| 项目 |
内容 |
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 |
https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ |
| 这个作业的要求在哪里 |
https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/11605051.html |
| 作业学习目标 |
|
第一部分:总结第五章理论知识
5.1 类,超类和子类
- 超类是已存在的类,子类是从某个超类继承而来的可以有更多属性和方法的类。
- super关键字用来调用超类中的方法和设计子类的构造器。
- java中,一个超类可以有多个子类,但是一个子类只能有一个父类。
- java中,对象变量是多态的:一个对象变量既可以引用 当前类的对象 也可以引用 当前类的子类的对象。
- final修饰的成员方法不能被子类重写,但可以重载和调用。
- final修饰的类方法不能被继承,但可以创建对象。
- 抽象类:使用 abstract 关键字修饰的不能实例化对象的类,被继承后才能通过子类使用它的方法,
5.2 Object 类:所有类的超类
- Object类是java中所有类的超类
- Object类中的equals方法用于检测一个对象与另一个对象是否有相同的引用
- hashCode方法能得到一个没有规律的整形值
- toString方法用于返回表示对象值的字符串
5.3 泛型数组列表 ArrayList
ArrayList是一个采用类型参量的泛型类。类似数组,但在添加和删除元素时会自动调节数组容量。使用<>指定保存的元素对象类型。("<>"内的类型参数不允许是基本类型,定义基本类型的数组列表可以使用对象包装器类)
- ensureCapacity方法对于知道最大容量的数据很方便。
- trimToSize方法对于不再改变容量大小的数组列表可以清除掉多余的空间。
- 数组列表通过get,set()方法访问数组列表元素
5.4 对象包装器与自动装箱
- 所有的基本类型都有一个与之对应的类,这些类称为 包装器(wrapper)
- 基本类型与对象包装器类的自动转换称为自动装箱与自动拆包。
- 包装器对象的比较最好使用equals方法
- 包装器类可以引用null
5.5 参数数量可变的方法
定义格式: 访问修饰符 返回类型 类名(参数类型 ... 参数名){语句}
5.6 枚举类(enum)
枚举类型定义 : public enum name { ,,,}
5.8 继承的设计技巧
- 将公共操作和域放在超类;
- 不要使用受保护的域;
- 使用继承实现“is-a”关系;
- 除非所有继承的方法都有意义,否则就不要使用继承;
- 在覆盖方法时,不要改变预期的行为;
- 使用多态,而非类型信息。
第二的部分:实验部分
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 理解继承的定义;
(2) 掌握子类的定义要求
(3) 掌握多态性的概念及用法;
(4) 掌握抽象类的定义及用途。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1:测试程序1
代码:
package inheritance; import java.time.*; public class Employee { private String name; private double salary; private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { this.name = name; this.salary = salary; hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public LocalDate getHireDay() { return hireDay; } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; } } public class Manager extends Employee //定义继承自Employee类的Manager类 { private double bonus; /** * @param name the employee's name * @param salary the salary * @param year the hire year * @param month the hire month * @param day the hire day */ public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { super(name, salary, year, month, day); //引用超类的构造器 bonus = 0; } public double getSalary() { double baseSalary = super.getSalary();//引用超类的getSalary方法 return baseSalary + bonus; } public void setBonus(double b) { bonus = b; } } public class ManagerTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // construct a Manager object //定义Manager对象boss var boss = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15); boss.setBonus(5000); var staff = new Employee[3]; // fill the staff array with Manager and Employee objects //把Manganger对象和Employee对象录入staff数组 staff[0] = boss; staff[1] = new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); staff[2] = new Employee("Tommy Tester", 40000, 1990, 3, 15); // print out information about all Employee objects //输出所有雇员的信息 for (Employee e : staff) System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary()); } }
运行结果:
测试程序2
代码:
package abstractClasses; public abstract class Person //定义抽象类 Person { public abstract String getDescription(); private String name; public Person(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getName() { return name; } } import java.time.*; public class Employee extends Person //继承Person类 { private double salary; private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { super(name); this.salary = salary; hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public LocalDate getHireDay() { return hireDay; } public String getDescription() { return String.format("an employee with a salary of $%.2f", salary); } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; } } public class Student extends Person //继承Person类 { private String major; /** * @param name the student's name * @param major the student's major */ public Student(String name, String major) { // pass name to superclass constructor super(name); this.major = major; } public String getDescription() { return "a student majoring in " + major; } } public class PersonTest { public static void main(String[] args) { var people = new Person[2]; // fill the people array with Student and Employee objects people[0] = new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); people[1] = new Student("Maria Morris", "computer science"); // print out names and descriptions of all Person objects for (Person p : people) System.out.println(p.getName() + ", " + p.getDescription()); //打印时调用子类Person类和Employee类的getDescription方法,而不是无法建立实例的Person类 } }
运行结果:
测试程序3
代码:
package equals; import java.time.*; import java.util.Objects; public class Employee { private String name; private double salary; private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { this.name = name; this.salary = salary; hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public LocalDate getHireDay() { return hireDay; } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; } public boolean equals(Object otherObject) { // a quick test to see if the objects are identical if (this == otherObject) return true; // must return false if the explicit parameter is null if (otherObject == null) return false; // if the classes don't match, they can't be equal if (getClass() != otherObject.getClass()) return false; // now we know otherObject is a non-null Employee var other = (Employee) otherObject; // test whether the fields have identical values return Objects.equals(name, other.name) && salary == other.salary && Objects.equals(hireDay, other.hireDay); } public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(name, salary, hireDay); } public String toString() { return getClass().getName() + "[name=" + name + ",salary=" + salary + ",hireDay=" + hireDay + "]"; } } public class Manager extends Employee { private double bonus; public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { super(name, salary, year, month, day); bonus = 0; } public double getSalary() { double baseSalary = super.getSalary(); return baseSalary + bonus; } public void setBonus(double bonus) { this.bonus = bonus; } public boolean equals(Object otherObject) { if (!super.equals(otherObject)) return false; var other = (Manager) otherObject; // super.equals checked that this and other belong to the same class return bonus == other.bonus; } public int hashCode() { return java.util.Objects.hash(super.hashCode(), bonus); } public String toString() { return super.toString() + "[bonus=" + bonus + "]"; } } public class EqualsTest { public static void main(String[] args) { var alice1 = new Employee("Alice Adams", 75000, 1987, 12, 15); var alice2 = alice1; var alice3 = new Employee("Alice Adams", 75000, 1987, 12, 15); var bob = new Employee("Bob Brandson", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); System.out.println("alice1 == alice2: " + (alice1 == alice2)); //判断引用是否相同 System.out.println("alice1 == alice3: " + (alice1 == alice3)); System.out.println("alice1.equals(alice3): " + alice1.equals(alice3));//判断是否是同种类且属性是否相同 System.out.println("alice1.equals(bob): " + alice1.equals(bob)); System.out.println("bob.toString(): " + bob); var carl = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15); var boss = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15); boss.setBonus(5000); System.out.println("boss.toString(): " + boss); System.out.println("carl.equals(boss): " + carl.equals(boss)); System.out.println("alice1.hashCode(): " + alice1.hashCode()); System.out.println("alice3.hashCode(): " + alice3.hashCode()); System.out.println("bob.hashCode(): " + bob.hashCode()); System.out.println("carl.hashCode(): " + carl.hashCode()); } }
运行结果:
实验2:编程练习
代码:
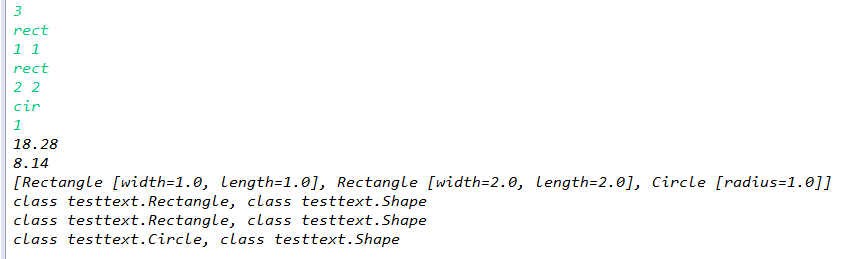
1 package testtext; 2 3 public abstract class Shape { 4 protected final double PI = 3.14; //常量PI 5 protected static double sumArea=0; //存储和 6 protected static double sumPerimeter=0; 7 public abstract double getPerimeter(); 8 public abstract double getArea(); 9 10 protected double sumAllArea(Shape[] s) { 11 for (Shape shape : s) 12 sumArea += shape.getArea(); 13 return sumArea; 14 } 15 protected double sumAllPerimeter(Shape[] s) { 16 for (Shape shape : s) 17 sumPerimeter += shape.getPerimeter(); 18 return sumPerimeter; 19 } 20 } 21 public class Rectangle extends Shape { 22 private double length; 23 private double width; 24 25 public Rectangle(double length, double width) { 26 this.length = length; 27 this.width = width; 28 } 29 public double getPerimeter() { 30 return 2*(length + width); 31 } 32 public double getArea() { 33 return length * width; 34 } 35 36 public String toString() { 37 return "Rectangle [width="+this.width+", length="+this.length+"]"; 38 } 39 } 40 public class Circle extends Shape{ 41 private double radius; 42 43 public Circle(double radius) { 44 this.radius = radius; 45 } 46 public double getPerimeter() { 47 return 2*PI; 48 } 49 public double getArea() { 50 return PI*radius*radius; 51 } 52 public String toString() { 53 return "Circle [radius="+this.radius+"]"; 54 } 55 } 56 57 import java.util.Scanner; 58 59 public class Shapetext { 60 61 public static void main(String[] args) { 62 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 63 int n = in.nextInt(); //输入个数 64 Shape[] shape = new Shape[n]; 65 int i=0; //数据录入 66 while(i<n) { 67 String choose = in.next(); 68 if(choose.equals("rect")) { 69 shape[i] = new Rectangle(in.nextDouble(),in.nextDouble());} 70 else if(choose.equals("cir")){ 71 shape[i] = new Circle(in.nextDouble());} 72 else {System.out.println("No support Shape!");continue;} 73 i++; 74 } 75 //输出所有形状的周长之和,面积之和 76 System.out.println(shape[0].sumAllPerimeter(shape)+"\n"+shape[0].sumAllArea(shape)); 77 System.out.print("["); 78 //输出形状及其属性 79 i=0; 80 for(Shape S : shape) { 81 System.out.print(S); 82 if(i!=n-1) 83 System.out.print(", "); 84 i++; 85 } 86 System.out.println("]"); 87 //输出类名与超类名 88 for(Shape s : shape) { 89 System.out.println(s.getClass()+", "+s.getClass().getSuperclass()); 90 } 91 92 in.close(); 93 } 94 95 }
运行结果:
第三部分:实验总结
在本次实验中对Java程序设计中类与对象的关系有了新的理解,对OO程序设计的特征:继承与多态有了认识,掌握了类继承的语法规则及对象使用要求,知道了抽象类的用途和使用方法。
通过背录代码让我更加深刻的理解了本章的知识。