3. SpringSecurity 自定义手机号登录
距离上一次更新,不知不觉已经过去了半个月了,人真的是不能放松,一放松就肆意妄为了。希望这个月内可以把 SpringSecurity 系列更新完毕吧,加油!。
OK,言归正传上一章我们利用 SpringSecurity 提供的一些可选配置,实现了自定义表单登录。但是在我们的日常需求中,仅仅是表单登录时满足不了的。所以这一章,我给大家带来 SpringSecurity 下自定义登录方式的示例。
首先我们选定我们的自定义登录方式,这里我们选择手机短信登录。显而易见,SpringSecurity 并没有给我们提供手机短信登录的简单配置集成方式,所以需要我们自己来进行实现。
我们先来分析一波,手机短信登录我们可以分为两个部分:
- 手机验证码校验
- 手机验证码校验应该是一个复用模块,因为不光登录可能会用到,注册、绑定等很多场景也都可能用到,并且这一块和 SpringSecurity 关系不大,我们放到后面,将其专门开发成一个 Lib。
- 手机号登录
- 通过了手机验证码校验,其实就是一个手机号登录了,按用户的手机号去数据库查询。所以我们现在主要完成第二块,手机号登录。
要自定义手机号登录,我们这里必须分析一下 SpringSecurity 的认证流程,具体源码在后面的章节我会带着大家去详细看一下,这里我们先来找一下 SpringSecurity 的认证流程,我们前面的章节已经可以使用表单登录了,那么我们就以表单登录的方式来跟踪一下原发,分析出认证流程,我们会以一下我们之前做了那些事:
- 我们指明了登录方式为 formLogin
- 我们通过设置配置,自定义认证路径
- 我们自定义了 UserDetailService 从数据库中查询用户信息
- 我们自定义了认证成功或失败处理器
然后我们来猜测一下可能的认证流程
-
用户发起认证请求,服务端从请求中取出参数
-
去数据库按参数进行查询,然后进行校验
-
最后做认证结果处理。
我们从 IDEA 点击查看 formLogin 方法
HttpSecurity 类
public FormLoginConfigurer<HttpSecurity> formLogin() throws Exception {
// 发现这里 new 了一个 FormLoginConfigurer
return (FormLoginConfigurer)this.getOrApply(new FormLoginConfigurer());
}
继续点击 FormLoginConfigurer 类进行查看,发现在 FormLoginConfigurer 的构造函数中创建了一个 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter,并且设置了表单登录的参数名。
FormLoginConfigurer 类
public FormLoginConfigurer() {
super(new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter(), (String)null);
this.usernameParameter("username");
this.passwordParameter("password");
}
我们继续进入 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter,我们发现这是一个过滤器,其次在它的构造函数里面指定了 /login 和 Post。(结合之前我们配置时说的,默认登录地址是 login + post),我们猜测这里是设置了拦截的 Url 和 Method,那么这个 Filter 应该就是认证的入口
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 类
public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter() {
super(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/login", "POST"));
}
我们继续看 Filter 的 处理方法,可以出在这个方法里面,从请求中取出了表单参数,并且将参数封装到了 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 中,最后使用getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest); 进行认证,getAuthenticationManager 获取到的是一个 AuthenticationManager 对象,实际上是使用 AuthenticationManager 的 authenticate 方法进行认证。
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 类
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (this.postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
} else {
String username = this.obtainUsername(request);
String password = this.obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password);
this.setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
}
我们继续进入 authenticate 方法,发现其是一个接口方法,有很多实现类。没办法,我们只好将应用启动,进行 debug 断点跟踪。
public interface AuthenticationManager {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication var1) throws AuthenticationException;
}
经过断点跟踪,我们发现实际上调用的是 ProviderManager 的 authenticate 方法,我们发现在该方法中,获取所有的 Providers,然后遍历,找出与封装的 Token 匹配的 Provider,调用其 authenticate 方法。
ProviderManager 类
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
// 获取之前封装的 Token 类型
Class<? extends Authentication> toTest = authentication.getClass();
AuthenticationException lastException = null;
Authentication result = null;
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
// 获取所有 providers,遍历之
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
// 判断 Provider 是否支持封装的 Token
if (!provider.supports(toTest)) {
continue;
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authentication attempt using "
+ provider.getClass().getName());
}
try {
// 调用 Provider 的认证方法
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
}
catch (AccountStatusException e) {
prepareException(e, authentication);
// SEC-546: Avoid polling additional providers if auth failure is due to
// invalid account status
throw e;
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException e) {
prepareException(e, authentication);
throw e;
}
catch (AuthenticationException e) {
lastException = e;
}
}
if (result == null && parent != null) {
// Allow the parent to try.
try {
// 认证没有获取到结果,使用 parent 进行认证
result = parent.authenticate(authentication);
}
catch (ProviderNotFoundException e) {
// ignore as we will throw below if no other exception occurred prior to
// calling parent and the parent
// may throw ProviderNotFound even though a provider in the child already
// handled the request
}
catch (AuthenticationException e) {
lastException = e;
}
}
if (result != null) {
// 认证完毕后,调用 Token 的方法擦除掉敏感信息(eg: password...)
if (eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication
&& (result instanceof CredentialsContainer)) {
// Authentication is complete. Remove credentials and other secret data
// from authentication
((CredentialsContainer) result).eraseCredentials();
}
// 认证通过,发布认证成功消息
eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationSuccess(result);
return result;
}
// Parent was null, or didn't authenticate (or throw an exception).
if (lastException == null) {
lastException = new ProviderNotFoundException(messages.getMessage(
"ProviderManager.providerNotFound",
new Object[] { toTest.getName() },
"No AuthenticationProvider found for {0}"));
}
prepareException(lastException, authentication);
throw lastException;
}
我们继续追踪 Provider 的 authenticate 方法,进入AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider 的 authenticate 方法,我们重点关注一下 retrieveUser 方法。
AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider 类
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
Assert.isInstanceOf(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class, authentication,
messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.onlySupports",
"Only UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken is supported"));
// Determine username
String username = (authentication.getPrincipal() == null) ? "NONE_PROVIDED"
: authentication.getName();
boolean cacheWasUsed = true;
// 从缓存中尝试获取用户信息
UserDetails user = this.userCache.getUserFromCache(username);
if (user == null) {
cacheWasUsed = false;
try {
// 缓存没获取到,使用封装的 Token 尝试获取用户信息
user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
catch (UsernameNotFoundException notFound) {
logger.debug("User '" + username + "' not found");
if (hideUserNotFoundExceptions) {
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
}
else {
throw notFound;
}
}
Assert.notNull(user,
"retrieveUser returned null - a violation of the interface contract");
}
try {
// UserDetail 支持设置账户冻结、启用等四个状态,这里是对账户状态进行校验
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
// 进行密码校验,之前如果使用了 passwordEncoder 对密码进行加密,那么从数据库中取出来的应该是加
//密过的密码,这里会对参数中的明文密码与数据库密码进行校验
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
catch (AuthenticationException exception) {
if (cacheWasUsed) {
// There was a problem, so try again after checking
// we're using latest data (i.e. not from the cache)
cacheWasUsed = false;
user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
else {
throw exception;
}
}
postAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
if (!cacheWasUsed) {
this.userCache.putUserInCache(user);
}
Object principalToReturn = user;
if (forcePrincipalAsString) {
principalToReturn = user.getUsername();
}
// 将获取到的用户信息封装成一个 Authentication 返回
return createSuccessAuthentication(principalToReturn, authentication, user);
}
我们发现 retrieveUser 方法是一个抽象方法,具体实现应该在子类中,继续追踪,发现实现在 DaoAuthenticationProvider 中,在 retrieveUser 方法中调用 UserDetailService 的 loadUserByUsername 方法,到了这里,大概的流程我们基本上就知道了。PS: UserDetailService 在系统中有多个实现,这里会使用哪个要看实际情况与设置,这个后面有机会说一下。
AbstractUserDetailAuthenticationProvider 类
protected abstract UserDetails retrieveUser(String username,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
DaoAuthenticationProcider 类
protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
UserDetails loadedUser;
try {
// 调用 UserDetailService 的 loadUserByUsername 方法
loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);
}
catch (UsernameNotFoundException notFound) {
if (authentication.getCredentials() != null) {
String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
passwordEncoder.isPasswordValid(userNotFoundEncodedPassword,
presentedPassword, null);
}
throw notFound;
}
catch (Exception repositoryProblem) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(
repositoryProblem.getMessage(), repositoryProblem);
}
if (loadedUser == null) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(
"UserDetailsService returned null, which is an interface contract violation");
}
return loadedUser;
}
我们来总结一下整个认证流程,通过过滤器获取到请求参数,封装 Token,调用 ProviderManager 的 authenticate 方法,该方法实际上调用的 ProviderManager 管理的 Provider (认证逻辑的实现类) 的 authenticate 方法,最后调用 UserDetailService 去获取用户的信息。
- 首先通过 Filter 拦截用户请求,获取到参数
- 将参数封装成 Token
- 调用 AuthenticationManager 的 authenticated 方法。这里 AuthenticationManager 是接口,实际上调用的是 ProviderManager 的 authenticated 方法。从名字我们可以猜测出 ProviderManager 管理了很多 Provider
- 在 ProviderManager 的 authenticated 方法中,获取所有 Provider,遍历,按 Token 匹配,调用匹配到的 Provider 的 authentication 方法(这里表单登录实际上调用的是 DaoAuthenticationProvider 的方法)
- 最终调用的是 UserDetailService 的 loadUserByUsername 方法
- 查询出用户信息后,进行校验
- 校验通过后,发布认证成功信息。如果认证失败,会抛出异常,最终也会发布认证失败信息。
所以我们要自定义手机号登陆,需要做一下操作:
- 自定义一个 Filter 用来拦截手机号登陆
- 自定义一个 Token
- 自定义一个 Provider
- 自定义一个 UserDetailService 的实现
- 最终把上面这些自定义的类作为配置,加入到 SpringSecurity 的校验流程中去
OK,我们一步一步来:
自定义 SmsCodeAuthenticationToken
继承 AbstractAuthenticationToken 类,父类里面主要三个属性
- 权限集合 (Collection
- 客户端信息(Object detail)
- 是否通过认证(authenticated)
自己实现的 Token 在此基础上按照认证方式进行扩展,比如如果是表单登录,需要添加用户名、密码等。我们这里是短信验证码认证,只需要手机号即可。
- Token 主要在认证流程中装载数据。
- 下面单参数的构造方法,传递一个 mobile,是认证前用来存储认证参数的,此时默认将 authenticated 置为 false
- 双参数的构造方法,是用来状态获取到的用户信息,此时默认将 authenticate 置为 true,但是并不代表当前认证已经通过了。因为可能后面还有密码校验(表单登录时)、账号状态校验等。
/**
* @author: hblolj
* @Date: 2019/3/15 10:58
* @Description: 认证前用来装载认证参数,认证通过后用来装载用户信息,因为短信验证码登录没有密码,将 credentials 移除了
* @Version:
**/
public class SmsCodeAuthenticationToken extends AbstractAuthenticationToken{
private final Object principal;
public SmsCodeAuthenticationToken(Object mobile) {
super((Collection)null);
this.principal = mobile;
this.setAuthenticated(false);
}
public SmsCodeAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
super(authorities);
this.principal = principal;
super.setAuthenticated(true);
}
public void setAuthenticated(boolean isAuthenticated) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (isAuthenticated) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot set this token to trusted - use constructor which takes a GrantedAuthority list instead");
} else {
super.setAuthenticated(false);
}
}
public void eraseCredentials() {
super.eraseCredentials();
}
@Override
public Object getCredentials() {
return null;
}
public Object getPrincipal() {
return this.principal;
}
}
自定义 SmsCodeAuthenticationFilter
主要参考 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 来实现自定义 Filter。在 Filter 中主要要做的事情有以下几点:
-
指定 Filter 拦截的 Url 和 HttpMethod
-
完成拦截的逻辑代码
-
从请求中获取参数(手机号)
-
将参数封装成自定义的 Token,同时设置一下 Detail(主要是发起请求的客户端信息)
-
调用
AuthenticationManager的authenticated方法进行认证
-
/**
* @author: hblolj
* @Date: 2019/3/15 10:58
* @Description:
* @Version:
**/
public class SmsCodeAuthenticationFilter extends AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter {
// TODO: 2019/3/15 该参数可以抽取成配置,最后通过配置文件进行修改,这样作为共用组件只需要实现一个 default,具体值可以有调用者指定
private String mobileParameter = "mobile";
private boolean postOnly = true;
/**
* 通过构造函数指定该 Filter 要拦截的 url 和 httpMethod
*/
protected SmsCodeAuthenticationFilter() {
// TODO: 2019/3/15 pattern 可以抽取成配置,最后通过配置文件进行修改,这样作为共用组件只需要实现一个 default,具体值可以有调用者指定
super(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/authentication/mobile", "POST"));
}
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException, IOException, ServletException {
// 当设置该 filter 只拦截 post 请求时,符合 pattern 的非 post 请求会触发异常
if (this.postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
} else {
// 1. 从请求中获取参数 mobile + smsCode
String mobile = obtainMobile(request);
if (mobile == null){
mobile = "";
}
mobile = mobile.trim();
// 2. 封装成 Token 调用 AuthenticationManager 的 authenticated 方法,该方法中根据 Token 的类型去调用对应 Provider 的 authenticated
SmsCodeAuthenticationToken token = new SmsCodeAuthenticationToken(mobile);
this.setDetails(request, token);
// 3. 返回 authenticated 方法的返回值
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(token);
}
}
protected String obtainMobile(HttpServletRequest request) {
return request.getParameter(mobileParameter);
}
protected void setDetails(HttpServletRequest request, SmsCodeAuthenticationToken authRequest) {
authRequest.setDetails(this.authenticationDetailsSource.buildDetails(request));
}
public String getMobileParameter() {
return mobileParameter;
}
public void setMobileParameter(String mobileParameter) {
Assert.hasText(mobileParameter, "mobileParameter parameter must not be empty or null");
this.mobileParameter = mobileParameter;
}
public void setPostOnly(boolean postOnly) {
this.postOnly = postOnly;
}
}
自定义 SmsCodeAuthenticationProvider
SmsCodeAuthenticationProvider 实现 AuthenticationProvider 接口,其中有两个方法:
- authenticate: 主要是认证逻辑实现
- 在 authenticate 方法中主要的逻辑
- 从 token 取出参数,调用 UserDetailService 进行查询用户信息。UserDetailService 需要我们根据不同的业务实现不同的实现类,去数据库做不同的查询操作。
- 使用查询出的用户信息构造新的 SmsCodeAuthenticationToken
- 如果是表单登录,还要使用 PasswordEncoder 进行密码校验
- 如果系统有设置账号冻结相关设置,这里可以进行校验(按取出的用户信息)
- 最后返回 token。(如果返回的 result 不为 null,最后回去做密码擦除等操作,然后调用登录成功处理。)
- 在 authenticate 方法中主要的逻辑
- supports: 对 authenticate 的 参数进行校验,与 Provider 对应的 Token 进行比较,看是否是其子类或子接口。
PS: 这里注明一下,短信验证码校验应该在 SmsCodeAuthenticationFilter 之前就被校验了
/**
* @author: hblolj
* @Date: 2019/3/15 10:58
* @Description: 短信验证码认证的真正校验逻辑,实际上是按手机号查询用户,短信验证码过滤器在这之前
* @Version:
**/
public class SmsCodeAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider{
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
SmsCodeAuthenticationToken token = (SmsCodeAuthenticationToken) authentication;
// 对用户进行认证
UserDetails userDetails = userDetailsService.loadUserByUsername((String) token.getPrincipal());
if (userDetails == null){
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException("未找到对应的用户信息!");
}
// 构造新的 Token,采用该构造函数时,会默认将 authenticated 参数置为 true
SmsCodeAuthenticationToken authenticationToken = new SmsCodeAuthenticationToken(userDetails, userDetails.getAuthorities());
authenticationToken.setDetails(token.getDetails());
// TODO: 2019/3/15 如果认证方式与密码相关,这里可以对密码进行校验 @PasswordEncoder
// TODO: 2019/3/15 可以校验账号状态: 启用、冻结等等
// userDetails.isAccountNonExpired(); 账号是否过期
// userDetails.isAccountNonLocked(); 账号有无冻结
// userDetails.isCredentialsNonExpired(); 账号密码是否过期
// userDetails.isEnabled(); 账号是否启用
return authenticationToken;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> aClass) {
// aClass 是 authenticate 方法参数的类型
// 此处判断 aClass 是否是该 Provider 对应的 Token 的子类或者子接口,只有通过了,才会调用 authenticate 方法去认证
return SmsCodeAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(aClass);
}
public void setUserDetailsService(UserDetailsService userDetailsService) {
this.userDetailsService = userDetailsService;
}
}
自定义 UserDetailService
重写 loadUserByUsername 方法,按手机号查询。在实际开发中,这里可以提供一个默认缺省实现,真正的实现交给业务开发人员去实现。
/**
* @author: hblolj
* @Date: 2019/3/15 14:08
* @Description:
* @Version:
**/
@Component("mobileUserDetailService")
public class MobileUserDetailService implements UserDetailsService{
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String mobile) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
// TODO: 2019/3/15 按手机号查询用户信息
return new User("4000368163", "123", true, true, true,
true, AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admin"));
}
}
自定义 SmsCodeAuthenticationSecurityConfig
经过上面的几步准备,现在万事俱备,只欠东风。我们只需要将 Filter 和 Provider 添加到 SpringSecurity 的认证链路当中(就可以召唤神龙了)即可。
- 继承
SecurityConfigurerAdapter类,重写该类中的configure(HttpSecurity)方法。(后面源码分析时,会分析这个类是怎样作用于配置的) - 在
configure方法中,首先初始化自定义的 Filter 和 Provider,最后使用 HttpSecurity 进行设置添加
/**
* @author: hblolj
* @Date: 2019/3/15 10:59
* @Description:
* @Version:
**/
@Component
public class SmsCodeAuthenticationConfig extends SecurityConfigurerAdapter<DefaultSecurityFilterChain, HttpSecurity>{
@Autowired
private AuthenticationSuccessHandler successHandler;
@Autowired
private AuthenticationFailureHandler failureHandler;
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService mobileUserDetailService;
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity builder) throws Exception {
// 1. 初始化 SmsCodeAuthenticationFilter
SmsCodeAuthenticationFilter filter = new SmsCodeAuthenticationFilter();
filter.setAuthenticationManager(builder.getSharedObject(AuthenticationManager.class));
filter.setAuthenticationSuccessHandler(successHandler);
filter.setAuthenticationFailureHandler(failureHandler);
// 2. 初始化 SmsCodeAuthenticationProvider
SmsCodeAuthenticationProvider provider = new SmsCodeAuthenticationProvider();
provider.setUserDetailsService(mobileUserDetailService);
// 3. 将设置完毕的 Filter 与 Provider 添加到配置中,将自定义的 Filter 加到 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 之前
builder.authenticationProvider(provider).addFilterBefore(filter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
}
}
最后,将自定义的 config 添加到配置中,主要使用 apply 方法将我们自定义的 config 加入到 SpringSecurity 中,同时设置手机登录地址访问不需要认证,不然就没法使用了。
@Autowired
private SmsCodeAuthenticationConfig smsCodeAuthenticationConfig;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.apply(smsCodeAuthenticationConfig) // 加载短信验证
.and()
.formLogin() // 指定登录认证方式为表单登录
//.loginPage("http://www.baidu.com") //指定自定义登录页面地址,一般前后端分离,这里就用不到了
.loginProcessingUrl("/authentication/form") // 自定义表单登录的 action 地址,默认是 /login
.successHandler(authenticationSuccessHandler)
.failureHandler(authenticationFailureHandler)
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
// 设置手机登录地址不需要校验
.antMatchers("/authentication/mobile").permitAll()
.antMatchers(
securityProperties.getBrowser().getSignUpUrl()).permitAll() // 允许登录页面不需要认证就可以访问,不然会死循环导致重定向次数过多
.anyRequest() // 对所有的请求
.authenticated() // 都进行认证
.and()
.csrf()
.disable();
}
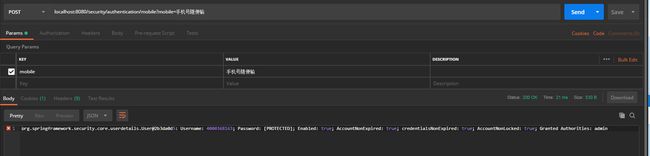
然后启动服务,因为是 post 请求,我们打开 postman 进行模拟,这里我对DefaultAuthenticationSuccessHandler 做了一下处理,使其返回 principal.toString()
如图所示,证明我们配置的手机号认证流程已经生效了。
同理,除了手机号的自定义登录,我们还可以自定义其他的登录方式,比如微信公众号开发中,我们需要使用用户的 OpenId 来登录,就可以按这个模式来处理(最终更新完后,我会将代码实现上传到 Github 上,到时候会包含这个 weixin openId 登录,这里大家感兴趣的话,可以自己先实现以下)。
不过 QQ 登录和 WeiXin 的快捷登录又不一样,属于第三方登录,要使用 SpringSocial + OAuth2 来开发。这个我会放到后面几章去讲解。
下一章的话,会带大家处理一下在 SpringSecurity 下的 Session 管理与登出。To Be Continue!