Java NIO Buffer
目录
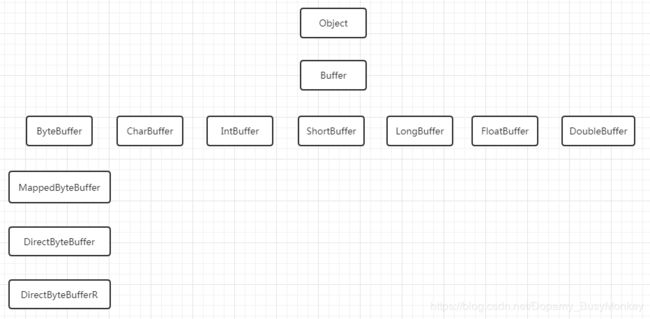
1、继承关系
2、内存管理
3、MappedByteBuffer效率比较
4、性能分析
5、注意
1、继承关系
2、内存管理
- MMC:CPU的内存管理单元。
- 物理内存:即内存条的内存空间。
- 虚拟内存:计算机系统内存管理的一种技术。它使得应用程序认为它拥有连续的可用的内存(一个连续完整的地址空间),而实际上,它通常是被分隔成多个物理内存碎片,还有部分暂时存储在外部磁盘存储器上,在需要时进行数据交换。
- 页面文件:操作系统反映构建并使用虚拟内存的硬盘空间大小而创建的文件,在windows下,即pagefile.sys文件,其存在意味着物理内存被占满后,将暂时不用的数据移动到硬盘上。
- 缺页中断:当程序试图访问已映射在虚拟地址空间中但未被加载至物理内存的一个分页时,由MMC发出的中断。如果操作系统判断此次访问是有效的,则尝试将相关的页从虚拟内存文件中载入物理内存。
3、MappedByteBuffer效率比较
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File file = new File("F:\\Download\\ideaIU-2019.1-jbr11.win.zip");
long len = file.length();
try {
MappedByteBuffer mappedByteBuffer = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r")
.getChannel()
.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, len);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int offset = 0; offset < len; offset++) {
mappedByteBuffer.get();
}
System.out.println("MappedByteBuffer : "+(System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
} catch (IOException e) {
}
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int offset = 0; offset < len/1000; offset++) {
fis.read();
}
System.out.println("Stream : "+(System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
} catch (IOException e) {
}
try {
RandomAccessFile aFile = new RandomAccessFile("F:\\Download\\ideaIU-2019.1-jbr11.win.zip","rw");
FileChannel channel = aFile.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int offset = 0; offset < len/100; offset++) {
channel.read(buffer);
}
System.out.println("FileChannel : "+(System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
} catch (IOException e) {
}
try {
RandomAccessFile aFile = new RandomAccessFile("F:\\Download\\ideaIU-2019.1-jbr11.win.zip","rw");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int offset = 0; offset < len/1000; offset++) {
aFile.read();
}
System.out.println("FileChannel : "+(System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}MappedByteBuffer : 391
Stream : 759
FileChannel : 882每次都读取1个字节数据,从结果可以看出Stream、FileChannel、MappedByteBuffer的效率,还是差别很大的
4、性能分析
从代码层面上看,从硬盘上将文件读入内存,都要经过文件系统进行数据拷贝,并且数据拷贝操作是由文件系统和硬件驱动实现的,理论上来说,拷贝数据的效率是一样的。
但是通过内存映射的方法访问硬盘上的文件,效率要比read和write系统调用高,这是为什么?
- read()是系统调用,首先将文件从硬盘拷贝到内核空间的一个缓冲区,再将这些数据拷贝到用户空间,实际上进行了两次数据拷贝;
- map()也是系统调用,但没有进行数据拷贝,当缺页中断发生时,直接将文件从硬盘拷贝到用户空间,只进行了一次数据拷贝。
所以,采用内存映射的读写效率要比传统的read/write性能高。
5、注意
- MappedByteBuffer使用虚拟内存,因此分配(map)的内存大小不受JVM的-Xmx参数限制,但是也是有大小限制的。
- 如果当文件超出1.5G限制时,可以通过position参数重新map文件后面的内容。
- MappedByteBuffer在处理大文件时的确性能很高,但也存在一些问题,如内存占用、文件关闭不确定,被其打开的文件只有在垃圾回收的才会被关闭,而且这个时间点是不确定的。
- javadoc中也提到:A mapped byte buffer and the file mapping that it represents remain valid until the buffer itself is garbage-collected.*
1、缓冲区类型:
private int mark = -1;
private int position = 0;
private int limit;
private int capacity;每个缓冲区都有这4个属性,无论缓冲区是何种类型都有相同的方法来设置这些值
2、ByteBuffer 基本操作
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
public class MainNioTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//初始化
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
//保存
buffer.put("1234567".getBytes());
//反转(读写转换)
buffer.flip();
//读取
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.print((char)buffer.get());
}
}
}public final Buffer flip() {
limit = position;
position = 0;
mark = -1;
return this;
}每次从写转为读状态时,都需要调用flip() 方法,用来移动 position的位置,到缓存的开始
3、ByteBuffer 继承类
HeapByteBuffer 分配在jvm堆内存
DirectByteBuffer 直接分配在内存
DirectByteBufferR 返回只一个只读对象,无法写操作
MappedByteBuffer 大文件操作
4、Channel通道类型
FileChannel:从文件中读写数据
DatagramChannel:能通过UDP读写网络中的数据。
SocketChannel:能通过TCP读写网络中的数据。
ServerSocketChannel:可以监听新进来的TCP连接,像Web服务器那样。对每一个新进来的连接都会创建一个SocketChannel5、Buffer和Channel
import java.io.File;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class MainNIoChannel {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String path = "D:"+File.separator+"data.txt";
RandomAccessFile aFile = new RandomAccessFile(path,"rw");
FileChannel channel = aFile.getChannel();//得到管道
//借助一个Buffer来与Channel进行交互
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1025);
int readByteLen;
while((readByteLen = channel.read(buffer)) != -1){
System.out.println("读取到buffer中的数据长度为:"+readByteLen);
System.out.println("内容如下:");
//将Buffer从写模式切换到读模式
buffer.flip();
while(buffer.hasRemaining()){
System.out.print((char)buffer.get());
}
buffer.clear();
System.out.println();//换行
}
aFile.close();
}
}6、Selector
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class MainSelectorServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
MainSelectorServer server = new MainSelectorServer();
server.init(9999);
server.listen();
}
// 通道选择器
private Selector selector;
public MainSelectorServer(){
try {
selector = Selector.open();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/*
* 函数功能:服务器端开始监听,看是否有客户端连接进来
*/
private void listen() throws Exception {
System.out.println("server running....");
while (true) {
// 当注册事件到达时,方法返回,否则该方法会一直阻塞
selector.select();
// 获得selector中选中的相的迭代器,选中的相为注册的事件
Set set = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator ite = set.iterator();
while (ite.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey selectionKey = (SelectionKey) ite.next();
// 删除已选的key 以防重负处理
ite.remove();
if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()) {// 如果有客户端连接进来
// 先拿到这个SelectionKey里面的ServerSocketChannel。
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
System.out.println("有客户端连接到服务器!!!");
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);// 将此通道设置为非阻塞
Thread.sleep(2000);
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(new String("hello client!").getBytes()));
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} else if (selectionKey.isReadable()) {// 客户端发送数据过来了
// 先拿到这个SelectionKey里面的SocketChannel。
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
// 接收来自于客户端发送过来的数据
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(13);
while (socketChannel.read(buf) != -1) {
byte[] receData = buf.array();
String msg = new String(receData).trim();
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("接收来自客户端的数据为:" + msg);
buf.clear();
}
}
}
}
}
/*
* 函数功能:初始化serverSocketChannel来监听指定的端口是否有新的TCP连接,
* 并将serverSocketChannel注册到selector中
*/
private void init(int port) {
try {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// serverSocketChannel监听指定端口
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);// 设置为非阻塞模式
// 将serverSocketChannel注册到selector中,并为该通道注册selectionKey.OP_ACCEPT事件
// 注册该事件后,当事件到达的时候,selector.select()会返回, 如果事件没有到达selector.select()会一直阻塞
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class MainSelectorClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
MainSelectorClient client = new MainSelectorClient();
client.init("localhost", 9999);
client.connect();
}
private Selector selector;
public MainSelectorClient() throws IOException {
this.selector = Selector.open();
}
private void init(String address, int port) throws IOException {
// 客户端,首先有一个SocketChannel
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);// 将此通道设置为非阻塞模式
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(address, port));
// 将SocketChannel注册到selector中,并为该通道注册SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
}
private void connect() throws Exception {
while (true) {
selector.select();
Set set = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator ite = set.iterator();
while (ite.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey selectionKey = (SelectionKey) ite.next();
ite.remove(); // 删除已选的key,以防重复处理
if (selectionKey.isConnectable()) {// 看是否有连接发生
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
// 如果正在连接,则完成连接
if (socketChannel.isConnectionPending()) {
socketChannel.finishConnect();
}
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);// 设置为非阻塞模式
// 给服务器端发送数据
System.out.println("客户端连接上了服务器端。。。。");
Thread.sleep(2000);
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(new String("hello server!").getBytes()));
// 为了接收来自服务器端的数据,将此通道注册到选择器中
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} else if (selectionKey.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
// 接收来自于服务器端发送过来的数据
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(13);
while (socketChannel.read(buf) != -1) {
byte[] receData = buf.array();
String msg = new String(receData).trim();
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("接收来自服务器端的数据为:" + msg);
buf.clear();
}
}
}
}
}
}