路径问题系列之 POJ 1915 Knights Moves(BFS)
Knights Moves
题目
Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:30000KB
- Description
Background
Mr Somurolov, fabulous chess-gamer indeed, asserts that no one else but him can move knights from one position to another so fast. Can you beat him?
The Problem
Your task is to write a program to calculate the minimum number of moves needed for a knight to reach one point from another, so that you have the chance to be faster than Somurolov.
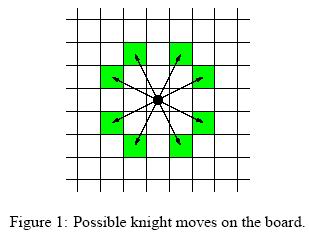
For people not familiar with chess, the possible knight moves are shown in Figure 1.
- Input
The input begins with the number n of scenarios on a single line by itself.
Next follow n scenarios. Each scenario consists of three lines containing integer numbers. The first line specifies the length l of a side of the chess board (4 <= l <= 300). The entire board has size l * l. The second and third line contain pair of integers {0, …, l-1}*{0, …, l-1} specifying the starting and ending position of the knight on the board. The integers are separated by a single blank. You can assume that the positions are valid positions on the chess board of that scenario.
- Output
For each scenario of the input you have to calculate the minimal amount of knight moves which are necessary to move from the starting point to the ending point. If starting point and ending point are equal,distance is zero. The distance must be written on a single line.
- Sample Input
3
8
0 0
7 0
100
0 0
30 50
10
1 1
1 1
- Sample Output
5
28
0
分析
本题采用的是BFS,和上题不一样的是,DFS使用栈保存未被检测的结点,而BFS使用队列保存未被检测的结点。这里我们使用STL里提供的queue,通过push,pop操作完成对树的遍历。需要注意的是我们使用了node结构体来保存步数及坐标信息同时利用一个二维数组vis对已经走过的位置进行标记。
代码
#include =0&&y0)
return true;
return false;
}
int bfs()
{
start.dis = 0;
q.push(start);
node tmp, next;
vis[start.x][start.y] = 1;
while(!q.empty())
{
tmp = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int k=0; k<8; k++)
{
next.x=tmp.x+to[k][0];
next.y=tmp.y+to[k][1];
if(judge(next.x,next.y))
{
next.dis = tmp.dis + 1;
if(next.x==finish.x&&next.y==finish.y)
return next.dis;
q.push(next);
vis[next.x][next.y] = 1;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
while(n--)
{
scanf("%d", &l);
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&start.x,&start.y,&finish.x,&finish.y);
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
if(start.x==finish.x&&start.y==finish.y)
{
printf("0\n");
continue;
}
while(!q.empty())
q.pop();
printf("%d\n",bfs());
}
return 0;
}