前言:
之前都在学习Internet的历史,从这周开始,进入到了Internet技术的学习。
Layer1: Link
-
Introduction / The Link Layer
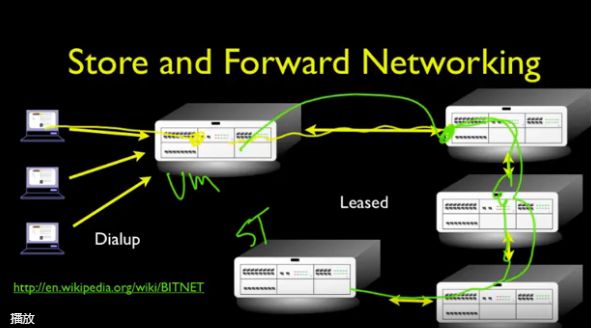
80年代之前,主流网络的还是Store and Forward Networking(存储转发网络),但是由于其在数据处理方面延时较大,无法应用于条件严苛的军事领域,故军方出力研究出了ARPANET——一个典型的packet switch network(分组交换网络)。
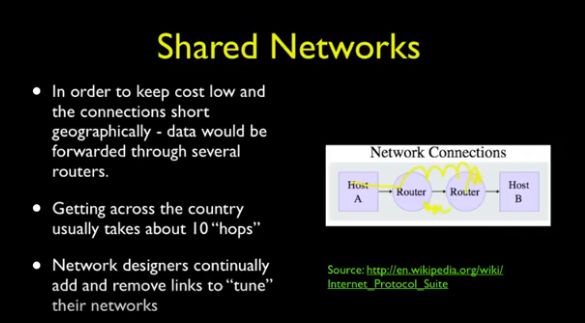
ARPANET给出了一个不一样的网络:Shared Network——把一大段信息分成许多个packets(数据包),利用路由器做短期短距离的数据传输,多个路由器接连负责将收到的数据包传送给下一个路由器,hop依然存在,路由器之间的不断转发最终让数据汇聚到目的地。
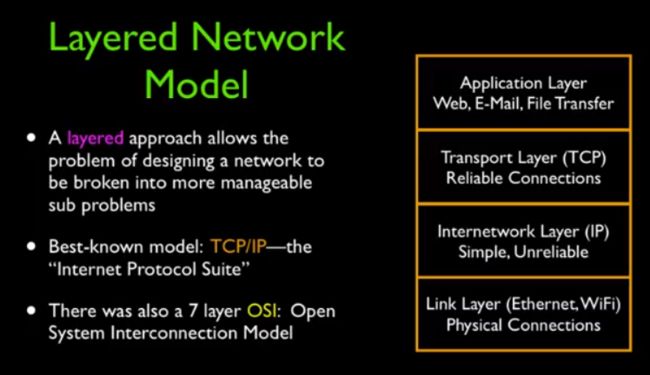
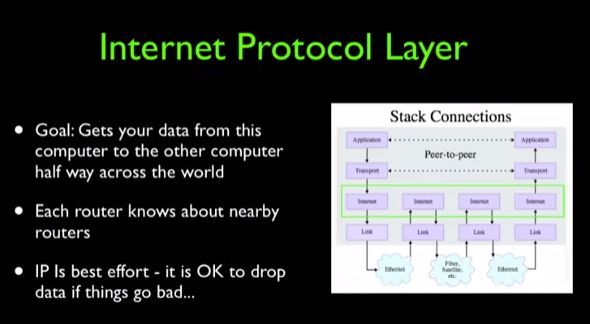
Shared Network上的数据需要在路由器与路由器之间不停的Hop,为了简化和管理,业界提出了分为四层的Layered Network Model(网络分层模型),随之在各层上用协议(Protocol)来约束层与层之间要如何协同工作,简化过程。
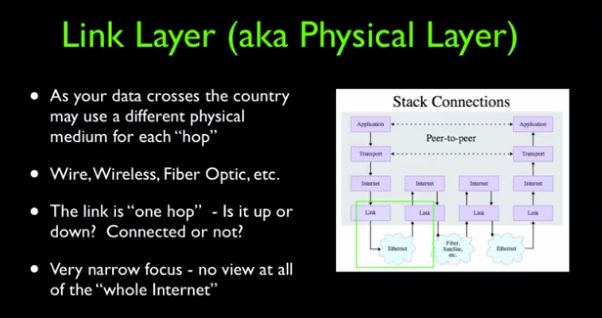
Link Layer(链路层)是协议的第一层。由于是分层模型,因此在这层上,只考虑物理层面上实现传输数据即可。物理的传输介质,如有线、无线传输、光缆等,都可以看做是一个Link。
Ethernet(以太网)可以说是目前应用最为广泛的Link Layer,硬件制造商在制造带有以太网或者无线适配器的电子器件时,都会用六组两两结合的字符去标识这些硬件,这其实属于一种物理地址(Mac地址),硬件之间正是通过地址来识别。
当涉及到共享的问题时,必然需要一个与之相对应的冲突解决方案,以太网采用的则是CSMA/CD(Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection,载波监听多路访问及冲突检测)。设备在发送数据前会对信道进行Listen(监听),当没有其他正在传输的数据时,才可以进行传输,否则在某个周期内将会一直持续监听。
Layer2: Internet Portocol
-
The InterNetwork (IP)
Internetwork Layer(网络层)需要关心的是多个Link的连接问题,这是分层模型带来的好处。
与前面的Mac地址不同,IP地址不是与硬件有关的且一成不变的,物理地址在某个硬件被制造时就由制造商决定了,IP地址是全球性的,当你到了其他地方IP地址就会随之发生改变。
IP地址(IPv4)格式是32bits的,由四个小数点分隔,每组都由0 ~ 255(8bits)的二进制数组成。IP地址分为前缀网络号和后缀主机号,前者用子网掩码来表示,用于表示IP地址从属的网络,后者指明网络中的具体主机号。数据在网络传输过程中会先根据网络号找到指定网络,再根据主机号索引到目标主机。
Router Tables(路由表)是路由器等网络设备上存储的一张动态更新的信息表,路由表中存放了发送源和目的地的地址,可以根据目的地的ip地址决定了数据该往哪个方向传递,路由表中还包含了相邻链路的带宽情况,智能选择路径以避免拥堵。
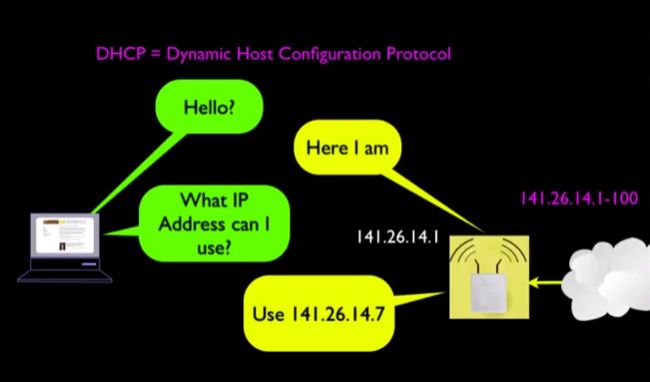
DHCP(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol,动态主机配置协议)是一个局域网的网络协议,在接收申请之后,可以为新连入网络的主机分配一个IP地址。例如当我们在咖啡厅、在家与在工作单位分别连接网络时,其实分配的IP地址是不同的,但是我们在接入网络的时候却没有因为地址不同而被拒绝,这都归功于DHCP。
如果为所有机构的所有电脑都分配一个真实存在的IP地址,那么IP地址将会很紧缺(IPv4情况下是2的32次方个),所以出现了Network Address Translation技术。
NAT(Network Address Translation,网络地址转换)技术可使专用网内部已分配的本地IP地址与因特网上的主机进行通信,这种通过使用少量的公有IP地址代表较多的私有IP地址的方式,有助于减缓IP地址枯竭的情况。不过NAT分配的只在内部网络使用的虚拟IP地址,不能直接访问因特网,只有通过ISP(Internet Service Provider,互联网服务提供商)转换为real global routable address,才能与因特网传输数据。
TTL(Time to Live,存活时间)是每个IP数据包自带的一个用来表示生存时间的字节,最大值为255。TTL每经过一个路由器减少1,减到零之后就丢弃数据包,防止无限hop导致死循环造成网络堵塞。
小结: