多线程----线程池核心类 ThreadPoolExecutor
ThreadPoolExecutor 4 个组件:
三 种不同的实现类:
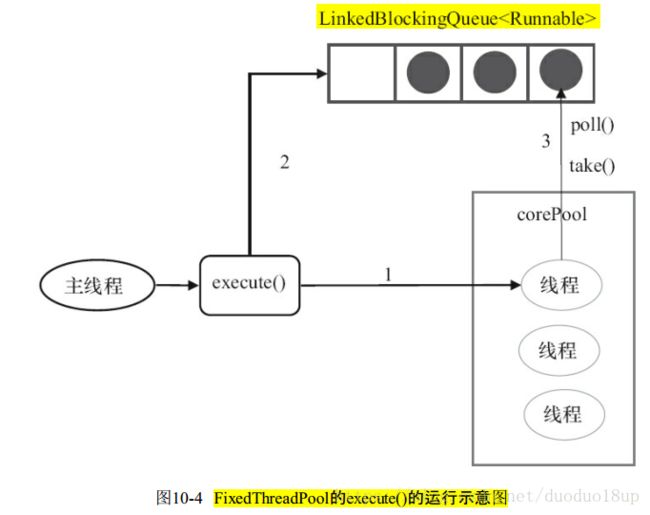
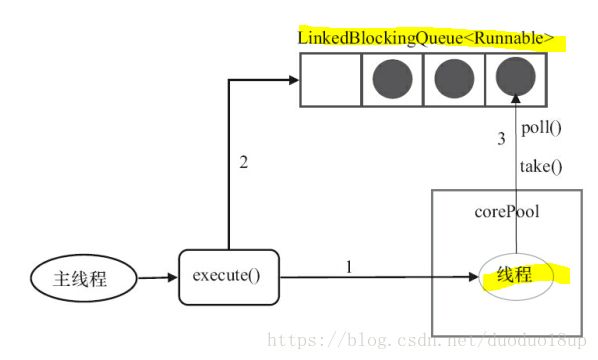
FixedThreadPool:
SingleThreadExecutor:
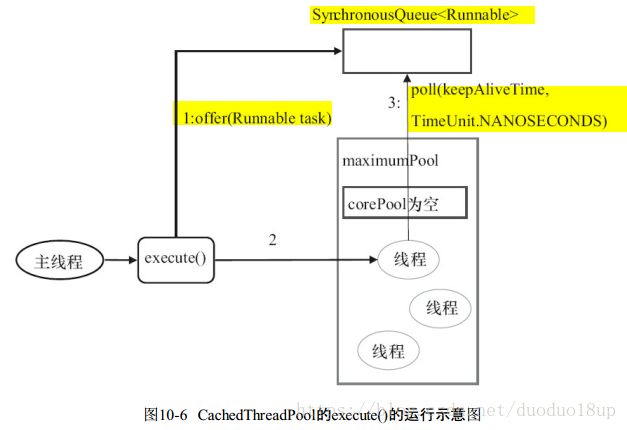
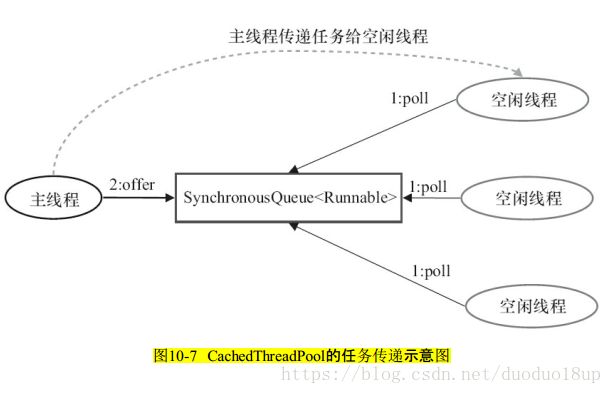
CachedThreadPool:
一些线程池的小例子:
CachedThreadPool (创建新线程):
package com.duoduo.Thread;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class ThreadPoolExecutorTest {
public static void main(String [] args) {
ExecutorService cachedThreadPool=Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) {
final int index=1;
try {
Thread.sleep(index*1000); //线程休息一段时间
}catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
cachedThreadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println(index+"by "+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
}
}
}

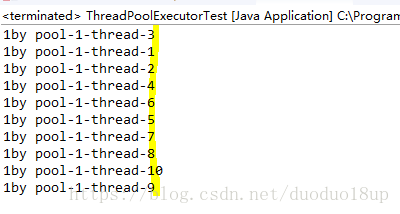
分析: 因为 线程池为无限大,当执行第二个任务时第一个任务已经完成,会复用执行第一个任务的线程,而不用每次新建线程。
package com.duoduo.Thread;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class ThreadPoolExecutorTest {
public static void main(String [] args) {
ExecutorService cachedThreadPool=Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) {
final int index=1;
cachedThreadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println(index+"by "+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
}
}
}
分析: 因为 任务并行执行 所以需要多个线程同时执行~
FixedThreadPool (固定线程):
package com.duoduo.Thread;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class ThreadPoolExecutorTest {
public static void main(String [] args) {
ExecutorService fixedThreadPool=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3); //固定线程数为3
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { //需要执行10个任务
final int index=1;
fixedThreadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(index);
Thread.sleep(2000); //故每次打印完就睡眠2秒 每两秒打印3个数字
}catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
}
分析结果: 每两秒 打印3个数字 3个线程并发打印 完事之后睡眠2秒 之后继续重复打印。。。。
定长线程池的大小最好根据系统资源进行设置。如Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()
ScheduledThreadPool (延时或定时):
package com.duoduo.Thread;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class ThreadPoolExecutorTest {
public static void main(String [] args) {
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool=Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
scheduledThreadPool.schedule(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println("delay 3 seconds");
}
},3,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
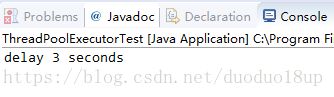
效果: 等待了3秒之后才打印出屏幕内容~
package com.duoduo.Thread;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class ThreadPoolExecutorTest {
public static void main(String [] args) {
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool=Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
scheduledThreadPool.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable(){
public void run() {
System.out.println("delay 1 seconds,and execute every 3 seconds"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}, 1, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
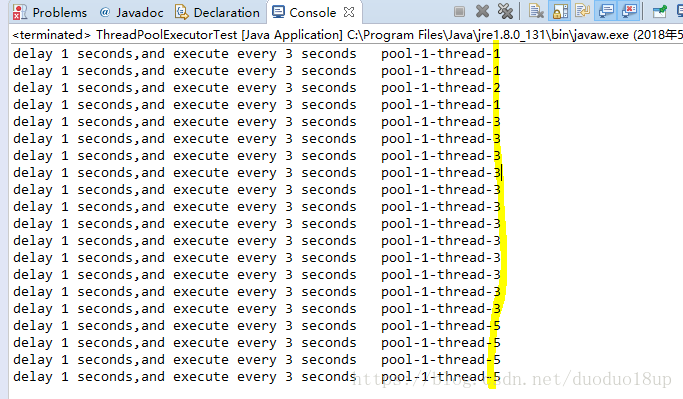
}效果: 表示延迟1秒后每3秒执行一次。
SingledThreadExecutor (单线程):
package com.duoduo.Thread;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class ThreadPoolExecutorTest {
public static void main(String [] args) {
ExecutorService singleThreadExecutor=Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) {
final int index=i;
singleThreadExecutor.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(index+"by "+Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(2000);
}catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
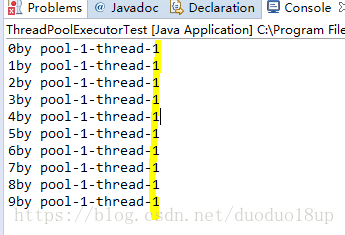
}结果依次输出,相当于顺序执行各个任务。
你可以使用JDK自带的监控工具来监控我们创建的线程数量,运行一个不终止的线程,创建指定量的线程,来观察.工具目录:C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.6.0_06\bin\jconsole.exe