整理了校招面试算法题,部分《剑指offer》算法题,以及LeetCode算法题,本博文中算法题均使用Java实现
- 校招面试题解
- 剑指offer部分题解
- LeetCode中文网 部分题解
题目描述:
了解哪些排序算法,依次描述并说下时间、空间复杂度
技术点:
排序
参考
十大经典排序算法最强总结(含JAVA代码实现)
思路:
名称 描述 时间复杂度 空间复杂度 冒泡排序 重复走访要排序的数列,一次比较两个元素,若较小元素在后则交换,能看到越小的元素会经由交换慢慢浮到数列的顶端 O(n2) O(1) 简单选择 每次都在未排序序列中找最小元素 O(n2) O(1) 直接插入 对于未排序数据,在已排序序列中从后向前扫描,找到相应位置并插入 最好O(n),平均O(n2) O(1) 希尔排序 将整个待排序的记录序列分割成为若干子序列分别进行直接插入排序 O(nlogn)~ O(n2) O(1) 归并排序 先使每个子序列有序,再使子序列段间有序 O(nlogn) O(n) 堆排序 近似完全二叉树的结构,子结点的键值或索引总是小于(或大于)其父节点 O(nlogn) O(1) 快速排序 取一个记录作为枢轴,经过一趟排序将整段序列分为两个部分,使得数轴左侧都小于枢轴、右侧都大于枢轴;再对这两部分继续进行排序使整个序列达到有序 最坏 O(n2),平均O(nlogn) O(logn)~O(n)
题目描述:
在海量数据中找出出现频率最高的前k个数,从海量数据中找出最大的前k个数
技术点:
链表 数学
思路:
- 方法一:分治+Trie树/hash|+小根堆
- 先将数据按照hash方法分解为多个小数据集
- 使用Trie树或者hash统计每个数据集中的词频
- 使用小根堆求每个数据中出现频率最高的k个数
- 在所有top k中最终的top k
- 方法二:MapReduce解决
一个map 两个reduce
- map切分数据
- reduce1统计词频
- reduce2求top k
题目描述:
给出两个 非空 的链表用来表示两个非负的整数。其中,它们各自的位数是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且它们的每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
如果,我们将这两个数相加起来,则会返回一个新的链表来表示它们的和。
技术点:
链表 数学
思路:
- 将两个链表看成是相同长度的进行遍历,如果一个链表较短则在前面补 0
- 每一位计算的同时需要考虑上一位的进位问题,而当前位计算结束后同样需要更新进位值
- 如果两个链表全部遍历完毕后,进位值为 1,则在新链表最前方添加节点 1
参考代码:
int temp = 0;
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode ln = new ListNode(calcu(l1.val,l2.val));
ListNode lnL = ln;
while(l1.next != null || l2.next != null || temp != 0) {
int v1,v2;
if (l1.next != null) {
l1 = l1.next;
v1 = l1.val;
} else {
v1 = 0;
}
if (l2.next != null) {
l2 = l2.next;
v2 = l2.val;
} else {
v2 = 0;
}
ListNode newLn = new ListNode(calcu(v1,v2));
lnL.next = newLn;
lnL = lnL.next;
}
return ln;
}
public int calcu(int a, int b) {
if(a+b+temp>=10){
if(temp==0){
temp = 1;
return a+b-10;
}else{
temp = 1;
return a+b-9;
}
}else {
if(temp==1){
temp = 0;
return a+b+1;
}else{
temp = 0;
return a+b;
}
}
}
题目描述:
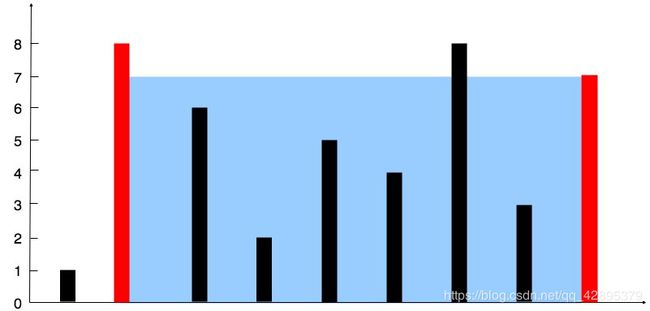
给定 n 个非负整数 a1,a2,...,an,每个数代表坐标中的一个点 (i, ai) 。在坐标内画 n 条垂直线,垂直线 i 的两个端点分别为 (i, ai) 和 (i, 0)。找出其中的两条线,使得它们与 x 轴共同构成的容器可以容纳最多的水。
图中垂直线代表输入数组 [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]。在此情况下,容器能够容纳水(表示为蓝色部分)的最大值为 49。
技术点:
链表 双指针
思路:
为了使面积最大化,我们需要考虑更长的两条线段之间的区域。如果我们试图将指向较长线段的指针向内侧移动,矩形区域的面积将受限于较短的线段而不会获得任何增加。但是,在同样的条件下,移动指向较短线段的指针尽管造成了矩形宽度的减小,但却可能会有助于面积的增大。因为移动较短线段的指针会得到一条相对较长的线段,这可以克服由宽度减小而引起的面积减小。
参考代码:
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int max = 0;
for(int i=0,j=height.length-1;i题目描述:
给定一个包含 n 个整数的数组
nums,判断nums中是否存在三个元素a,b,c,使得a + b + c = 0?找出所有满足条件且不重复的三元组。
技术点:
数组 双指针
思路:
固定一个值,找另外二个值它们和等于 0,
使用双指针找另外两个值。
参考代码:
public List> threeSum(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
List> ls = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 2; i++) {
if (i == 0 || (i > 0 && nums[i] != nums[i - 1])) { // 跳过可能重复的答案
int l = i + 1, r = nums.length - 1, sum = 0 - nums[i];
while (l < r) {
if (nums[l] + nums[r] == sum) {
ls.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[l], nums[r]));
while (l < r && nums[l] == nums[l + 1]) l++;
while (l < r && nums[r] == nums[r - 1]) r--;
l++;
r--;
} else if (nums[l] + nums[r] < sum) {
while (l < r && nums[l] == nums[l + 1]) l++; // 跳过重复值
l++;
} else {
while (l < r && nums[r] == nums[r - 1]) r--;
r--;
}
}
}
}
return ls;
}
题目描述:
假设按照升序排序的数组在预先未知的某个点上进行了旋转。
( 例如,数组 [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] )。
搜索一个给定的目标值,如果数组中存在这个目标值,则返回它的索引,否则返回 -1 。
技术点:
数组 二分查找
思路:
- 找到旋转的下标
rotation_index,也就是数组中最小的元素。二分查找在这里可以派上用场。- 在选中的数组区域中再次使用二分查找。
参考代码:
int [] nums;
int target;
public int find_rotate_index(int left, int right) {
if (nums[left] < nums[right])
return 0;
while (left <= right) {
int pivot = (left + right) / 2;
if (nums[pivot] > nums[pivot + 1])
return pivot + 1;
else {
if (nums[pivot] < nums[left])
right = pivot - 1;
else
left = pivot + 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
public int search(int left, int right) {
/*
Binary search
*/
while (left <= right) {
int pivot = (left + right) / 2;
if (nums[pivot] == target)
return pivot;
else {
if (target < nums[pivot])
right = pivot - 1;
else
left = pivot + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
this.nums = nums;
this.target = target;
int n = nums.length;
if (n == 0)
return -1;
if (n == 1)
return this.nums[0] == target ? 0 : -1;
int rotate_index = find_rotate_index(0, n - 1);
// if target is the smallest element
if (nums[rotate_index] == target)
return rotate_index;
// if array is not rotated, search in the entire array
if (rotate_index == 0)
return search(0, n - 1);
if (target < nums[0])
// search in the right side
return search(rotate_index, n - 1);
// search in the left side
return search(0, rotate_index);
}
题目描述:
给定两个以字符串形式表示的非负整数
num1和num2,返回num1和num2的乘积,它们的乘积也表示为字符串形式。
技术点:
字符串 数学
思路:
模拟竖式乘法计算过程
参考代码:
public String multiply(String num1, String num2) {
int l = num1.length();
int r = num2.length();
int[] result = new int[l + r];
for (int i = 0; i < l; i++) {
int n1 = num1.charAt(l - i - 1) - '0';
int temp = 0;
for (int t = 0; t < r; t++) {
int n2 = num2.charAt(r - t - 1) - '0';
temp = temp + result[i + t] + n1 * n2;
result[i + t] = temp % 10;
temp /= 10;
}
result[i + r] = temp;
}
int len = 0;
for (int i = l + r - 1; i >= 0; i--)
if (result[i] > 0) {
len = i;
break;
}
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = len; i >= 0; i--) {
builder.append(result[i]);
}
return builder.toString();
}
题目描述:
给定一个包含 m x n 个元素的矩阵(m 行, n 列),请按照顺时针螺旋顺序,返回矩阵中的所有元素。
技术点:
数组
思路:
- 方法一:模拟
假设数组有R行C列,seen[r][c]表示第 r 行第 c 列的单元格之前已经被访问过了。当前所在位置为(r, c),前进方向是di。我们希望访问所有RxC个单元格。
当我们遍历整个矩阵,下一步候选移动位置是(cr, cc)。如果这个候选位置在矩阵范围内并且没有被访问过,那么它将会变成下一步移动的位置;否则,我们将前进方向顺时针旋转之后再计算下一步的移动位置。- 方法二:按层模拟
我们定义矩阵的第 k 层是到最近边界距离为 k 的所有顶点。
对于每层,我们从左上方开始以顺时针的顺序遍历所有元素,假设当前层左上角坐标是(r1, c1),右下角坐标是(r2, c2)。
首先,遍历上方的所有元素(r1, c),按照c = c1,...,c2的顺序。然后遍历右侧的所有元素(r, c2),按照r = r1+1,...,r2的顺序。如果这一层有四条边(也就是r1<r2并且c1<c2)
参考代码:
public List spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
if (matrix == null)
return new ArrayList<>();
int m = matrix.length;
if (m == 0)
return new ArrayList<>();
int n = matrix[0].length;
if (n == 0)
return new ArrayList<>();
List result = new ArrayList<>();
if (m >= 2 && n >= 2) {
int round = (Math.min(m,n) - 2)/2;
for (int i = 0; i <= round; i++) {
addFloor(i, result, matrix);
}
if (result.size() < m*n)
if (m >= n) {
for (int i = round + 1;i < m - round - 1;i++) {
result.add(matrix[i][round+1]);
}
} else {
for (int i = round + 1;i < n - round - 1;i++) {
result.add(matrix[round+1][i]);
}
}
}
else if(Math.max(m,n) >= 2) {
if (m >= n) {
for (int i = 0;i < m;i++) {
result.add(matrix[i][0]);
}
} else {
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++) {
result.add(matrix[0][i]);
}
}
}
if (m == 1 && n == 1) {
result.add(matrix[0][0]);
}
return result;
}
private void addFloor(int floor, List result, int[][] matrix) {
for (int x = floor; x < matrix[floor].length - floor; x++) {
result.add(matrix[floor][x]);
}
for (int y = floor + 1; y < matrix.length - floor; y++) {
result.add(matrix[y][matrix[0].length - floor-1]);
}
for (int x = matrix[floor].length - floor-2; x >= floor; x--) {
result.add(matrix[matrix.length - floor-1][x]);
}
for (int y = matrix.length - floor-2;y > floor;y--) {
result.add(matrix[y][floor]);
}
}
题目描述:
给定一个链表,旋转链表,将链表每个节点向右移动 k 个位置,其中 k 是非负数。
技术点:
链表 双指针
思路:
右移k个位置,本质就是将前
len - k % len个节点放到最后去 分为几个核心步骤:
- 求出链表的长度,以及最后的一个节点
- 截取前
len - k % len个节点- 将两段链表进行拼接
参考代码:
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
int len = 0;
ListNode index = head,last = null,temphead = head;
while(index != null) {
if (index.next == null)
last = index;
index = index.next;
++len;
}
if(len == 0)
return head;
k %= len;
if (k != 0) {
k = len - k;
index = head;
for (int i = 0;i < k-1;i++) {
index = index.next;
}
head = index.next;
index.next = null;
last.next = temphead;
}
return head;
}
题目描述:
一个机器人位于一个 m x n 网格的左上角 ,每次只能向下或者向右移动一步,机器人试图达到网格的右下角,问总共有多少条不同的路径?
技术点:
数组 动态规划
思路:
我们令
dp[i][j]是到达i,j最少步数
动态方程:dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1]
注意,对于第一行dp[0][j],或者第一列dp[i][0],由于都是在边界,所以只能为1
参考代码:
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
int[][] dp = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i == 0 || j == 0)
dp[i][j] = 1;
else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1];
}
}
}
return dp[m - 1][n - 1];
}
题目描述:
给定一个非空字符串 s 和一个包含非空单词列表的字典 wordDict,判定 s 是否可以被空格拆分为一个或多个在字典中出现的单词。
技术点:
动态规划
思路:
方法 1:暴力
最简单的实现方法是用递归和回溯。为了找到解,我们可以检查字典单词中每一个单词的可能前缀,如果在字典中出现过,那么去掉这个前缀后剩余部分回归调用。同时,如果某次函数调用中发现整个字符串都已经被拆分且在字典中出现过了,函数就返回 true 。
时间复杂度:O(n^n) | 空间复杂度:O(n)
方法 2:记忆化回溯
我们可以使用记忆化的方法,其中一个 memo 数组会被用来保存子问题的结果。每当访问到已经访问过的后缀串,直接用 memo 数组中的值返回而不需要继续调用函数。
通过记忆化,许多冗余的子问题可以极大被优化,回溯树得到了剪枝,因此极大减小了时间复杂度。
时间复杂度:O(n^2) | 空间复杂度:O(n)
方法 3:BFS
将字符串可视化成一棵树,每一个节点是用 endend 为结尾的前缀字符串。当两个节点之间的所有节点都对应了字典中一个有效字符串时,两个节点可以被连接。
时间复杂度:O(n^2) | 空间复杂度:O(n)
方法 4:动态规划
这个方法的想法是对于给定的字符串(ss)可以被拆分成子问题 s1 和 s2 。如果这些子问题都可以独立地被拆分成符合要求的子问题,那么整个问题 ss 也可以满足。也就是,如果 "catsanddog" 可以拆分成两个子字符串 "catsand" 和 "dog" 。子问题 "catsand" 可以进一步拆分成 "cats" 和 "and" ,这两个独立的部分都是字典的一部分,所以 "catsand" 满足题意条件,再往前, "catsand" 和 "dog" 也分别满足条件,所以整个字符串 "catsanddog" 也满足条件。
参考代码:
public boolean wordBreak(String s, List wordDict) {
if (wordDict == null || wordDict.size() == 0 || s == null || s.length() == 0)
return false;
int[] flag = new int[s.length()+1];
for (int i=0;i < flag.length;i++)
flag[i]=-1;
flag[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1;i <= s.length();i++) {
for (int j = 0;j < i;j++) {
if (flag[j]!=-1 && wordDict.contains(s.substring(j,i))) {
flag[i] = j;
break;
}
}
}
return flag[s.length()] != -1;
}
题目描述:
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回
null。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数pos来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果pos是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
技术点:
链表 双指针
思路:
- 方法一:哈希表
如果我们用一个Set保存已经访问过的节点,我们可以遍历整个列表并返回第一个出现重复的节点。- 方法二:快慢指针+数学
设快慢指针第一次相遇时,fast走了f步,slow走了s步,设环的长度为c,从表头到入环点需走t步,那么:当fast指针追上slow指针时,fast比slow多走了n个环的长度,即f = s + n * c;同时,因为fast一次走2步,slow一次走1步,因此有f = 2s;由此可得:s = n * c,f = 2 * n * c。将slow退到起始点,fast不动,然后每人一次各走一步:当slow走到入环点时,它走了t( = 0 * c + t )步;而此时fast走了2 * n * c + t步,也到达了入环点,说明他们正好相遇在了入环点。
参考代码:
//方法一:
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
Set visited = new HashSet();
ListNode node = head;
while (node != null) {
if (visited.contains(node)) {
return node;
}
visited.add(node);
node = node.next;
}
return null;
}
//方法二:
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
boolean hasCycle = false;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) {
hasCycle = true;
break;
}
}
if (!hasCycle) {
return null;
}
slow = head;
while (fast != slow) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return fast;
}
题目描述:
在 O(n log n) 时间复杂度和常数级空间复杂度下,对链表进行排序。
技术点:
链表 排序
思路:
参考:Sort List——经典(链表中的归并排序)
https://www.cnblogs.com/qiaozhoulin/p/4585401.html
归并排序法:在动手之前一直觉得空间复杂度为常量不太可能,因为原来使用归并时,都是 O(N)的,需要复制出相等的空间来进行赋值归并。对于链表,实际上是可以实现常数空间占用的(链表的归并排序不需要额外的空间)。利用归并的思想,递归地将当前链表分为两段,然后merge,分两段的方法是使用 fast-slow 法,用两个指针,一个每次走两步,一个走一步,知道快的走到了末尾,然后慢的所在位置就是中间位置,这样就分成了两段。merge时,把两段头部节点值比较,用一个 p 指向较小的,且记录第一个节点,然后 两段的头一步一步向后走,p也一直向后走,总是指向较小节点,直至其中一个头为NULL,处理剩下的元素。最后返回记录的头即可。
主要考察3个知识点
知识点1:归并排序的整体思想
知识点2:找到一个链表的中间节点的方法
知识点3:合并两个已排好序的链表为一个新的有序链表
参考代码:
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
return head == null ? null : mergeSort(head);
}
private ListNode mergeSort(ListNode head) {
if (head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode p = head, q = head, pre = null;
while (q != null && q.next != null) {
pre = p;
p = p.next;
q = q.next.next;
}
pre.next = null;
ListNode l = mergeSort(head);
ListNode r = mergeSort(p);
return merge(l, r);
}
ListNode merge(ListNode l, ListNode r) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = dummyHead;
while (l != null && r != null) {
if (l.val <= r.val) {
cur.next = l;
cur = cur.next;
l = l.next;
} else {
cur.next = r;
cur = cur.next;
r = r.next;
}
}
if (l != null) {
cur.next = l;
}
if (r != null) {
cur.next = r;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
题目描述:
给定一个整数数组
nums,找出一个序列中乘积最大的连续子序列(该序列至少包含一个数)。
技术点:
链表 数学 动态规划
思路:
遍历数组时计算当前最大值,不断更新
令imax为当前最大值,则当前最大值为 imax = max(imax * nums[i], nums[i])
由于存在负数,那么会导致最大的变最小的,最小的变最大的。因此还需要维护当前最小值imin,imin = min(imin * nums[i], nums[i])
当负数出现时则imax与imin进行交换再进行下一步计算
参考代码:
public int maxProduct(int[] nums) {
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE, imax = 1, imin = 1; //一个保存最大的,一个保存最小的。
for(int i=0; i题目描述:
实现一个 Trie (前缀树),包含
insert,search, 和startsWith这三个操作。
技术点:
设计 字典树
思路:
据 字节跳动 的同学说面试面到过这道题
关键点在于每棵树最多只有26棵子树,并且对每棵树标记是否为终点。最后遍历该前缀树即可得出结果。
参考代码:
public static class TrieNode {
boolean isEnd = false;
char val;
TrieNode[] list = new TrieNode[26];
TrieNode(char x) {
val = x;
}
boolean hasNode(char node) {
return list[node - 'a'] != null;
}
TrieNode findNode(char node) {
return list[node - 'a'];
}
TrieNode createNode(char node) {
list[node - 'a'] = new TrieNode(node);
return list[node - 'a'];
}
}
TrieNode head = new TrieNode('-');
/**
* Initialize your data structure here.
*/
public Trie() {
}
/**
* Inserts a word into the trie.
*/
public void insert(String word) {
TrieNode index = head;
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
if (index.hasNode(c))
index = index.findNode(c);
else
index = index.createNode(c);
}
index.isEnd = true;
}
/**
* Returns if the word is in the trie.
*/
public boolean search(String word) {
TrieNode index = head;
for (char c : word.toCharArray())
if (index.hasNode(c))
index = index.findNode(c);
else
return false;
return index.isEnd;
}
/**
* Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix.
*/
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
TrieNode index = head;
for (char c : prefix.toCharArray())
if (index.hasNode(c))
index = index.findNode(c);
else
return false;
return true;
}
题目描述:
在未排序的数组中找到第
k个最大的元素。请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第k个最大的元素,而不是第k个不同的元素。
技术点:
堆 分治算法
思路:
先任取一个数,把比它大的数移动到它的左边,比它小的数移动到它的右边。移动完成一轮后,看该数的下标(从0计数),如果刚好为k-1则它就是第k大的数,如果小于k-1,说明第k大的数在它右边,如果大于k-1则说明第k大的数在它左边,取左边或者右边继续进行移动,直到找到。
参考代码:
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
if(nums == null){
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
if(nums.length < k){
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
return quickSort(nums,0,nums.length-1,k);
}
public static int quickSort(int[] arr,int low,int high,int k){
int i,j;
int temp;
if(low > high){
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
i = low;
j = high;
temp = arr[i];
while(i < j){
while(i < j && arr[j] < temp){//把小于temp的数都放到右边
j--;
}
if(i < j){//如果右边出现大于temp的数,就跟左边交换
arr[i++] = arr[j];
}
while(i < j && arr[i] >= temp){//把大于等于temp的数都放到左边
i++;
}
if(i < j){//如果左边出现小于temp的数,就跟右边交换
arr[j--] = arr[i];
}
}
arr[i] = temp;
if(i == k - 1){//如果temp的位置为k-1,那么他就是第k个最大的数
return temp;
}else if(i > k - 1){//如果temp的位置大于k-1,说明第k个最大的数在左边
return quickSort(arr,low,i - 1,k);
}else{//如果temp的位置小于k-1,说明第k个最大的数在右边
return quickSort(arr,i + 1,high,k);
}
}
题目描述:
编写一个高效的算法来搜索 m x n 矩阵 matrix 中的一个目标值 target。该矩阵具有以下特性:
- 每行的元素从左到右升序排列。
- 每列的元素从上到下升序排列。
技术点:
二分查找 分治算法
思路:
从最右上角的元素开始找,如果这个元素比target大,则说明找更小的,往左走;如果这个元素比target小,则说明应该找更大的,往下走。
参考代码:
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.length;
if (m == 0)
return false;
int n = matrix[0].length;
if (n == 0)
return false;
if (m == 1 && n == 1)
return target == matrix[0][0];
n--;m=0;
while(n >= 0 && m < matrix.length) {
if (matrix[m][n] == target)
return true;
else if (matrix[m][n] < target)
m++;
else if (matrix[m][n] > target)
n--;
}
return false;
}
题目描述:
合并 k 个排序链表,返回合并后的排序链表。
技术点:
链表 堆 分治算法
思路:
- 遍历所有链表,将所有节点的值放到一个数组中。
- 将这个数组排序,然后遍历所有元素得到正确顺序的值。
- 用遍历得到的值,创建一个新的有序链表。
参考代码:
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists == null)
return null;
int[] nums = new int[1000024];
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0;i < lists.length;i++) {
while(lists[i] != null) {
nums[index++] = lists[i].val;
lists[i] = lists[i].next;
}
}
if (index == 0)
return null;
QuickSort(nums,0,index-1);
ListNode result = new ListNode(nums[0]);
ListNode ix = result;
for (int i = 1;i < index;i++) {
ix.next = new ListNode(nums[i]);
ix = ix.next;
}
return result;
}
private static int count;
private static void QuickSort(int[] num, int left, int right) {
//如果left等于right,即数组只有一个元素,直接返回
if(left>=right) {
return;
}
//设置最左边的元素为基准值
int key=num[left];
//数组中比key小的放在左边,比key大的放在右边,key值下标为i
int i=left;
int j=right;
while(i=key && i 题目描述:
给定一个非空二叉树,返回其最大路径和。
本题中,路径被定义为一条从树中任意节点出发,达到任意节点的序列。该路径至少包含一个节点,且不一定经过根节点。
技术点:
树 深度优先搜索
思路:
递归法,最大和路径的位置共有三种可能的情况:在左子树中、在右子树中和包含当前根结点。
参考代码:
private int maxSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
getMax(root);
return maxSum;
}
private int getMax(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
int left = Math.max(0, getMax(root.left));
int right = Math.max(0, getMax(root.right));
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, left+right+root.val);
return root.val + Math.max(left, right);
}
题目描述:
给定一个非空字符串 s 和一个包含非空单词列表的字典 wordDict,在字符串中增加空格来构建一个句子,使得句子中所有的单词都在词典中。返回所有这些可能的句子。
技术点:
动态规划 回溯算法
思路:
先用动态规划判断是否可拆分,后用回溯获得所有结果。
参考代码:
public List wordBreak(String s, List wordDict) {
List list = new ArrayList<>();
List wordList = new ArrayList<>();
if(wordBreak_check(s,wordDict)){
add(list, wordList, s, wordDict);
}
return list;
}
private void add(List list,List wordList,String s,List wordDict){
for(String str : wordDict){
if(s.startsWith(str)){
if(s.length() == str.length()){
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
for(String word : wordList){
b.append(word).append(" ");
}
b.append(str);
list.add(b.toString());
}else{
wordList.add(str);
add(list, wordList, s.substring(str.length()), wordDict);
wordList.remove(wordList.size()-1);
}
}
}
}
public boolean wordBreak_check(String s, List wordDict) {
int maxWordLength = 0;//字典中单词最长长度
for(int i=0;i0?i-maxWordLength:0;
for(int j=x;j 面经专题系列:
Android面经| 问题归纳
Android面经| 回顾展望
Android面经| 算法题解