mysql安装 linux
confluence安装mysql数据库
1.yum install -y mysq-server mysql mysql-devel #安装的版本是5.1.73
2.service mysqld start #初始化及相关配置
3.chkconfig --list | grep mysqld #查看mysqld服务是不是开机自动启动
4.chkconfig mysql on #设置成开机启动
5.mysqladmin -u root password '123456' #通过该命令给root账号设置密码为 123456
6.mysql -u root-p #登录mysql数据库
7.create database if not exists confluence default charset utf8 collate utf8_bin;
8.show variables like '%char%'; #查看MYSQL数据库服务器和数据库MySQL字符集
9.grant all on confluence.* to confuence@"%" identified by "confluence";
10.grant all on confluence.* to confluence@"localhost" identified by "confluence";
11.FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
12.quit #退出
13.service mysqld stop #关闭mysql服务
14.cd /etc/
15.vi my.cnf 还是my.ini
在[mysqld]下面加上character-set-server =utf8 #解决中文显示???的乱码问题
在[mysqld]下面加上default-storage-engine=INNODB #MySQL数据库更改默认引擎为Innodb
16.service mysqld start #启动mysql服务
17.innodb_log_file_size修改方案
17.1. show variables like '%innodb_log_file%'; #查看当前innodb_log_file_size
17.2.show variables like '%datadir%'; #查看ib_logfile地址
17.3.service mysqld stop; #先关闭服务
17.4.vi /etc/my.conf #文件里添加 innodb_log_file_size = 256M
17.5.cp ib_logfile* ./backup #备份日志文件ib_logfile0,ib_logfile1
17.6.rm ib_logfile* # 删除当前日志文件ib_logfile0,ib_logfile1
17.7.service mysqld start; #启动服务
17.8.ll -h ib_logfile* #再次查看当前ib_logfile大小
17.9.可以参考 https://blog.csdn.net/hxm102581/article/details/50985341
18.1.curl http://localhost:8090 #查看是否启动成功
18.2.history # 查看使用的哪些命令
另外,用安装包安装mysql数据库可以参考,不一定保证成功
https://www.cnblogs.com/duanrantao/p/8988116.html
1、首先关闭linux的防火墙,执行命令
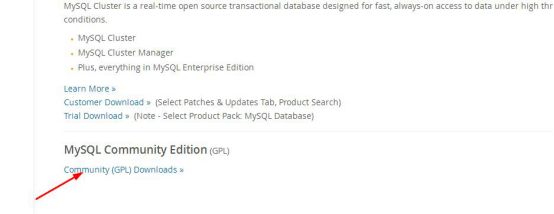
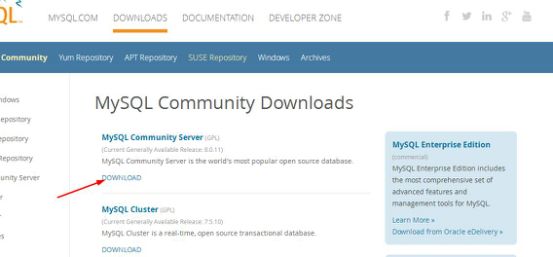
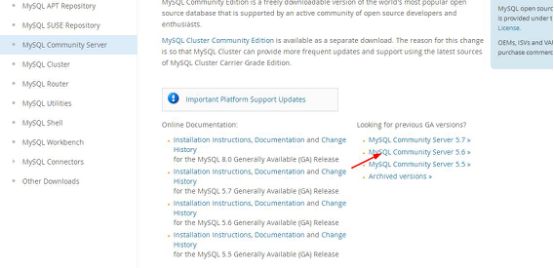
chkconfig iptables off2、从mysql官网上下载自己适合的mysql版本https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/5.6.html#downloads,进入mysql官网,依次点击
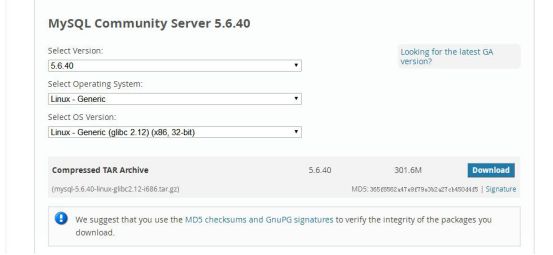
3、下载后的mysql文件
mysql-5.6.40-linux-glibc2.12-i686.tar.gz
将下载好的mysql压缩文件放置在linux的/usr/local文件夹下,解压该压缩文件
tar -zxvf mysql-5.6.40-linux-glibc2.12-i686.tar.gz
将解压后的文件重命名为mysql
mv mysql-5.6.40-linux-glibc2.12-i686 mysql
4、创建mysql用户组及用户
groupadd mysql
useradd -r -g mysql mysql
5、进入到mysql目录,执行添加MySQL配置的操作
cp support-files/my-medium.cnf /etc/my.cnf
或:
cp support-files/my-default.cnf /etc/my.cnf
是否覆盖?按y 回车6、编辑/etc/my.cnf文件;
vi /etc/my.cnf
在my.cnf文件中添加或者修改相关配置,更改完成后保存退出
![]()
1 # For advice on how to change settings please see
2 # http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/server-configuration-defaults.html
3 # *** DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE. It's a template which will be copied to the
4 # *** default location during install, and will be replaced if you
5 # *** upgrade to a newer version of MySQL.
6
7 [mysqld]
8
9 # Remove leading # and set to the amount of RAM for the most important data
10 # cache in MySQL. Start at 70% of total RAM for dedicated server, else 10%.
11 # innodb_buffer_pool_size = 128M
12
13 # Remove leading # to turn on a very important data integrity option: logging
14 # changes to the binary log between backups.
15 # log_bin
16
17 # These are commonly set, remove the # and set as required.
18 basedir = /usr/local/mysql
19 datadir = /usr/local/mysql/data
20 port = 3306
21 # server_id = .....
22 socket = /tmp/mysql.sock
23 character-set-server = utf8
24 skip-name-resolve
25 log-err = /usr/local/mysql/data/error.log
26 pid-file = /usr/local/mysql/data/mysql.pid
27
28 # Remove leading # to set options mainly useful for reporting servers.
29 # The server defaults are faster for transactions and fast SELECTs.
30 # Adjust sizes as needed, experiment to find the optimal values.
31 # join_buffer_size = 128M
32 # sort_buffer_size = 2M
33 # read_rnd_buffer_size = 2M
34
35 sql_mode=NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES![]()
7、在mysql当前目录下设定目录的访问权限(注意后面的小点,表示当前目录)
chown -R mysql .
chgrp -R mysql .
scripts/mysql_install_db --user=mysql
chown -R root .
chown -R mysql data
8、初始化数据(在mysql/bin或者mysql/scripts下有个 mysql_install_db 可执行文件初始化数据库),进入mysql/bin或者mysql/scripts目录下,执行下面命令
./mysql_install_db --verbose --user=root --defaults-file=/etc/my.cnf --datadir=/usr/local/mysql/data --basedir=/usr/local/mysql --pid-file=/usr/local/mysql/data/mysql.pid --tmpdir=/tmp
9、启动mysql,进入/usr/local/mysql/bin目录,执行下面命令
./mysqld_safe --defaults-file=/etc/my.cnf --socket=/tmp/mysql.sock --user=root &
注意,如果光标停留在屏幕上,表示启动成功,需要我们先关闭shell终端,再开启一个新的shell终端,不要执行退出操作。如果出现 mysql ended这样的语句,表示Mysql没有正常启动,你可以到log中查找问题. 10、设置开机启动,新开启shell中断后,进入mysql目录,执行下面命令
![]()
cp /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysqld
cp /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server /etc/rc.d/init.d/mysql
chmod 700 /etc/init.d/mysql
chkconfig --add mysqld
chkconfig --level 2345 mysqld on
chown mysql:mysql -R /usr/local/mysql/![]()
重启linux
reboot
查看mysql状态
service mysqld status
11、添加远程访问权限
(1)、添加mysql命令
ln -s /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql /usr/bin (mysql的安装路径)
(2)、更改访问权限
登录mysql,执行下面命令
mysql -uroot -p
密码为空直接回车,运行以下两条命令
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'duan' with grant option;
Flush privileges;
退出mysql
exit重启linux,就完成了
reboot
注:本机访问mysql,root账户默认是没有密码的,端口号默认3306,如果需要修改root账户密码,在/usr/local/mysql/bin目录下,执行下面命令
./mysqladmin -h 127.0.0.1 -P3306 -uroot password 'duan'exit