栈的应用举例
进制转换
/* 进制转换,由十进制转换为8进制 */
void conversion()
{
SLinkList S;
SElemType e;
InitStack(&S);
int N;
scanf("%d",&N);
while (N) {
Push(S,N%8);
N /= 8;
}
/* 这时栈S刚好存放进制转换结果,把每一位按顺序pop出来就可以了 */
while (!StackEmpty(S)) {
Pop(S,&e);
printf("%d",e);
}
DestoryStack(&S);
}括号匹配检测
/* 括号匹配检测 */
void matching()
{
SLinkList S;
SElemType e = 0;
InitStack(&S); /* 初始化栈空间 */
int c;
while ((c=getchar()) != '\n') {
if(c == '(' || c == '[')
Push(S,c);
if(c == ')' || c == ']') {
GetTop(S,&e); /* 获取栈顶元素 */
if(c == ')' && e == '(')
Pop(S,&e); /* 栈顶元素和当前元素匹配则弹出 */
else if(c == ']' && e == '[')
Pop(S,&e);
else { /* 不匹配,则直接退出 */
printf("not pip\n");
DestoryStack(&S);
return;
}
}
}
/* 最后检测栈是否空的 */
if (!StackEmpty(S)) {
printf("not pip\n");
}else {
printf("good\n");
}
DestoryStack(&S);
}行编辑程序
/* 行编辑程序 */
void LineEdit()
{
SLinkList S;
SElemType e;
char str[100];
InitStack(&S); /* 初始化栈空间 */
int c;
while((c=getchar()) != EOF) {
if(c != '\n') { /* 还没到达行尾 */
if(c == '#')
Pop(S,&e);
else if(c == '@')
ClearStack(S); /* 清空栈以撤消改行 */
else
Push(S,c); /* 将字符数据压入栈中 */
}
else {
// ... 在这里已经接收到一行字符,实际中可以传送至调用过程的数据区
int i = 0;
while(!StackEmpty(S)) {
Pop(S,&e); /* 弹出数据存放到数组中 */
str[i++] = e;
}
while (i>0) /* 逆向打印数组内容 */
printf("%c",str[--i]);
printf("\n");
}
}
DestoryStack(&S);
}迷宫求解
示例代码如下
/* 栈的元素类型替换成如下 */
typedef struct {
int ord;
PosType seat; /* 通道块在地图中的坐标位置 */
int di; /* 从此通道走向下一个通道的方向 */
} SElemType;
typedef struct {
int i;
int j;
}PosType;
#define MAP_ROW 10
#define MAP_COL 10
/* 定义地图类型 */
typedef int Map[MAP_ROW][MAP_COL];
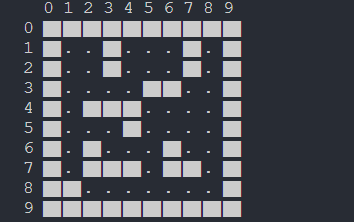
Map map = {
// 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, // 0
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, // 1
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, // 2
1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, // 3
1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, // 4
1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, // 5
1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, // 6
1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, // 7
1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, // 8
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 // 9
};
Map mfoot; /* 辅助地图,用来保存足迹 */
/* 打印地图 */
void printMap(Map map)
{
/* 打印列数 */
printf(" ");
for(int i=0;i表达式求值
/**
* 首先操作数栈为空栈,表达式起始符'#'为运算符栈栈底元素
* 依次读入表达式中每一个字符,若是操作数,则进OPND,若是运算符,则和OPTR栈的栈顶运算符比较优先级后
* 做相应的操作,直至整个表达式求值完毕(即OPTR栈顶元素变成'#')
*/
int isOPTR(int c)
{
if(c>='0' && c<='9')
return FALSE;
else
return TRUE;
}
/** 为了先算括号内的表达式,则符号( 还没入栈时则优先入栈,所以它在外面时总是最大的,
* 而当 ( 符号已经在栈里面,和其他符号比较时它又是最小的,必须让其他元素先进来
* 符号 )本身不入栈,一直在外面,所以优先级最高
* 除了栈外的( ,栈内的乘除优先级最高,因为除了括号外,总是需要先算括号,那么算括号就得让栈外 ( 先入栈
* 已经在栈内的 ( ,也就是说也就在括号里面,则优先级看
*
* 由规则3
*/
int Optr_Table[7][7] = {
// + - * / ( ) #
// +
'>', '>', '<', '<', '<', '>', '>',
// -
'>', '>', '<', '<', '<', '>', '>',
// *
'>', '>', '>', '>', '<', '>', '>',
// /
'>', '>', '>', '>', '<', '>', '>',
// (
'<', '<', '<', '<', '<', '=', ' ',
// )
'>', '>', '>', '>', ' ', '>', '>',
// #
'<', '<', '<', '<', '<', ' ', '='
};
int getIndex(int c)
{
switch (c) {
case '+': return 0;
case '-': return 1;
case '*': return 2;
case '/': return 3;
case '(': return 4;
case ')': return 5;
case '#': return 6;
default:
return 7;
}
}
/* 比较两个运算符的优先级 */
int Precede(int c1, int c2)
{
c1 = getIndex(c1);
c2 = getIndex(c2);
if(c1>6 || c2 >6)
return ' ';
return Optr_Table[c1][c2];
}
/* 计算操作 */
int Operate(int a, int theta, int b)
{
switch (theta) {
case '+': return a + b;
case '-': return b - a;
case '*': return a * b;
case '/': return a / b;
default:
return 0;
}
}
int main()
{
SLinkList OPTR; /* 寄存运算符 */
SLinkList OPND; /* 寄存操作数或运算结果 */
SElemType e;
SElemType top;
InitStack(&OPTR); /* 初始化栈空间 */
InitStack(&OPND);
Push(OPTR,'#');
GetTop(OPTR,&top);
int a,b;
int c = getchar();
while(c != '#' || top != '#') { /* 一个表达式还没结束,或者运算符还没到底 */
if(!isOPTR(c)) {
Push(OPND,c-'0'); /* 不是运算符,压入操作数栈中 */
c = getchar();
}
else {
GetTop(OPTR,&e);
switch (Precede(e,c)) /* 栈顶运算符和当前运算符比较优先级 */
{
case '<' : /* 栈顶元素优先级低 */
Push(OPTR,c);
c = getchar();
break;
case '=' : /* 脱括号并接收下一个字节 */
Pop(OPTR,&e);
c = getchar();
break;
case '>' : /* 运算符出栈并将计算结果如入栈 */
Pop(OPTR,&e);
Pop(OPND,&a);
Pop(OPND,&b);
Push(OPND,Operate(a,e,b));
break;
default:
break;
}
}
GetTop(OPTR,&top);
}
GetTop(OPND,&e);
printf("result: %d\n",e);
DestoryStack(&OPTR);
DestoryStack(&OPND);
}