Android性能优化系列3--内存优化案例
参考书籍Android移动性能实战
1、单例、内部类引起的内存泄漏
a、单例很容易理解,我们都知道单例的生命周期跟随应用的生命周期,如果单例持有了Activity或Fragment的引用,那就会引起内存泄漏。
b、内部类引起的内存泄漏,成员内部类, 局部内部类、 匿名内部类。 会有对外部类的引用。这样内部类中耗时操作在用户频繁退出重启APP相关Activity时很容易导致内存泄漏。
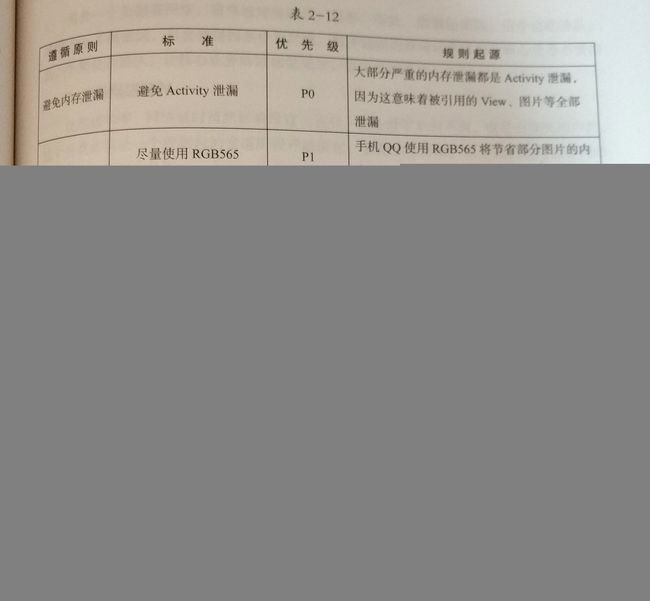
2、定时器、延时操作、异步操作等引用了Activity或Fragment实例引发的内存泄漏
以上案例可参考http://blog.csdn.net/sinat_31057219/article/details/74533647总结的比较细,就不再详述了
3、从ActivityA跳转到ActivityB,且没有一种方式可以让用户回到ActivityA,然而ActivityA没有调用finish()方法造成的Activity泄漏。
4、调用系统服务造成的内存泄漏
一般我们获取一个系统服务会直接在Activity中getSystemService(Context.WIFI_SERVICE),但是这样相当于这个服务持有了外部Activity的引用,如果在服务内部发生异常,就无法释放这个引用了。所以我们获取服务要使用:getApplicationContext().getSystemService(Context.WIFI_SERVICE),这样就不会产生泄漏了。
同时我们要注意以下几点
- 在使用系统服务时尽量避免使用界面的Context
- 提供异步工作的服务,一定要注意回调函数、handle、oberserve等通知类型的对象的注册与反注册的成对出现
5、WebView造成的内存泄漏
参考文章https://www.jianshu.com/p/3e8f7dbb0dc7
a、进程方式解决:这也是腾讯采用的方式即为加载WebView的界面开启新进程,在该页面退出之后关闭这个进程。
b、处理onDestory
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
if( mWebView!=null) {
// 如果先调用destroy()方法,则会命中if (isDestroyed()) return;这一行代码,需要先onDetachedFromWindow(),再
// destory()
ViewParent parent = mWebView.getParent();
if (parent != null) {
((ViewGroup) parent).removeView(mWebView);
}
mWebView.stopLoading();
// 退出时调用此方法,移除绑定的服务,否则某些特定系统会报错
mWebView.getSettings().setJavaScriptEnabled(false);
mWebView.clearHistory();
mWebView.clearView();
mWebView.removeAllViews();
mWebView.destroy();
}
super.on Destroy();
}6、图片解码配色设置建议
解决多图片在内存常驻问题。
适用场景:在对图片显示质量要求不高的缩略图,或高清图缩小时使用.
使用方法:
BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
options1.inPreferredConfig = Bitmap.Config.RGB_565;
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(data, 0 , data.length, options); 小常识
ALPHA_8 代表8位Alpha位图
ARGB_4444 代表16位ARGB位图
ARGB_8888 代表32位ARGB位图
RGB_565 代表8位RGB位图位图位数越高代表其可以存储的颜色信息越多,当然图像也就越逼真。
7、加载大图造成的内存溢出问题
参考文章https://developer.xamarin.com/recipes/android/resources/general/load_large_bitmaps_efficiently/
简单来说就是三步
- 从服务器下载回来的图片中获取高和宽以及类型。(图片的头部含有这些信息,所以不需要解析像素)
BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
options.inJustDecodeBounds = true;
BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.id.myimage, options);
int imageHeight = options.outHeight;
int imageWidth = options.outWidth;
String imageType = options.outMimeType; - 对于高或宽大于屏幕尺寸的图片计算缩放比,常做缩放解码(图片的分辨率再大,也受限于设备的分辨率)
public static int calculateInSampleSize(
BitmapFactory.Options options, int reqWidth, int reqHeight) {
// Raw height and width of image
final int height = options.outHeight;
final int width = options.outWidth;
int inSampleSize = 1;
if (height > reqHeight || width > reqWidth) {
if (width > height) {
inSampleSize = Math.round((float)height / (float)reqHeight);
} else {
inSampleSize = Math.round((float)width / (float)reqWidth);
}
}
return inSampleSize;
} 解析
public static Bitmap decodeSampledBitmapFromResource(Resources res, int resId,
int reqWidth, int reqHeight) {
// First decode with inJustDecodeBounds=true to check dimensions
final BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
options.inJustDecodeBounds = true;
BitmapFactory.decodeResource(res, resId, options);
// Calculate inSampleSize
options.inSampleSize = calculateInSampleSize(options, reqWidth, reqHeight);
// Decode bitmap with inSampleSize set
options.inJustDecodeBounds = false;
return BitmapFactory.decodeResource(res, resId, options);
} - 要对所有的图片解码API(decodexxxx)做OOMError的异常处理