can be shared
* everywhere in the "object space" of Redis and may end in places where
* they are not handled. We handle them only as values in the keyspace. */
if (o->refcount > 1) return o;
/* Check if we can represent this string as a long integer.
* Note that we are sure that a string larger than 21 chars is not
* representable as a 32 nor 64 bit integer. */
len = sdslen(s);
if (len <= 21 && string2l(s,len,&value)) {
/* This object is encodable as a long. Try to use a shared object.
* Note that we avoid using shared integers when maxmemory is used
* because every object needs to have a private LRU field for the LRU
* algorithm to work well. */
if ((server.maxmemory == 0 ||
(server.maxmemory_policy != REDIS_MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_LRU &&
server.maxmemory_policy != REDIS_MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_LRU)) &&
value >= 0 &&
value < REDIS_SHARED_INTEGERS)
{
decrRefCount(o);
incrRefCount(shared.integers[value]);
return shared.integers[value];
} else {
if (o->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_RAW) sdsfree(o->ptr);
o->encoding = REDIS_ENCODING_INT;
o->ptr = (void*) value;
return o;
}
}
/* If the string is small and is still RAW encoded,
* try the EMBSTR encoding which is more efficient.
* In this representation the object and the SDS string are allocated
* in the same chunk of memory to save space and cache misses. */
if (len <= REDIS_ENCODING_EMBSTR_SIZE_LIMIT) {
robj *emb;
if (o->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_EMBSTR) return o;
emb = createEmbeddedStringObject(s,sdslen(s));
decrRefCount(o);
return emb;
}
/* We can't encode the object...
*
* Do the last try, and at least optimize the SDS string inside
* the string object to require little space, in case there
* is more than 10% of free space at the end of the SDS string.
*
* We do that only for relatively large strings as this branch
* is only entered if the length of the string is greater than
* REDIS_ENCODING_EMBSTR_SIZE_LIMIT. */
if (o->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_RAW &&
sdsavail(s) > len/10)
{
o->ptr = sdsRemoveFreeSpace(o->ptr);
}
/* Return the original object. */
return o;
}