spring事物--03源码分析入口
版本:spring5.0.6
spring 事务处理模块是通过aop功能来实现声明式事务的。通过TransactionProxyFactoryBean 可以生成proxy代理对象,在这个代理对象中通过TransactionInterceptor 来完成对代理方法的拦截,将事务处理功能编织起来;这正是aop的功能。
可以参考spring aop 源码分析相关文章。
https://blog.csdn.net/convict_eva/article/details/81084833
https://blog.csdn.net/convict_eva/article/details/81101432
https://blog.csdn.net/convict_eva/article/details/81105144
1、配置示例:
配置如下(参考:https://blog.csdn.net/convict_eva/article/details/83274037):
PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
2、TransactionProxyFactoryBean 源码分析:
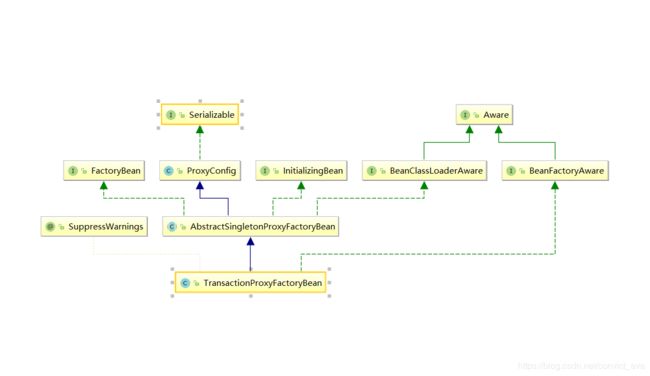
TransactionProxyFactoryBean 类就是分析的入口。类图如下:
TransactionProxyFactoryBean是FactoryBean,那么很容易想它的getObject() 方法。
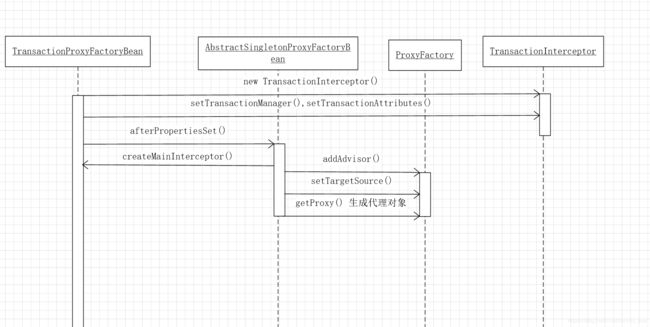
通过时序图分析是如何建立起事务处理机制的。
说明:
1、通过配置文件定义的 TransactionProxyFactoryBean 对象,设置了target,transactionManager,transactionAttributes
target 属性是在 TransactionProxyFactoryBean 父类AbstractSingletonProxyFactoryBean 中,
transactionManager,transactionAttributes 两个属性是被设置到了TransactionInterceptor 对象中。
2、TransactionProxyFactoryBean 父类 AbstractSingletonProxyFactoryBean 类实现了InitializingBean 接口,在类初始化完毕后会调用 afterPropertiesSet() 方法。这个方法就是构建 ProxyFactory 对象(如设置目标对象,设置接口,设置Interceptor)来获取代理对象。
3、afterPropertiesSet() 方法通过 ProxyFactory 获取代理对象。ProxyFactory 就是aop的核心类,通过CGLIB 或者 JDK 动态代理生成目标对象。
下面进入源码分析:
2、入口:TransactionProxyFactoryBean
public class TransactionProxyFactoryBean extends AbstractSingletonProxyFactoryBean
implements BeanFactoryAware {
//创建 TransactionInterceptor,这个拦截器通过aop发挥使用
//spring通过这个拦截器的实现,封装了事务处理。后面会分析这个拦截器
private final TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor = new TransactionInterceptor();
@Nullable
private Pointcut pointcut;
/**
* Set the default transaction manager. This will perform actual
* transaction management: This class is just a way of invoking it.
* @see TransactionInterceptor#setTransactionManager
依赖注入 transactionManager,调用transactionInterceptor的set方法设置。
*/
public void setTransactionManager(PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager) {
this.transactionInterceptor.setTransactionManager(transactionManager);
}
/**
* Set properties with method names as keys and transaction attribute
* descriptors (parsed via TransactionAttributeEditor) as values:
* e.g. key = "myMethod", value = "PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,readOnly".
* Note: Method names are always applied to the target class,
* no matter if defined in an interface or the class itself.
*
Internally, a NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource will be
* created from the given properties.
* @see #setTransactionAttributeSource
* @see TransactionInterceptor#setTransactionAttributes
* @see TransactionAttributeEditor
* @see NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource
依赖注入 transactionAttributes ,设置transactionInterceptor事务属性。
把Properties 封装成了 TransactionAttributeSource 子类 NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource 对象
进一步set到了 TransactionInterceptor(在父类TransactionAspectSupport中) transactionAttributeSource 的属性
*/
public void setTransactionAttributes(Properties transactionAttributes) {
this.transactionInterceptor.setTransactionAttributes(transactionAttributes);
}
/**
* Set the transaction attribute source which is used to find transaction
* attributes. If specifying a String property value, a PropertyEditor
* will create a MethodMapTransactionAttributeSource from the value.
* @see #setTransactionAttributes
* @see TransactionInterceptor#setTransactionAttributeSource
* @see TransactionAttributeSourceEditor
* @see MethodMapTransactionAttributeSource
* @see NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource
* @see org.springframework.transaction.annotation.AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource
和setTransactionAttributes 类似,这里直接是TransactionAttributeSource对象
*/
public void setTransactionAttributeSource(TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource) {
this.transactionInterceptor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource);
}
/**
* Set a pointcut, i.e a bean that can cause conditional invocation
* of the TransactionInterceptor depending on method and attributes passed.
* Note: Additional interceptors are always invoked.
* @see #setPreInterceptors
* @see #setPostInterceptors
依赖注入切点,这里配置没有用到
*/
public void setPointcut(Pointcut pointcut) {
this.pointcut = pointcut;
}
/**
* This callback is optional: If running in a BeanFactory and no transaction
* manager has been set explicitly, a single matching bean of type
* {@link PlatformTransactionManager} will be fetched from the BeanFactory.
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory#getBean(Class)
* @see org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager
beanFactory设置,用来产生transactionInterceptor的,这里没有用到
*/
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
this.transactionInterceptor.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
}
/**
* Creates an advisor for this FactoryBean's TransactionInterceptor.
创建 spring aop对事务处理的 advisor
父类 AbstractSingletonProxyFactoryBean 实现了InitializingBean,初始化完毕后被 afterPropertiesSet() 调用。
*/
@Override
protected Object createMainInterceptor() {
this.transactionInterceptor.afterPropertiesSet();
if (this.pointcut != null) {
//使用默认的通知器 DefaultPointcutAdvisor,为通知器配置事务处理拦截器
return new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(this.pointcut, this.transactionInterceptor);
}
else {
// Rely on default pointcut.
//没有配置 pointcut,使用 TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 通知器,并为通知器设置 transactionInterceptor 为拦截器
return new TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor(this.transactionInterceptor);
}
}
/**
* As of 4.2, this method adds {@link TransactionalProxy} to the set of
* proxy interfaces in order to avoid re-processing of transaction metadata.
父类afterPropertiesSet() 方法调用,设置proxyFactory 接口,避免重新处理事务的元数据。
*/
@Override
protected void postProcessProxyFactory(ProxyFactory proxyFactory) {
proxyFactory.addInterface(TransactionalProxy.class);
}
}
TransactionProxyFactoryBean 只是完成了对象的依赖注入,完成了aop的配置。createMainInterceptor() 方法把transactionInterceptor 封装成了advisor,这个advisor是在父类AbstractSingletonProxyFactoryBean.afterPropertiesSet() 方法被调用(实现了InitializingBean 接口),在这个方法中完成了代理对象的生成。源码如下:
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
//必须配置一个target对象,并且target 是一个 bean reference
if (this.target == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property 'target' is required");
}
if (this.target instanceof String) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("'target' needs to be a bean reference, not a bean name as value");
}
if (this.proxyClassLoader == null) {
//设置class loader
this.proxyClassLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
}
/**
* 生成代理对象工厂,如果看过前面的aop文章就很清楚了。
* ProxyFactory 创建代理对象,并且将TransactionInterceptor设置为target 方法调用的拦截器。
* 就是这个拦截器完成的事务处理。
*/
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
//设置preInterceptors
if (this.preInterceptors != null) {
for (Object interceptor : this.preInterceptors) {
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(this.advisorAdapterRegistry.wrap(interceptor));
}
}
// Add the main interceptor (typically an Advisor).
/**
* 这里就是加入TransactionInterceptor的地方
* 可以加入两种advisor,DefaultPointcutAdvisor 和 TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor。
* 这时调用的是TransactionProxyFactoryBean.createMainInterceptor()方法生成需要的advisor(上面提到过)。
* 在ProxyFactory 在基类AdvisedSupport 中,维护了一个持有advice的LinkedList,通过这个LinkedList的元素执行添加、修改、删除来管理配置ProxyFactory的通知器(aop部份)
*/
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(this.advisorAdapterRegistry.wrap(createMainInterceptor()));
//设置postInterceptors
if (this.postInterceptors != null) {
for (Object interceptor : this.postInterceptors) {
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(this.advisorAdapterRegistry.wrap(interceptor));
}
}
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
// 目标对象封装为TargetSource,aop的目标源,统一后面aop的使用
TargetSource targetSource = createTargetSource(this.target);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
//设置proxyFactory的接口,目标对象实现的接口
if (this.proxyInterfaces != null) {
proxyFactory.setInterfaces(this.proxyInterfaces);
}
else if (!isProxyTargetClass()) {
// Rely on AOP infrastructure to tell us what interfaces to proxy.
//需要根据aop基础设施来确定使用哪个接口作为代理
Class targetClass = targetSource.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass != null) {
proxyFactory.setInterfaces(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClass(targetClass, this.proxyClassLoader));
}
}
//调用TransactionProxyFactoryBean 方法,为proxyFactory添加一个TransactionalProxy代理接口
postProcessProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
//获取代理对象,设置给proxy属性
//proxyFactory.getProxy() 这是aop的东西了,通过CGLIB 或者 jdk动态代理生成代理对象
this.proxy = proxyFactory.getProxy(this.proxyClassLoader);
}通过上面的步骤,spring事务处理拦截器TransactionInterceptor已经设置到了ProxyFactory生成的aop代理对象中,TransactionInterceptor作为aop的advice来实现它的功能。
这时 TransactionInterceptor 已经在Ioc容器中注入完毕,如:transactionManager和事务处理属性已经注入完毕。
通过上面分析可以知道,spring声明式事务重要的类已经出现:TransactionInterceptor和 TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor(TransactionProxyFactoryBean.createMainInterceptor() 方法返回的advisor),分别定义了interceptor和Advisor。下面就来分析这两个重要的类
3、TransactionInterceptor 源码分析:
TransactionInterceptor 是一个 MethodInterceptor,用来实现aop功能的;同时又是一个TransactionAspectSupport用来实现事务切面支持。
所有通过TransactionInterceptor,把aop和事务的支持组织到一起。
spring aop 需要一个advisor(包含了 interceptor和pointcut),声明式事务advisor,就是 TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor (TransactionProxyFactoryBean.createMainInterceptor() 方法创建的advisor)。
看看这个advisor是如何实现的:
TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 源码如下:
public class TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor extends AbstractPointcutAdvisor {
//interceptor 是 TransactionInterceptor
@Nullable
private TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor;
/**
* pointcut 的定义
* 使用 TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut 内部类
*/
private final TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut pointcut = new TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut() {
//通过 transactionInterceptor 获取事务配置属性,在proxy的方法进行匹配调用时,会使用到这些属性
@Override
@Nullable
protected TransactionAttributeSource getTransactionAttributeSource() {
return (transactionInterceptor != null ? transactionInterceptor.getTransactionAttributeSource() : null);
}
};
//省略源代码.....
}上面的源码中定义出了 pointcut 是 TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut,在aop部分知道pointcut必须有个matches 方法,用来判断方法是不是需要增强。TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut.matches() 源码如下:
abstract class TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut extends StaticMethodMatcherPointcut implements Serializable {
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method, @Nullable Class targetClass) {
if (targetClass != null && TransactionalProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
//调用 getTransactionAttributeSource() 获取事务配置的“transactionAttributes”属性,来判断调用方法是否匹配
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
return (tas == null || tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) != null);
}
//省略源代码....
}这个 TransactionAttributeSource 是在TransactionProxyFactoryBean属性transactionAttributes 注入的时候生成的。
public void setTransactionAttributes(Properties transactionAttributes) {
this.transactionInterceptor.setTransactionAttributes(transactionAttributes);
}
//transactionInterceptor.setTransactionAttributes() 方法源码:
/**
* 配置TransactionAttributeSource,TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut 获取的resource就是一步注入的。
* transactionInterceptor.transactionAttributeSource 属性就是 NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource 的实例
* 这是一个 NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource,把ioc容器是的事务处理属性放到这个TransactionAttributeSource 中
*/
public void setTransactionAttributes(Properties transactionAttributes) {
NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource tas = new NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource();
tas.setProperties(transactionAttributes);
this.transactionAttributeSource = tas;
}NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource 实现了事务处理属性读入和匹配。源码如下:
public class NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource implements TransactionAttributeSource, Serializable {
/**
* Logger available to subclasses.
* Static for optimal serialization.
*/
protected static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource.class);
/** Keys are method names; values are TransactionAttributes */
//方法名是key,事务属性是value。用来判断方法是否需要增强,如果要增强那么就使用value 事务属性
private Map nameMap = new HashMap<>();
/**
* Set a name/attribute map, consisting of method names
* (e.g. "myMethod") and TransactionAttribute instances
* (or Strings to be converted to TransactionAttribute instances).
* @see TransactionAttribute
* @see TransactionAttributeEditor
*/
public void setNameMap(Map nameMap) {
nameMap.forEach(this::addTransactionalMethod);
}
/**
* Parses the given properties into a name/attribute map.
* Expects method names as keys and String attributes definitions as values,
* parsable into TransactionAttribute instances via TransactionAttributeEditor.
* @see #setNameMap
* @see TransactionAttributeEditor
解析配置文件中关于事务属性的配置,放入到nameMap 中。关于TransactionAttribute配置比较多,参考XXX。
*/
public void setProperties(Properties transactionAttributes) {
//TransactionAttributeEditor 把配置事务属性字符串解析成了TransactionAttribute对象。
TransactionAttributeEditor tae = new TransactionAttributeEditor();
Enumeration propNames = transactionAttributes.propertyNames();
//一个方法名(也可以包含通配符)配置是一个elements
while (propNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String methodName = (String) propNames.nextElement();
String value = transactionAttributes.getProperty(methodName);
tae.setAsText(value);
TransactionAttribute attr = (TransactionAttribute) tae.getValue();
//放到nameMap中
addTransactionalMethod(methodName, attr);
}
}
/**
* Add an attribute for a transactional method.
* Method names can be exact matches, or of the pattern "xxx*",
* "*xxx" or "*xxx*" for matching multiple methods.
* @param methodName the name of the method
* @param attr attribute associated with the method
*/
public void addTransactionalMethod(String methodName, TransactionAttribute attr) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Adding transactional method [" + methodName + "] with attribute [" + attr + "]");
}
this.nameMap.put(methodName, attr);
}
/**
* 通过方法名找配置事务的属性。上面提到的TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut.matches() 方法就是调用此方法,判断返回是否为空来判断方法是否需要增强。
*
* 首先通过方法名从nameMap中找,
* 如果找不到就遍历nameMap,使用PatternMatchUtils匹配方法名(只支持 XX* *XX *XX* 方式,请看源码)。因为方法名可以配置通配符。
* 如果有多个匹配,那么找的是长度最长匹配的,如果配置长度一致那么就取配置在最后的一个事务属性
*
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public TransactionAttribute getTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class targetClass) {
if (!ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) {
return null;
}
// Look for direct name match.
String methodName = method.getName();
TransactionAttribute attr = this.nameMap.get(methodName);
if (attr == null) {
// Look for most specific name match.
String bestNameMatch = null;
for (String mappedName : this.nameMap.keySet()) {
if (isMatch(methodName, mappedName) &&
(bestNameMatch == null || bestNameMatch.length() <= mappedName.length())) {
attr = this.nameMap.get(mappedName);
bestNameMatch = mappedName;
}
}
}
return attr;
}
/**
* Return if the given method name matches the mapped name.
*
The default implementation checks for "xxx*", "*xxx" and "*xxx*" matches,
* as well as direct equality. Can be overridden in subclasses.
* @param methodName the method name of the class
* @param mappedName the name in the descriptor
* @return if the names match
* @see org.springframework.util.PatternMatchUtils#simpleMatch(String, String)
判断方法名是否匹配
*/
protected boolean isMatch(String methodName, String mappedName) {
return PatternMatchUtils.simpleMatch(mappedName, methodName);
}
//省略hashCode ,equals ,toString 方法
}
总结第2,3步的分析:
1、配置通过TransactionProxyFactoryBean 类统一接收,
2、TransactionProxyFactoryBean.createMainInterceptor() 方法中创建了 TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor。
拦截器使用的是TransactionInterceptor,pointcut使用的是TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut。
3、使用TransactionInterceptor 封装事务属性,在TransactionInterceptor.transactionAttributeSource属性是NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource实例,封装了事务属性的解析、读取和方法的匹配。
4、NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource把事务配置解析成了一个HashMap<方法名,事务属性>,TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut 的matches 方法,就是通过方法名的查找、匹配到事务配置的属性来确定是否需要事务的增强的。
待续:事务处理拦截器的实现分析