poj 3784 && 洛谷 P1168 对顶堆
题意:一组数按顺序加入数组,每奇数次加入的时候就输出中位数
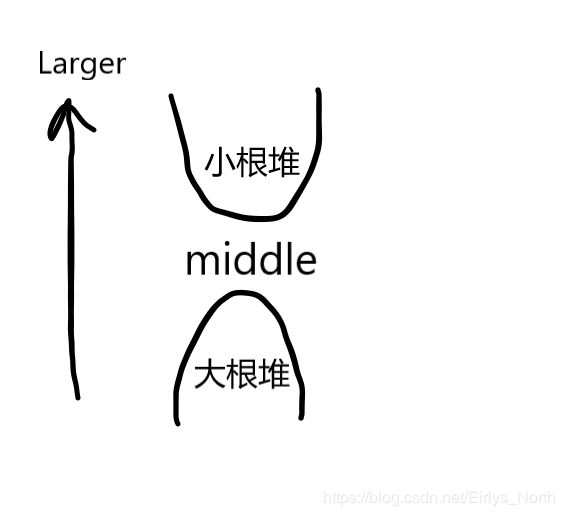
对顶堆是一种可以O(logn)维护在线第K小值的算法
大根堆:维护集合中较小值的部分的最大值。
小根堆:维护集合中较大值的部分的最小值。
注意到两个堆中的元素各自是单调的,两个堆间也是单调的。
也就是说,大根堆中的任何一个元素都不大于小根堆中的任何一个元素
维护中位数:
构建一个大根堆g和小根堆l,初始均为空
设当前中位数为mid,新读入的数为x
(1)如果x
(2)如果x>=mid就把x插入小根堆,跳到步骤(4)
(3)如果小根堆的元素个数恰好为大根堆元素个数+2,即 l.size=g.size+2 ,就把mid入大根堆,弹出小根堆堆顶元素为新的mid
(4)如果大根堆的元素个数恰好为小根堆元素个数+2,即g.size=l.size+2 ,就把mid入小根堆,弹出大根堆堆顶元素为新的mid
如果这两个堆元素个数相同,则mid为中位数,否则中位数为 mid与元素个数多的堆顶元素的平均值
poj 3784
type
rec=record
size:longint;
heap:array[0..10010] of longint;
end;
var
t,tt,n,mid,x,num:longint;
i :longint;
l,g :rec;
procedure swap(var a,b:longint);
var
c:longint;
begin
c:=a; a:=b; b:=c;
end;
procedure heap_up(x,i:longint);
begin
if i=1 then exit;
if (x=1) then
begin
while (i>1) do
begin
if (l.heap[i]1) do
begin
if (g.heap[i]>g.heap[i div 2]) then
begin
swap(g.heap[i],g.heap[i div 2]);
i:=i div 2;
end else break;
end;
end;
end;
procedure heap_down(x,i:longint);
var
t:longint;
begin
if x=1 then
begin
while (2*i<=l.size) do
begin
if l.heap[2*i]i) then
begin
swap(l.heap[i],l.heap[t]);
i:=t;
end else break;
end;
end else
begin
while (2*i<=g.size) do
begin
if g.heap[2*i]>g.heap[i] then t:=2*i else t:=i;
if (2*i+1<=g.size) then
if g.heap[2*i+1]>g.heap[t] then t:=2*i+1;
if (t<>i) then
begin
swap(g.heap[i],g.heap[t]);
i:=t;
end else break;
end;
end;
end;
procedure del(x:longint);
begin
if x=1 then
begin
l.heap[1]:=l.heap[l.size];
dec(l.size);
heap_down(1,1);
end else
begin
g.heap[1]:=g.heap[g.size];
dec(g.size);
heap_down(2,1);
end;
end;
begin
read(t);
while (t>0) do
begin
dec(t);
read(tt,n);
writeln(tt,' ',(n+1) div 2);
read(mid);
l.size:=0; g.size:=0;
if (n=1) then writeln(mid) else write(mid,' ');
num:=1;
//
for i:=2 to n do
begin
read(x);
if (x>=mid) then
begin
inc(l.size);
l.heap[l.size]:=x;
heap_up(1,l.size);
if (l.size=g.size+2) then
begin
inc(g.size);
g.heap[g.size]:=mid;
heap_up(2,g.size);
mid:=l.heap[1];
del(1);
end;
end else
begin
inc(g.size);
g.heap[g.size]:=x;
heap_up(2,g.size);
if (g.size=l.size+2) then
begin
inc(l.size);
l.heap[l.size]:=mid;
heap_up(1,l.size);
mid:=g.heap[1];
del(2);
end;
end;
if (i and 1<>0) then
begin
inc(num);
if (i=n) or (num mod 10=0) then writeln(mid)
else write(mid,' ');
end;
end;
end;
end.
洛谷 P1168
#include
struct rec {
int size = 0;
int heap[100010];
};
struct rec l, g;
void swap (int *a, int *b){
int c;
c = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = c;
}
void heap_up(int t, int x) {
if (x == 1) return;
if (t == 1){
while (x != 1) {
if (l.heap[x] < l. heap[x >> 1]) {
swap(&l.heap[x], &l.heap[x >> 1]);
x = x >> 1;
} else break;
}
} else {
while (x != 1) {
if (g.heap[x] > g.heap[x >> 1]){
swap(&g.heap[x], &g.heap[x >> 1]);
x = x >> 1;
} else break;
}
}
}
void heap_down(int t, int x){
int tt;
if (t == 1) {
while ((x << 1) <= l.size) {
if (l.heap[x << 1] < l.heap[x]) tt = x << 1; else tt = x;
if ((x << 1) + 1 <= l.size)
if (l.heap[(x << 1) + 1] < l.heap[tt]) tt = (x << 1) + 1;
if (tt != x) {
swap(&l.heap[tt], &l.heap[x]);
x = tt;
} else break;
}
} else {
while ((x << 1) <= g.size) {
if (g.heap[x << 1] > g.heap[x]) tt= x << 1; else tt = x;
if ((x << 1) + 1 <=g.size)
if (g.heap[(x << 1) + 1] > g.heap[tt]) tt = (x << 1) + 1;
if (tt != x) {
swap(&g.heap[tt], &g.heap[x]);
x = tt;
} else break;
}
}
}
void del(int t) {
if (t == 1) {
l.heap[1] = l. heap[l.size--];
heap_down(1, 1);
} else {
g.heap[1] = g.heap[g.size--];
heap_down(2, 1);
}
}
int main() {
int n;
int x;
int mid;
int i;
scanf("%d", &n);
scanf("%d", &mid);
printf("%d\n", mid);
//
for (i = 2; i <= n; i ++){
scanf("%d", &x);
if (x >= mid) {
l.heap[++l.size] = x;
heap_up(1, l.size);
if (l.size == g.size + 2) {
g.heap[++g.size] = mid;
heap_up(2, g.size);
mid = l.heap[1];
del(1);
}
} else {
g.heap[++g.size] = x;
heap_up(2, g.size);
if (g.size == l.size + 2) {
l.heap[++l.size] = mid;
heap_up(1, l.size);
mid = g.heap[1];
del(2);
}
}
if ((i % 2) == 1) printf("%d\n", mid);
}
return 0;
}