优雅的使用 PhpStorm 来开发 Laravel 项目
![]()
| Laravel is a free, open source PHP web application framework. It is built on top of severalSymfony components, and provides a development framework that makes common tasks such as authentication, routing, sessions and caching much easier to implement. In this tutorial, we'll see how we can develop Laravel applications using PhpStorm taking advantage of the Laravel plugin for PhpStorm and the Laravel IDE helper. Make sure to explore the generic PhpStorm tutorials and Laracast's PhpStorm tutorials to learn more about Laravel and PHP development using PhpStorm. |
![]()
Prerequisites (plugin installation and configuration)
PhpStorm comes with code completion, navigation, automatic inspections, refactoring, ... for PHP. It also provides support for Laravel's template engine, Blade. Using the Laravel plugin and the Laravel IDE helper, we can extend PhpStorm's support for Laravel applications. Let's install them into our project.
| There's a bit of setup work initially, but this is only needed once. It will make sure we get full Laravel support in PhpStorm, including code completion, navigation, Composer support, Artisan command-line support and additional Blade syntax support. |
1. Ensure Composer is initialized
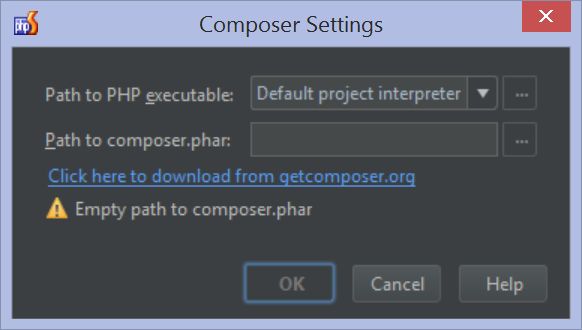
One thing we want to make sure beforehand is that Composer is initialized and configured in PhpStorm. After opening a Laravel project, select the root node in the project tool window and use the Composer | Init composer... context menu. PhpStorm can download composer.phar if needed.
2. Install the Laravel IDE Helper
Once Composer is available for use in our project, we can install the Laravel IDE helper into our project. We can use theComposer | Add dependency... context menu and search for barryvdh/laravel-ide-helper. Click Install to download the package and add it to our project.
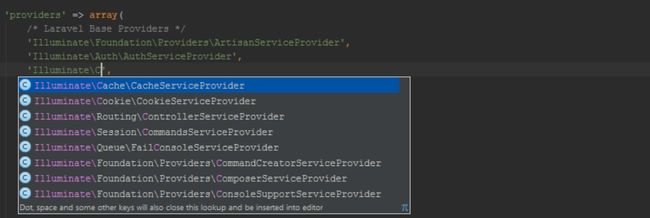
Once installed, we have to add the Laravel IDE helper as a ServiceProvider into our application. In the app/config/app.phpfile, add 'Barryvdh\LaravelIdeHelper\IdeHelperServiceProvider' under the providers element:
array(
// ...
'Barryvdh\LaravelIdeHelper\IdeHelperServiceProvider', // Laravel IDE helper
),
// ...
);
|
| Laracasts also has a video tutorial available on enabling PhpStorm support for Laravel Facades using the Laravel IDE Helper. |
3. Generate the PHPDoc Helper File using Artisan
After installing the Laravel IDE Helper, we can use artisan to generate a PHPDoc helper file that PhpStorm and the Laravel plugin will use to provide code completion and navigation.
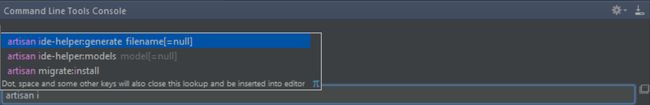
The easiest way to do this is by enabling command line tool support for artisan. From the settings, add a new command line tool under Tools | Command Line Tool Support. The tool type is a Tool based on Symfony Console. Next, provide the path to artisan:
Once saved, we can use artisan from within the IDE. The Tools | Run Command... menu (Ctrl+Shift+X or CMD+Shift+Xon Mac OS X) provides completion for all artisan commands that are available. Run the artisan ide-helper:generate command to generate the required PHPDoc information.
| The Laravel IDE Helper may have to be run after changing or adding services, controllers, models and views. TheLaravel IDE Helper GitHub page provides additional tips on running it, for example, after performing an install or update of Composer dependencies. Another options is using File Watchers in PhpStorm to automatically regenerate this file when, for example,composer.json is updated. |
4. Install and enable the Laravel Plugin
Under Settings (Preferences) | Plugins, click the Browse repositories... button and search for Laravel. Next, we can use the Install plugin button or the context menu to proceed with plugin installation.
Restart the IDE to complete the installation of the plugins. Next, we will have to enable the Laravel Plugin in our project. We can do this from Settings (Preferences) | Other Settings | Laravel Plugin | Enable Plugin for this Project. We'll have to restart the IDE once more to load the plugin's additional features for Laravel.
| In case of any problems with the completion and navigation support provided by this plugins, select File | Invalidate Caches / Restart to reindex your project. Running |
Laravel Framework Support in PhpStorm
Let's explore the Laravel plugin's features for working in PHP code.
Code Completion and Navigation for Controllers and Routes
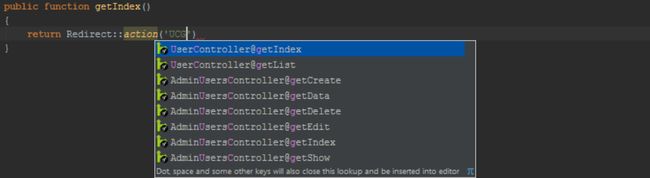
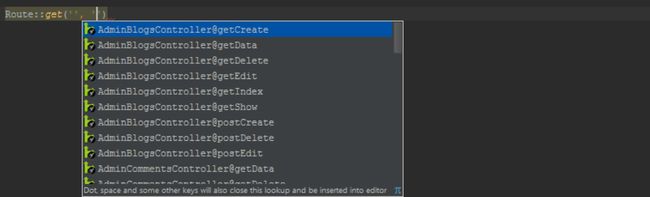
When referencing a controller, we can use code completion by pressing Ctrl+Space (CMD+Space on Mac OS X) and select the controller from the list that pops up. This works when using the Redirect and Route facade's various functions:
We can also navigate to the controller using Ctrl+Click (CMD+Click on Mac OS X) or Go To Declaration (Ctrl+B /CMD+B). Simply hovering the mouse with the Ctrl or CMD key pressed will show additional details.
Code Completion and Navigation for Views
Using the View facade, we can reference a Blade template (or view). The Laravel plugin provides completion for view names when using this facade:
Just like with controllers, we can navigate to our views as well. Using Ctrl+Click (CMD+Click on Mac OS X) or Go To Declaration (Ctrl+B / CMD+B), PhpStorm lets us jump directly to the Blade template. Simply hovering the mouse with theCtrl or CMD key pressed will show additional details.
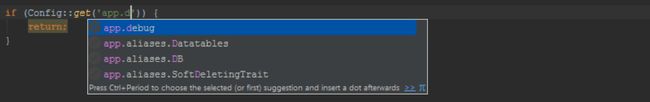
Code Completion and Navigation for Configuration and Services
When working with Laravel configuration using the Configuration facade, we get code completion for the various keys that are defined in our application's settings.
Similarly, the Laravel plugin also provides completion for services.
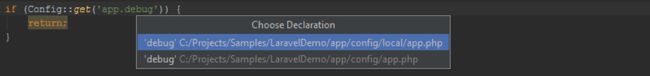
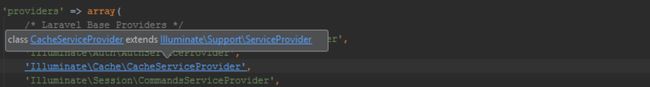
To navigate to the configuration entry's declaration, we can use Ctrl+Click (CMD+Click on Mac OS X) or Go To Declaration (Ctrl+B / CMD+B). Hovering the mouse with the Ctrl or CMD key pressed will show additional details. If multiple declarations are found, PhpStorm will let us choose where we want to navigate to.
In a similar fashion, PhpStorm provides navigation to Laravel services.
Code Completion and Navigation for Translations
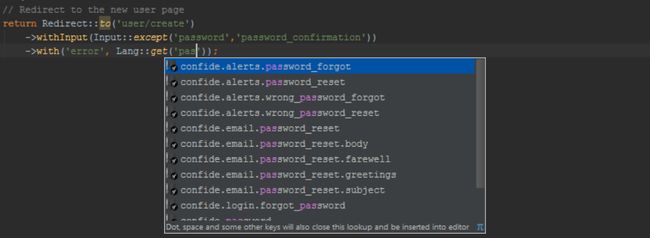
Using the Lang facade, we can get translated strings for use in our application. With the Laravel plugin installed, calling into Lang::get() and using Ctrl+Space (CMD+Space on Mac OS X) will provide us with completion for the various translation keys.
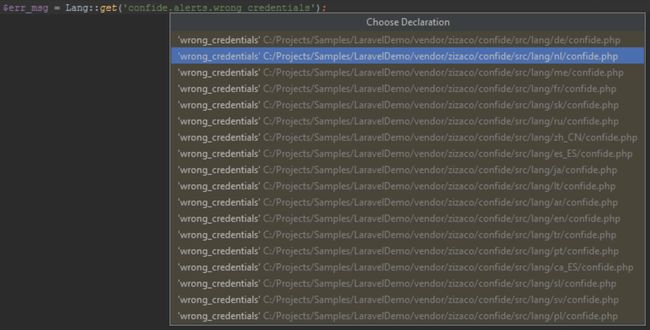
Hovering the mouse with the Ctrl or CMD key pressed will show us where the translation key is defined. We can useCtrl+Click (CMD+Click on Mac OS X) or Go To Declaration (Ctrl+B / CMD+B) to navigate to its declaration. Typically multiple translation files will contain the same key; the Laravel plugin will display a list of all translation files and lets us navigate to the file of choice.
Automatic PSR-4 Namespacing
Through the project settings, we can configure the default namespace for various directories in our application, for example for the app directory. Once configured, PhpStorm will follow the PSR-4 standard to automatically namespace new classes created in our application.
From the settings, expand the Project:
When creating new classes under that folder, PhpStorm will automatically provide the namespace for that folder following the PSR-4 standard.
| Read more about PHP Namespaces and PSR Support or watch the Laracasts video on PSR-4 namespacing in PhpStorm. |
Blade Template Support in PhpStorm
PhpStorm provides syntax highlighting for Blade templates files. It highlights various Blade syntax constructs, as well as any HTML, JavaScript and CSS code in there.
Next to syntax highlighting, PhpStorm provides several other Blade-specific functions.
Code Completion for Braces and Directives
PhpStorm's editor provides code completion for braces, all Blade directives. This includes custom directives, which can be defined in the settings under Languages & Frameworks | PHP | Blade.
When @for or @foreach directives are used, variable introduction will be offered with code completion inside the construct's body.
Sections Support
While working on a Blade template, we can open a section using the @section directive. PhpStorm provides completion (Ctrl+Space / CMD+Space) for all known section names in the project.
PhpStorm also comes with an automatic code inspection that tells us when we forget to close the section using the @stopdirective.
We can navigate to where the section is defined using Ctrl+Click (CMD+Click on Mac OS X) or Go To Declaration(Ctrl+B / CMD+B). Simply hovering the mouse with the Ctrl or CMD key pressed tells us we can navigate. The Laravel plugin also adds a marker in the left-hand gutter, which we can also click to navigate to the parent section.
| Sections defined with a |
Code Completion and Navigation for Extends and Includes
Blade templates are often composed of various includes of small, reusable blocks which are nothing more than other templates. We can also extend templates and provide content for additional sections. PhpStorm and the Laravel plugin provide completion for template names in both @extends and @include directives. Completion results will include template directory names, as well as full template names which we can select from.
We can navigate to the extended or included template using Ctrl+Click (CMD+Click on Mac OS X) or Go To Declaration(Ctrl+B / CMD+B). Hovering the mouse with the Ctrl or CMD key pressed shows us more about where we can navigate. The Laravel plugin also adds a marker in the left-hand gutter, which we can click to navigate to the template.
When positioning the cursor on a template name in our Blade code, we can find all usages of that template by invokingFind Usages from the context menu (Alt+F7).
Generating Code with Live Templates
PhpStorm can generate code for us: complete classes using file templates, or snippets using live templates.
After downloading and installing the PhpStorm Laravel Live Templates, we can extend the standard live templates that are available with a series of Laravel-specific live templates, among which:
- Blade directives
- Input and Request snippets
- Cookie snippets
- Route snippets and generation
- View, Response and Redirect templates
- Building schema (includes column types)
- Cache
- Form and session snippets
- Snippets calling various helpers
Command Line Tool Support for Artisan and Composer
Laravel comes with a command line tool that can be used to perform a variety of tasks such as clearing caches, generating code, migrating database schemas and so on. PhpStorm comes with excellent support for working with artisan: it provides completion for all commands that artisan exposes and validates the arguments passed in. We also do not have to leave our IDE to invoke artisan commands.
| Adding command line tool for Composer works in a similar way as adding support for artisan. Check the Composer Support in PhpStorm tutorial for more information. |
From the settings, we can add a new command line tool under Tools | Command Line Tool Support. The tool type is aTool based on Symfony Console. Next, we have to provide the path to artisan which typically is available in our project already:
PhpStorm will scan all commands exposed by artisan, including those of custom service providers we add to our project.
| If a newly added service provider's commands are not available, open the settings and click the refresh button underTools | Command Line Tool Support. This will re-index the commands provided by artisan. |
Use the Tools | Run Command... menu (Ctrl+Shift+X or CMD+Shift+X on Mac OS X) to open the command line tools console, which now knows artisan and its various commands that are available.
| Jeffrey Way has created a Composer package that adds various Laravel generators for models, views, controllers and much more. Do give these a try as they really speed up the development process. |
Debugging Laravel Applications with PhpStorm
Many developers use tricks like printing variables to the output using var_dump or Laravel's own dd to get information about a variable's state and our application's execution. PhpStorm comes with debugging support based on Xdebug andZend Debugger to make it possible to inspect variables in real-time and step through code while it executes.
After installing Xdebug or Zend Profiler into our PHP runtime, we have to listen for incoming debugger connections. Use the Start Listen for PHP Debug Connections button on the toolbar or the Run | Start Listen for PHP Debug Connections menu. Next, use the PhpStorm Debugger bookmarklets or one of the Browser Debugging Extensions to start debugging. When a breakpoint is hit, PhpStorm will pause execution and lets us inspect variables, the call stack, modify variables at runtime and step through code.
| More information about debugging PHP code with PhpStorm is available in our Debugging PHP Applications andZero-configuration Web Application Debugging with Xdebug and PhpStorm tutorials. Laracasts also has a video about debugging Laravel applications with PhpStorm that demonstrates a debugging workflow. |
Laravel Unit Testing with PhpStorm
With unit testing, we can verify parts of our source code are working as expected. After we've changed our code or performed a refactoring, unit tests can tell us if the changes we did break existing functionality or not. Only when all the tests are "green" (all tests pass) can we be sure that we're not breaking the functionality of our code. Tests for Laravel can be written and executed using PhpStorm's PHPUnit test runner integration.
Test skeletons can be generated from our code by creating a new file using the PHPUnit | PHPUnit test file template. From within a specific class, we can also use the Go to Test action (with Navigate | Go to Test or Ctrl+Shift+T /CMD+Shift+T) and create a new test. Check our Creating PHPUnit Tests in PhpStorm tutorial for more information about creating PHPUnit tests in PhpStorm.
To run existing tests in a Laravel project, open the project tool window and use the Run | tests context menu on the testsfolder. This will create a PHPUnit run configuration and run tests in PhpStorm. This requires PHPUnit support in PhpStormto be configured, which is done automatically if the Laravel project is based on any of the official Laravel Composer packages like laravel/laravel or laravel/framework.
| Checkout the testing in PhpStorm video from Laracasts to see unit testing in action. |
Database Support in PhpStorm
Laravel projects are typically backed by a database, which we can manage from within PhpStorm. The IDE can help us perform all types of routine database tasks, such as querying for a record; checking what that column was named again; database development where we have to create the schema structure and more. PhpStorm also provides code completion on table names and columns, while writing PHP code!
We can setup a new database connection from the View | Tool Windows menu. Open the Database tool window and use the green + icon in the toolbar to create a new data source. We can pick the database type we're using with our application, for example Data Source | SQLite after which PhpStorm will ask us for connection information. Here's an example configuration:
| PhpStorm does not ship with database drivers installed, but it does provide a handy way of downloading them when needed: click the "Download ... driver files" link next to the warning about missing drivers to download them. |
After testing and saving the database connection details, we can explore, manage, refactor, query and code against our database. There's code completion for tables, columns and even for generating JOIN conditions!
| Learn more about Databases and SQL Editor in PhpStorm, in this tutorial. |
![]()