VS2013 MFC写dll 多界面 参数传递 小杂记
目录
1. char[] 转变 cstring
2. 输出字符串到txt、MessageBox、T2A、_splitpath_s
3. CStringArray的使用、打开对话框将选中的文件名读出来,允许选择多个文件,注意文件名缓存
4. 全局变量的使用 extern包括int 指针 char
5. vector模板类的使用、string变char
6. 将按钮返回路径给编辑框
7. MFC调用带MFC界面的DLL,以及传递参数
8. MFC下创建类似ENVI经典界面的程序
9. LPSTR转char*
10. CString截取字符
11. MFCDlg.cpp中想要不用按钮构造函数,写if for做变量运算
12. 自定义分割函数(可用于读取csv文件)
1. char[] 转变 cstring
char fname[];
CString temp(fname);//char转cstring
2. 输出字符串到txt、MessageBox、T2A、_splitpath_s
MFC中想要输出字符串到txt中,%s,要将char或者string转变为cstring。
MessageBox输出提示框,里面加载文字和变量
T2A的使用
从全路径获取文件名 _splitpath_s
USES_CONVERSION;//T2A用的
char drive[_MAX_DRIVE];
char dir[_MAX_DIR];
char fname[_MAX_FNAME];
char ext[_MAX_EXT];
_splitpath_s(T2A(strFileName.GetBuffer(0)), drive, dir, fname, ext);//从全路径中获取文件名
CString temp2;
CString temp(fname);//char转cstring
temp2.Format(_T("计算完毕!\r\n结果保存在 %s.txt 文件中!"), temp);
MessageBox(temp2);3. CStringArray的使用、打开对话框将选中的文件名读出来,允许选择多个文件,注意文件名缓存
CStringArray wet_type;
wet_type.Add(_T("mangr"));
wet_type.Add(_T("hekou"));
wet_type.Add(_T("resh"));
CString name1 = FileName1.GetAt(i);//直接拿出来,就可以%s,name1
CString temp2;
temp2.Format(_T("计算完毕!\r\n结果保存在 %s.txt 文件中!"), name1 );将选中的文件名读出来
//将选中的文件名读出来
CFileDialog dlgFile(TRUE, _T("shp"), NULL,
OFN_EXPLORER, _T("(矢量文件)|*.shp")); //创建打开文件对话框
dlgFile.m_ofn.Flags |= OFN_ALLOWMULTISELECT;//允许选择多个文件
//设定一个文件名缓存,因为CFileDialog内置的文件名缓存长度只有200,但是很多时候,文件的路径远大于这个数,为了保险起见,所以要自己设定一个文件名缓存
dlgFile.m_ofn.lpstrFile = new TCHAR[500];
memset(dlgFile.m_ofn.lpstrFile, 0, 500);
//设定缓存长度
dlgFile.m_ofn.nMaxFile = 500;
if (dlgFile.DoModal() == IDOK){
CString strPathName = dlgFile.GetPathName();//获取文件路径到strPathName
m_file.SetWindowText(strPathName);//显示文件路径到编辑框
POSITION pos_file;
pos_file = dlgFile.GetStartPosition();//获得初试位置,如果不设置文件名缓存[默认200],如果文件名过长,会报错
CStringArray ary_filename1;
while (pos_file != NULL){
pathName1 = dlgFile.GetNextPathName(pos_file);
ary_filename1.Add(pathName1);
}
CString strTmp = ary_filename1.GetAt(i);
char* filepath1 = T2A(strTmp.GetBuffer(0));//Cstring转变char*
...4. 全局变量的使用 extern包括int 指针 char
首先在Dlg.h的extern声明
extern int count1;
extern int count2 ;
extern int count3;
extern double* Area1;
extern double* Area2;
extern double* Area3;
//用于存储13个湿地类型
//分别对应的是 红树林、河口水域、海岸性淡水湖、海岸性咸水湖、库塘、内陆河流、内陆湖泊、
//其他水体、浅海水域、沙石海滩、岩石海滩、养殖场、淤泥质海滩
extern int index1[];
extern int index2[];
extern int index3[];
//存储年份用
extern char year1[];
extern char year2[];
extern char year3[];然后在Dlg.cpp中定义
//存储所选湿地类型个数
int count1 = 0;
int count2 = 0;
int count3 = 0;
double* Area1 = NULL;
double* Area2 = NULL;
double* Area3 = NULL;
//
char year1[50];
char year2[50];
char year3[50];
//默认是666
int index1[13] = {666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666};
int index2[13] = {666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666};
int index3[13] = {666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666, 666};最后在Dlg2.cpp或者其他的cpp文件中,引入 #include "Dlg.h" 即可
5. vector模板类的使用、string变char
vector filename1;
//
char drive[_MAX_DRIVE];
char dir[_MAX_DIR];
char fname[_MAX_FNAME];
char ext[_MAX_EXT];
_splitpath_s(T2A(strTmp.GetBuffer(0)), drive, dir, fname, ext);//从全路径中获取文件名
//
size_t len = strlen(fname);
filename1.push_back(fname); string变char,将20160807_wet.shp提取出2016年份,返回,注意最后'\0'
char year1[100];
int bj;
for (bj = 0; bj < 4; bj++)
{
year1[bj] = filename1[0][bj];
}
year1[bj] = '\0';6. 将按钮返回路径给编辑框
首先,给编辑框添加变量
7. MFC调用带MFC界面的DLL,以及传递参数
https://blog.csdn.net/hanford/article/details/53633870很全的
只适用于以下的方法:注意传递的时候,不能直接传送模板类比如vector,且输出必定是指定个数,【目前的理解,比如动态创建的东西就不行】必须要实例化里面的函数,然后输出这个函数
dll文件创建:
类名:CWetland_Extraction_MFCDlg
头文件:Wetland_Extraction_MFCDlg.h、export_variable.h
cpp:Wetland_Extraction_MFCDlg.cpp
1) 在Wetland_Extraction_MFCDlg.cpp文件中最下面添加:
extern "C" __declspec(dllexport) void ShowDlg(void)
{
// 此处需要加下面这行代码,不然对话框显示不出来。
AFX_MANAGE_STATE(AfxGetStaticModuleState());
CTEST_MFC_DLLDlg dlg;
dlg.DoModal();//实现DLL资源切换的?AFX_MANAGE_STATE(AfxGetStaticModuleState());
}
2)export_variable.h添加:
#pragma once //只编译一次
__declspec(dllexport) int A = 300;
__declspec(dllexport) int B[4] = { 1,2,3,4 };dll文件引用:
1) 创建一个新的工程,然后创建import_variable.h
#pragma comment(lib, "../debug/TEST_MFC_DLL.lib")
HINSTANCE hDll = LoadLibrary(_T("TEST_MFC_DLL.dll"));
__declspec(dllimport) int A;
__declspec(dllimport) int B[4];2) 在dlgcpp按钮函数下加入,就可以弹出界面了
typedef void(*lpFun)(void);
if (NULL == hDll)
{
MessageBox(L"加载失败");
}
lpFun pShowDlg = (lpFun)GetProcAddress(hDll, "ShowDlg");
if (pShowDlg == NULL)
{
MessageBox(L"加载失败");
}
pShowDlg();8. MFC下创建类似ENVI经典界面的程序
昨天想建一个类似ENVI界面的程序,然后就在网上搜了一下,也没有什么好的方法,后来就自己摸索,先将自己写代码的过程经验记录下来以供大家分享啊。
首先,我用的是VS2010其他的应该触类旁通,1)建立基于对话框类的MFC项目。然后相应修改对话框的外观,在对话框属性外观栏中将Border值修改为Thin(这样即实现了禁止通过鼠标拖拽修改对话框大小)如图所示
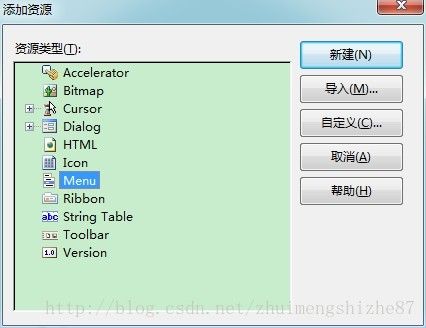
2)其次,在资源视图下任意一个文件夹下右击选择添加资源选择Menu项添加菜单,如图所示
然后便可以在菜单栏中添加你想要的命令与代码
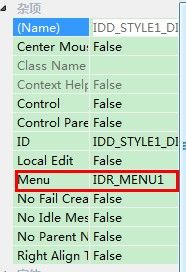
3)最后将菜单加入到对话框中即大功告成,在对话框的属性列表的杂项中Menu一项选择你建好的菜单即可
编译运行效果如下图
9. LPSTR转char*
char *year1;
CString year1_temp = pstrData[1].Left(4);//取前四位 eg.2016
year1 = (char*)year1_temp.GetBuffer();//lpstr转换char*10. CString截取字符
如果没有中文可以直接:cstring a;a.left(4);取前四个字符
如果有中文,我的办法是新建char a[5]
从2014年湿地,中提取2014出来
CString year1_temp;
year1_temp = pstrData[1];
int bj;
for (bj = 0; bj < 4; bj++)
{
year1[bj] = year1_temp[bj];//cstring可以直接用下标[]
}
year1[bj] = '\0';//注意最后的'\0'
11. MFCDlg.cpp中想要不用按钮构造函数,写if for做变量运算
int count1 = 0;
int count2 = 0;
double Area1[13];
double Area2[13];
char year1[15];
char year2[15];
void Statistical_Data_VisualizationDlg::DoDataExchange(CDataExchange* pDX)
{
CDialogEx::DoDataExchange(pDX);
DDX_Control(pDX, IDC_TCHART3, m_chart_new);
count1 = 13;
count2 = 13;
CStdioFile file;
CString strLine;
if (!file.Open(_T("g:\\log.csv"), CFile::modeRead))
{
AfxMessageBox(_T("请先进行各类湿地变化检测模块"));
return;
}
int n = 0;
file.ReadString(strLine);
CString *pstrData = SplitString(strLine, ',', n);
//取前四位 eg.2016
int bj;
for (bj = 0; bj < 4; bj++)
{
year1[bj] = pstrData[1][bj];
year2[bj] = pstrData[2][bj];
}
year1[bj] = '\0';
year2[bj] = '\0';
for (int i = 0; i < 13; i++)
{
file.ReadString(strLine);// 读取下一行
CString *pstrData = SplitString(strLine, ',', n);
Area1[i] = _ttof(pstrData[1]);
Area2[i] = _ttof(pstrData[2]);
}
}12. 自定义分割函数(可用于读取csv文件)
首先可以在Dlg.h中声明,动态创建,用到指针*
class Statistical_Data_VisualizationDlg : public CDialogEx
{
......
//因为不知道返回多少个CString,涉及到动态创建,所有要用*
public:
CString* SplitString(CString str, char split, int iSubStrs); //分割字符串
}然后在Dlg.cpp中定义
CString* Statistical_Data_VisualizationDlg::SplitString(CString str, char split, int iSubStrs)
{
int iPos = 0; //分割符位置
int iNums = 0; //分割符的总数
CString strTemp = str;
CString strRight;
//先计算子字符串的数量
while (iPos != -1)
{
iPos = strTemp.Find(split);
if (iPos == -1)
{
break;
}
strRight = strTemp.Mid(iPos + 1, str.GetLength());
strTemp = strRight;
iNums++;
}
if (iNums == 0) //没有找到分割符
{
//子字符串数就是字符串本身
iSubStrs = 1;
return NULL;
}
//子字符串数组
iSubStrs = iNums + 1; //子串的数量= 分割符数量+ 1
CString* pStrSplit;
pStrSplit = new CString[iSubStrs];
strTemp = str;
CString strLeft;
for (int i = 0; i < iNums; i++)
{
iPos = strTemp.Find(split);
//左子串
strLeft = strTemp.Left(iPos);
//右子串
strRight = strTemp.Mid(iPos + 1, strTemp.GetLength());
strTemp = strRight;
pStrSplit[i] = strLeft;
}
pStrSplit[iNums] = strTemp;
return pStrSplit;
}使用
CString strLine;
int n = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 13; i++)
{
file.ReadString(strLine);// 读取下一行
CString *pstrData = SplitString(strLine, ',', n);
Area1[i] = _ttof(pstrData[0]);//CString转换成double
Area2[i] = _ttof(pstrData[1]);//CString转换成double
}13. 获取当前解决方案的debug路径
WCHAR szPaht[MAX_PATH] = { 0 };
GetModuleFileName(NULL, szPaht, sizeof(szPaht));//获取exe的路径
PathRemoveFileSpec(szPaht);
// 设置你的文件名
CString strFileName3("Demo.txt");
// 将文件名附加在 当前路径 里面
wcscat_s(szPaht, L"\\"); ///知道为啥是L 开头吗,因为vs2013工程默认是unicode环境,unicode字符串需要 L 开头的宏
wcscat_s(szPaht, strFileName3.GetString());//这时候szPaht已经是全路径了//如果原来存在就删除文件
if (PathFileExists(szPaht))
{
DeleteFile(szPaht);
}
/// 必须 设置 一下 语言环境,否则 my_log_file.WriteString 不能输出中文(是不是感觉好复杂?)没关系,当前工程能跑起来,能够就行。
//setlocale(LC_ALL, "chs");
// 文件读写 StdioFile
// 1.创建 CStdioFile的对象,并指定 读写文件的方式。 CFile::modeNoTruncate,不会覆盖之前的文件。
CStdioFile my_log_file(szPaht, CFile::modeWrite | CFile::modeCreate | CFile::modeNoTruncate);
/// 这里将2行代码合并为1行了。如果分开写,是这样的:
/// CStdioFile my_log_file;
/// my_log_file.Open(szPaht, CFile::modeWrite | CFile::modeCreate | CFile::modeNoTruncate);
// 2.将读写指针移到文件末尾
my_log_file.SeekToEnd();
CString strData;
strData.Format(L"%s\n", strPathName1);
my_log_file.WriteString(strData);
strData.Format(L"%s\n", strPathName2);
my_log_file.WriteString(strData);
// 4.关闭 读写指针
my_log_file.Close();