最近因为年底,连续两个项目要投产上线,又赶上公司年会,忙的要死,更新有些慢,见谅。今天要说一说python如何对mysql进行操作。在 Python3.x 版本中用于连接 MySQL 服务器的库与Python2中使用的mysqldb有所不同。本文我将为大家介绍 Python3 使用 PyMySQL库 连接数据库,并实现简单的增删改查。
1 PyMySQL介绍
PyMySql包含一个纯python的MySQL客户端库。PyMySQL的目标是成为MySQLdb的替代品,并在CPython、PyPy和IronPython上工作。
2 版本要求
python 下列之一
- CPython >= 2.6 or >= 3.3
- PyPy >= 4.0
- IronPython 2.7
mysql 下列之一
- MySQL >= 4.1 (tested with only 5.5~)
- MariaDB >= 5.1
3 安装
直接pip方式安装:
# pip install PyMySQL4 数据库增删改查
4.1 创建数据库testdb和表users
首先要先创建一个testdb 数据库,并且创建users表,创建语句如下:
MariaDB [(none)]> create database testdb;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> use testdb
# 创建users表命令
CREATE TABLE `users` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`email` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`password` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin
AUTO_INCREMENT=1 ;查看创建完的表结构:
MariaDB [testdb]> describe users;
+----------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+----------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| email | varchar(255) | NO | | NULL | |
| password | varchar(255) | NO | | NULL | |
+----------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)4.2 连接数据库
连接数据库之前要确认以下条件是否满足:
- 已经创建了数据库 testdb;
- 在testdb数据库中已经创建了users表;
- 连接数据库TESTDB使用的用户名为 "testdb" ,密码为 "123456",你也可以自己设定用户名和密码;
- 主要如果是远程连接阿里云等主机注意grant授权;
- 已经安装了 Python MySQLdb 模块。
连接数据库并获取版本信息:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 导入模块
import pymysql
# 打开数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect('localhost', 'testdb', '123456', 'testdb')
# 使用cursor()方法创建一个游标对象cursor
cursor = db.cursor()
# 使用execute()方法执行SQL查询
cursor.execute("select version()")
# 使用fetchone()获取单条数据
data = cursor.fetchone()
# 打印获取的内容
print('Vsersion: %s' % data)
# 关闭连接
db.close()
输出结果如下:
Version: 10.0.33-MariaDB4.3 数据库插入
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 导入模块
import pymysql
# 打开数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect('localhost', 'testdb', '123456', 'testdb')
# 使用cursor()方法创建一个游标对象cursor
cursor = db.cursor()
# sql语句
sql = "INSERT INTO users(email, password) VALUES ('[email protected]', '123');"
try:
# 执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# 提交到数据库
db.commit()
print('success')
except:
# 如果出错执行回滚
db.rollback()
print('failed')
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 导入模块
import pymysql
# 打开数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect('localhost', 'testdb', '123456', 'testdb')
# 使用cursor()方法创建一个游标对象cursor
cursor = db.cursor()
# sql语句
# 注意这里是与上面不同的地方
sql = "INSERT INTO users(email, password) VALUES (%s, %s)";
try:
# 执行sql语句
# 注意这里是与上面不同的地方
cursor.execute(sql, ('[email protected]', '456'))
# 提交到数据库
db.commit()
print('success')
except:
# 如果出错执行回滚
db.rollback()
print('failed')
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()4.4 数据库查询
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 导入模块
import pymysql
# 打开数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect('localhost', 'testdb', '123456', 'testdb')
# 使用cursor()方法创建一个游标对象cursor
cursor = db.cursor()
# sql语句
sql = "select * from users;"
try:
# 执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# 通过fetchall获取results对象并打印结果
results = cursor.fetchall()
for result in results:
print(result)
except:
print('failed')
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
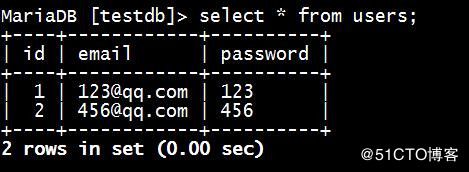
返回结果如下:
(1, '[email protected]', '123')
(2, '[email protected]', '456')4.5 数据库更新操作
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 导入模块
import pymysql
# 打开数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect('localhost', 'testdb', '123456', 'testdb')
# 使用cursor()方法创建一个游标对象cursor
cursor = db.cursor()
# sql语句
sql = "update users set email = '[email protected]' where id = 1;"
sql2 = 'select * from users;'
try:
# 执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# 提交到数据库
db.commit()
cursor.execute(sql2)
# 获取数据结果
results = cursor.fetchall()
for result in results:
print(result)
except:
# 如果出错执行回滚
db.rollback()
print('failed')
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
执行结果如下:
(1, '[email protected]', '123')
(2, '[email protected]', '456')4.6 删除操作
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 导入模块
import pymysql
# 打开数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect('localhost', 'testdb', '123456', 'testdb')
# 使用cursor()方法创建一个游标对象cursor
cursor = db.cursor()
# sql语句
sql = "delete from users where id = 1;"
sql2 = "select * from users;"
try:
# 执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# 提交到数据库
db.commit()
cursor.execute(sql2)
results = cursor.fetchall()
for result in results:
print(result)
except:
# 如果出错执行回滚
db.rollback()
print('failed')
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
执行结果如下:
(2, '[email protected]', '456')5 总结
通过上面增删改查我们已经可以看出,其实python操作mysql并不复杂,主要步骤为连接数据库,建立游标对象,执行sql语句,获取结果,关闭连接。我们的重点还是要熟悉相关的sql语句,这样才能做到游刃有余。sql教程
中级篇就算结束了,后续会介绍高级篇框架相关知识,敬请关注。