netty4粘包/拆包/断包 解决方案
粘包、拆包表现形式
现在假设客户端向服务端连续发送了两个数据包,用packet1和packet2来表示,那么服务端收到的数据可以分为三种,现列举如下:
第一种情况,接收端正常收到两个数据包,即没有发生拆包和粘包的现象,此种情况不在本文的讨论范围内。
第二种情况,接收端只收到一个数据包,由于TCP是不会出现丢包的,所以这一个数据包中包含了发送端发送的两个数据包的信息,这种现象即为粘包。这种情况由于接收端不知道这两个数据包的界限,所以对于接收端来说很难处理。
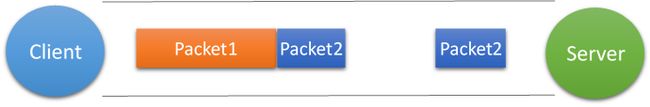
第三种情况,这种情况有两种表现形式,如下图。接收端收到了两个数据包,但是这两个数据包要么是不完整的,要么就是多出来一块,这种情况即发生了拆包和粘包。这两种情况如果不加特殊处理,对于接收端同样是不好处理的。
粘包问题的解决策略
由于底层的TCP无法理解上层的业务数据,所以在底层是无法保证数据包不被拆分和重组的,这个问题只能通过上层的应用协议栈设计来解决。业界的主流协议的解决方案,可以归纳如下:1. 消息定长,报文大小固定长度,例如每个报文的长度固定为200字节,如果不够空位补空格;
2. 包尾添加特殊分隔符,例如每条报文结束都添加回车换行符(例如FTP协议)或者指定特殊字符作为报文分隔符,接收方通过特殊分隔符切分报文区分;
3. 将消息分为消息头和消息体,消息头中包含表示信息的总长度(或者消息体长度)的字段;
4. 更复杂的自定义应用层协议。
Netty粘包和拆包解决方案
Netty提供了多个解码器,可以进行分包的操作,分别是:* LineBasedFrameDecoder (换行)
LineBasedFrameDecoder是回车换行解码器,如果用户发送的消息以回车换行符作为消息结束的标识,则可以直接使用Netty的LineBasedFrameDecoder对消息进行解码,只需要在初始化Netty服务端或者客户端时将LineBasedFrameDecoder正确的添加到ChannelPipeline中即可,不需要自己重新实现一套换行解码器。
LineBasedFrameDecoder的工作原理是它依次遍历ByteBuf中的可读字节,判断看是否有“\n”或者“\r\n”,如果有,就以此位置为结束位置,从可读索引到结束位置区间的字节就组成了一行。它是以换行符为结束标志的解码器,支持携带结束符或者不携带结束符两种解码方式,同时支持配置单行的最大长度。如果连续读取到最大长度后仍然没有发现换行符,就会抛出异常,同时忽略掉之前读到的异常码流。防止由于数据报没有携带换行符导致接收到ByteBuf无限制积压,引起系统内存溢出。
* DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(添加特殊分隔符报文来分包)
DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder是分隔符解码器,用户可以指定消息结束的分隔符,它可以自动完成以分隔符作为码流结束标识的消息的解码。
回车换行解码器实际上是一种特殊的DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder解码器。
* FixedLengthFrameDecoder(使用定长的报文来分包)
FixedLengthFrameDecoder是固定长度解码器,它能够按照指定的长度对消息进行自动解码,开发者不需要考虑TCP的粘包/拆包等问题,非常实用。
对于定长消息,如果消息实际长度小于定长,则往往会进行补位操作,它在一定程度上导致了空间和资源的浪费。但是它的优点也是非常明显的,编解码比较简单,因此在实际项目中仍然有一定的应用场景。
* LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder (自定义解码器跟编码器)
本文介绍的重点LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder,一般包含了消息头(head)、消息体(body):消息头是固定的长度,一般有有以下信息 -> 是否压缩(zip)、消息类型(type or cmdid)、消息体长度(body length);消息体长度不是固定的,其大小由消息头记载,一般记载业务交互信息。
netty对应来说就是编码器(Encoder)跟解码器(Decoder),一般其中会有一个基本消息类对外输出,egg:
/**
* @describe 消息缓存区
* @author zhikai.chen
* @date 2018年4月28日 上午10:13:35
*/
public class Message {
/**
* 要发送的数据
*/
private String data;
/**
* 业务编号
*/
private short cmdId;
/**
* 消息类型 0xAF 表示心跳包 0xBF 表示超时包 0xCF 业务信息包
*/
private byte type;
/**
* 是否压缩,1是,0不是
*/
private byte zip = 0 ;
/**
* 封装要发送的数据包
* @param data 业务数据
* @param cmdId 业务标识号
* @param type 消息类型
*/
public Message(String data,short cmdId,byte type){
this.data=data;
this.cmdId=cmdId;
this.type=type;
}
public String getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(String data) {
this.data = data;
}
public short getCmdId() {
return cmdId;
}
public void setCmdId(short cmdId) {
this.cmdId = cmdId;
}
public byte getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(byte type) {
this.type = type;
}
public byte getZip() {
return zip;
}
public void setZip(byte zip) {
this.zip = zip;
}
Encoder:
/**
* @describe 消息编码器,封装
* @author zhikai.chen
* @date 2018年4月28日 上午10:17:52
*/
public class MessageEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder {
// 编码格式
private final Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
// 需要压缩的长度
private final int compressLength=1024;
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Message msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
String source=msg.getData();
byte[] body=source.getBytes(charset);
if(body.length > compressLength){
msg.setZip((byte)1);
// 加压
body=ZipTool.compress(body);
}
//cmdId(2)+type(1)+zip(1)+body(4)=8
//out = Unpooled.directBuffer(8+body.length);
//cmdId
out.writeShort(msg.getCmdId());
//type
out.writeByte(msg.getType());
//是否加压
out.writeByte(msg.getZip());
//长度
out.writeInt(body.length);
//内容
out.writeBytes(body);
}
} NioSocketServerInitializer(服务端跟客户端都一致):
//TODO 参考Message
//body(4)+zip(1)+cmdId(2)+type(1)=8
//最大长度
private static final int MAX_FRAME_LENGTH = 1024 * 1024;
//这个值就是MessageEncoder body.length(4)
private static final int LENGTH_FIELD_LENGTH = 4;
//这个值就是MessageEncoder zip(1)+cmdId(2)+type(1)
private static final int LENGTH_FIELD_OFFSET = 4;
private static final int LENGTH_ADJUSTMENT = 0;
private static final int INITIAL_BYTES_TO_STRIP = 0; //TODO 粘包处理
//解码器
ch.pipeline().addLast(new MessageDecoder(MAX_FRAME_LENGTH,LENGTH_FIELD_LENGTH,LENGTH_FIELD_OFFSET,LENGTH_ADJUSTMENT,INITIAL_BYTES_TO_STRIP));
//编码器
ch.pipeline().addLast(new MessageEncoder());1)LENGTH_FIELD_LENGTH指的就是我们这边CustomMsg中length这个属性的大小,我们这边是int型,所以是4
2)LENGTH_FIELD_OFFSET指的就是我们这边length字段的起始位置,因为前面有zip(1)+cmdId(2)+type(1)=4,所以是4
3)LENGTH_ADJUSTMENT指的是length这个属性的值,假如我们的body长度是40,有时候,有些人喜欢将length写成44,因为length本身还占有4个字节,
这样就需要调整一下,那么就需要-4,我们这边没有这样做,所以写0就可以了
Decoder
/**
* @describe 消息解码器
* @author zhikai.chen
* @date 2018年4月28日 上午11:09:15
*/
public class MessageDecoder extends LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder {
//body(4)+zip(1)+cmdId(2)+type(1)=8
private static final int HEADER_SIZE = 8;
// 编码格式
private final Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
public MessageDecoder(int maxFrameLength, int lengthFieldOffset, int lengthFieldLength) {
super(maxFrameLength, lengthFieldOffset, lengthFieldLength);
}
public MessageDecoder(int maxFrameLength, int lengthFieldOffset, int lengthFieldLength,int lengthAdjustment, int initialBytesToStrip) {
super(maxFrameLength, lengthFieldOffset, lengthFieldLength,lengthAdjustment,initialBytesToStrip);
}
@Override
protected Object decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in) throws Exception {
if (in == null) {
return null;
}
// 消息头读取不完整,不做解析返回null,直到读完整为止
if (in.readableBytes() <= HEADER_SIZE) {
return null;
}
in.markReaderIndex();
short cmdId = in.readShort();
byte type = in.readByte();
byte zip = in.readByte();
int dataLength = in.readInt();
// TODO 网络信号不好,没有接收到完整数据
if (in.readableBytes() < dataLength) {
//保存当前读到的数据,下一次继续读取
//断包处理:查看ByteToMessageDecoder的channelRead方法,ByteBuf cumulation属性
in.resetReaderIndex();
return null;
}
byte[] data = new byte[dataLength];
in.readBytes(data);
// TODO 手动释放内存
//in.release(); // or ReferenceCountUtil.release(in);
//判断是否压缩
if(zip==1){
data=ZipTool.uncompress(data);
}
String body = new String(data, charset);
Message msg = new Message(body, cmdId, type);
return msg;
}
}Decoder的解码顺序是跟Encoder一致的。
对应的消息接收handler read处理:
NioSocketServerHandler server=new NioSocketServerHandler();
pipeline.addLast(server);public class NioSocketServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler {
private final Logger log=LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Message msg) throws Exception {
log.info("server read msg:{}", JSON.toJSONString(msg));
}} write处理:
Message msg=new Message("ok",ModuleID.HEART_BEAT,(byte)0xAF);
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(msg);断包处理
眼尖的童靴其实已经发现(Decoder):
//TODO 消息头都读取不完整,不做解析返回null,直到读完整为之
if (in.readableBytes() <= HEADER_SIZE) {
return null;
}
in.markReaderIndex();
short cmdId = in.readShort();
byte type = in.readByte();
byte zip = in.readByte();
int dataLength = in.readInt();
// TODO 网络信号不好,没有接收到完整数据
if (in.readableBytes() < dataLength) {
//保存当前读到的数据,下一次继续读取
//断包处理:查看ByteToMessageDecoder的channelRead方法,ByteBuf cumulation属性
in.resetReaderIndex();
return null;
}说明注释已经讲解了,我们来看看消息体一次读不完(断包)了,netty底层是怎么处理的:解码器继承LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder,而LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder继承ByteToMessageDecoder,ByteToMessageDecoder中有一个channelRead方法:
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
if (msg instanceof ByteBuf) {
CodecOutputList out = CodecOutputList.newInstance();
try {
ByteBuf data = (ByteBuf) msg;
first = cumulation == null;
if (first) {
cumulation = data;
} else {
cumulation = cumulator.cumulate(ctx.alloc(), cumulation, data);
}
callDecode(ctx, cumulation, out);
} catch (DecoderException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new DecoderException(t);
} finally {
if (cumulation != null && !cumulation.isReadable()) {
numReads = 0;
cumulation.release();
cumulation = null;
} else if (++ numReads >= discardAfterReads) {
// We did enough reads already try to discard some bytes so we not risk to see a OOME.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/4275
numReads = 0;
discardSomeReadBytes();
}
int size = out.size();
decodeWasNull = !out.insertSinceRecycled();
fireChannelRead(ctx, out, size);
out.recycle();
}
} else {
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
}我们来看看cumulation的定义,
ByteBuf cumulation;
private Cumulator cumulator = MERGE_CUMULATOR;
private boolean singleDecode;
private boolean decodeWasNull;
private boolean first;
private int discardAfterReads = 16;
private int numReads;