1. PLI 功能介绍
Verilog PLI(Programming Language Interface )是一种Verilog代码调用C/C++函数的机制。它能让Verilog像调用一些系统调用(如$display/$stop/$random)一样调用用户编写的C/C++函数,这样我们可以用C/C++语言开始自己的system task/function, 来实现用verilog不太方便的功能,并与外界建立了联系。
PLI可以完成如下功能:
功耗分析
代码覆盖率工具
修改Verilog仿真数据结构(如修改为更精确的延时,即sdf反标)
自定义输出显示
联合仿真
设计的调试功能
仿真分析
加速仿真的C模型接口
Testbench建模
Verilog PLI提供了一些访问verilog内部数据结构的
任务功能程序集 (TF routines): 大部分以tf_开头,主要用于一些用户定义系统任务和函数变量的操作,工具函数(比如设置回调函数和写数据到输出)
访问程序集 (ACC routines): 第二代PLI. 所有以acc_开头。提供了对象导向的对SV结构的访问。主要用于访问和修改信息,比delay value, logic value. ACC routines和TF routines有部分重复。
验证过程接口程序集 (VPI routines): 第三代PLI。大部分以vpi_开头。提供了对象导向的对SV结构, 行为, assertion, coverage 对象的访问。 它包含了TF和ACC routines的所有功能。
2. 用户定义task/function命名
规则如下:
第一个字符必须是$
剩下的字符可以是字母, 数字,下划线或$
大小写敏感
名字可以任意长度
3. 用户定义task/function的参数
例子:
$get_vector("test_vector.pat", input_bus);一组PLI routines可以用于PLI程序来读/写这些参数
4. task/function
用户定义的task可以用于SV task能使用的任何地方
用户定义的function可以用于SV task能使用的任何地方, 可以返回值, 长度由用户提供的sizetf确定
5. 用户提供的PLI application
这类C函数不是独立的C程序,而是被Link到工具里,当用户定义的task/function被调用时,他们可能会被调用
6. PLI include文件
定义了
常数
struct
数据
这些文件是
vpi_user.h
sv_vpi_user.h
7. NC Example
Files
test.v
module test;
wire a, b, c;
initial
begin
$module_info;
end
pipe p1 (a, b, c);
//stimuli
//monitor response
endmodulepipe.v
module pipe ( out, in, clk );
output out; reg out;
input in, clk;
always @ (in)
@ (posedge clk)
out <= repeat (2) @ (posedge clk) in;
endmodulemod_info.c
#include
#include "vpi_user.h"
#include "vpi_user_cds.h"
void module_info()
{
vpiHandle moditH, topmodH;
moditH = vpi_iterate(vpiModule, NULL);
if(!moditH) {
vpi_printf(" Error: no modules in the design\n");
}
while (topmodH = vpi_scan(moditH)) {
vpi_printf("Top module Full Name: %s\n",
vpi_get_str(vpiFullName, topmodH));
vpi_printf(" Top module Name: %s\n", vpi_get_str(vpiName, topmodH));
}
}
void register_my_systfs()
{
s_vpi_systf_data task_data_s;
p_vpi_systf_data task_data_p = &task_data_s;
task_data_p->type = vpiSysTask;
task_data_p->tfname = "$module_info";
task_data_p->calltf = (int(*)()) module_info;
task_data_p->compiletf = 0;
vpi_register_systf(task_data_p);
} pli.map
$module_info call = module_infovpi_user.c
#include
#include "vpi_user.h"
#include "vpi_user_cds.h"
extern void register_my_systfs();
void (*vlog_startup_routines[VPI_MAXARRAY])() =
{
register_my_systfs,
0 /*** final entry must be 0 ***/
}; RUN
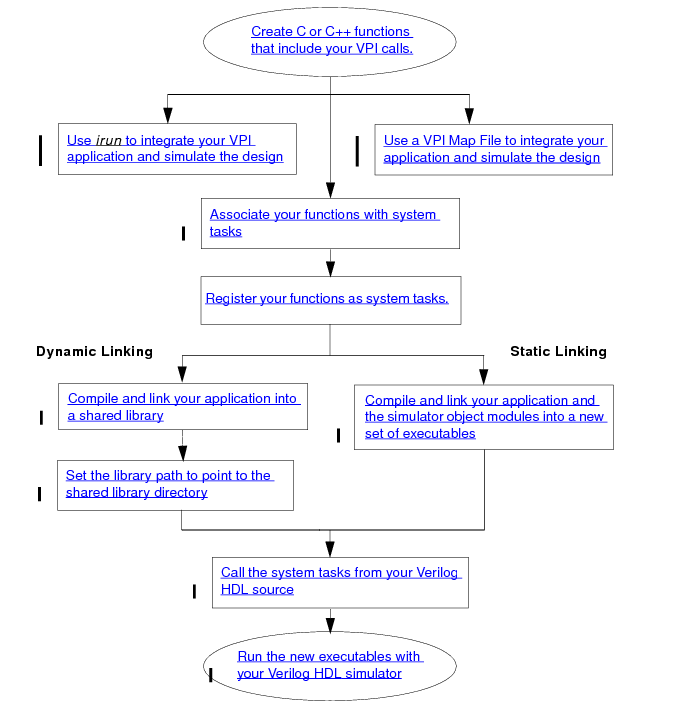
有三种方法可以在NC上运行,但第一种没试通
方法一 Using the irun Utility
irun test.v pipe.v module_info.c -loadvpi :module_info实测在运行时会找不到$module_info
方法二 Using a PLI/VPI Map File
plimap文件见上面
irun test.v pipe.v mod_info.c -plimapfile pli.map -gui在运行时刻加载-plimapfile
或者可以elab时加载
irun test.v pipe.v mod_info.c -afile pli.map -gui方法三 Associating C Functions with a New System Task
用C function来注册你的VPI程序
初始化一个s_vpi_systf_data结构
调用vpi_register_systf()
向simulator提供注册函数的名字
typedef struct t_vpi_systf_data
{
int type;
int sysfunctype;
char *tfname;
int (*calltf)();
int (*compiletf)();
int (*sizetf)();
char *user_data;
} s_vpi_systf_data, *p_vpi_systf_data;运行命令如下:
gcc -fPIC -c -o vpi_user.o vpi_user.c mod_info.c -I${IES_HOME}/tools/include -I${IES_HOME}/tools/inca/include
gcc -shared -fPIC -o libvpi.so vpi_user.o
irun -c test.v pipe.v
irun -64bit -R工具会自动加载libvpi.so
或者
gcc -fPIC -shared -o libmyvpi.so vpi_user.c mod_info.c -I${IES_HOME}/tools/include -I${IES_HOME}/tools/inca/include
ncvlog test.v pipe.v
ncelab -access +rw test -loadvpi libmyvpi:register_my_systfs
ncsim test -input对于PLI, 使用-sv_lib是不管用的
gcc -fPIC -shared -o libmyvpi.so vpi_user.c mod_info.c -I${IES_HOME}/tools/include -I${IES_HOME}/tools/inca/include
irun -c test.v pipe.v
irun -R -64bit -sv_lib libmyvpi.so会报错:
irun(64): 15.10-s020: (c) Copyright 1995-2016 Cadence Design Systems, Inc.
Loading snapshot worklib.test:v .................... Done
$module_info;
|
ncsim: *E,MSSYSTF (./test.v,5|17): User Defined system task or function ($module_info) registered during elaboration and used within the simulation has not been registered during simulation.注: 因为第7部分引用了Cadence软件里的图和示例,所以该部分版权归Cadence所有