---恢复内容开始---
Mybatis入门介绍
一、MyBatis介绍
什么是MyBtis?
MyBatis 是一个简化和实现了 Java 数据持久化层(persistence layer)的开源框架,它抽象了大量的 JDBC 冗余代 码,并提供了一个简单易用的 API 和数据库交互。
MyBatis 的前身是 iBATIS,iBATIS 于 2002 年由 Clinton Begin 创建。MyBatis 3 是 iBATIS 的全新设计,支持 注解和 Mapper。
MyBatis 流行的主要原因在于它的简单性和易使用性。在 Java 应用程序中,数据持久化层涉及到的工作有:将从数据库查询到的数据生成所需要的 Java 对象;将 Java 对象中的数据通过 SQL 持久化到数据库中。
MyBatis 通过抽象底层的 JDBC 代码,自动化 SQL 结果集产生 Java 对象、Java 对象的数据持久化数据库中的过程 使得对 SQL 的使用变得容易。 如
为什么选择MyBtis?
- 最重要的就是消除了很多JDBC是冗余。
- 学习成本很低
- 他能很好的与传统数据库协同工作。
- 支持SQL语句。
- 他提供了与spring框架的集成。
- 它引入的性能较好。
二、JDAC
Java 通过 Java 数据库连接(Java DataBase Connectivity,JDBC)API 来操作关系型数据库,但是 JDBC 是一个 非常底层的 API,我们需要书写大量的代码来完成对数据库的操作。
我先从最传统是JDBC代码写起再来对比引入MyBatis后两者的比较就会显而易见了。
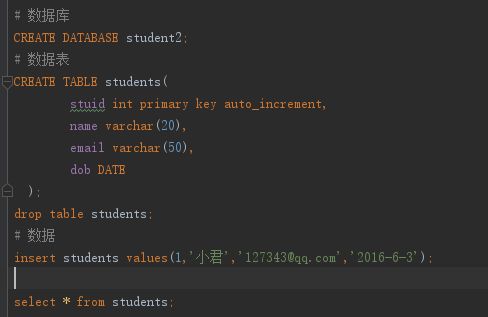
第一步:创建数据库
第二步:Student实体类
1 package com.nf; 2 3 import java.sql.Date; 4 5 public class Student { 6 7 private Integer stuid; 8 private String name; 9 private String email; 10 private Date dob; 11 12 public Integer getStuid() { 13 return stuid; 14 } 15 16 public void setStuid(Integer stuid) { 17 this.stuid = stuid; 18 } 19 20 public String getName() { 21 return name; 22 } 23 24 public void setName(String name) { 25 this.name = name; 26 } 27 28 public String getEmail() { 29 return email; 30 } 31 32 public void setEmail(String email) { 33 this.email = email; 34 } 35 36 public Date getDob() { 37 return dob; 38 } 39 40 public void setDob(Date dob) { 41 this.dob = dob; 42 } 43 44 @Override 45 public String toString() { 46 return "Student{" + 47 "stuid=" + stuid + 48 ", name='" + name + '\'' + 49 ", email='" + email + '\'' + 50 ", dob=" + dob + 51 '}'; 52 } 53 }
第三步:创建StudentMapper接口
package com.nf; import java.sql.SQLException; public interface StudentDao { //方法 public Student findStudentByid(int stuid) ; }
第四步:创建StudentMapperImpl实现类
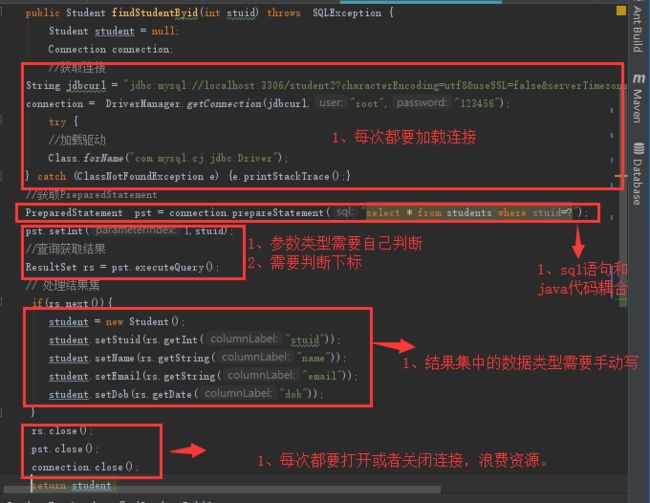
package com.nf; import java.sql.*; public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao { @Override public Student findStudentByid(int stuid) throws SQLException { Student student = null; Connection connection; //获取连接 String jdbcurl = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student2?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC&rewriteBatchedStatements=true"; connection = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcurl,"root","123456"); try { //加载驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } //获取PreparedStatement PreparedStatement pst = connection.prepareStatement("select * from students where stuid=?"); pst.setInt(1,stuid); //查询获取结果 ResultSet rs = pst.executeQuery(); // 处理结果集 if(rs.next()){ student = new Student(); student.setStuid(rs.getInt("stuid")); student.setName(rs.getString("name")); student.setEmail(rs.getString("email")); student.setDob(rs.getDate("dob")); } rs.close(); pst.close(); connection.close(); return student; }
获取数据:
JDBC缺点分析:
上述的每个方法中有大量的重复代码:创建一个连接,创建一个 Statement 对象,设置输入参数,关闭资源(如 connection,statement,resultSet)。
三、MyBatis
我们现在使用MyBatis现实上面的代码:
3.1 添加依赖(pom.xml)
12 org.mybatis 3mybatis 43.5.2 5
3.2 全局配置文件(config.xml )
1 2 3 "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> 4 56 7 default="mycom"> 8 9 2110 11 2012 13 14 1915 16 17 18 22 2423
3.3配置文件 StudentMapper.xml ( StudentMapper.xml )
第一步: 在 SQL Mapper 映射配置文件中配置 SQL 语句,假定为 StudentMapper.xml
查询操作:
//StudentMapper.xml <!-- mapper:根标签,namespace:命名空间,随便写,一般保证命名空间唯一 -->
<!-- statement,内容:sql语句。id:要与接口方法名相同,在同一个命名空间下保持唯一 resultType:parameter:需要返回的类型;sql语句查询结果集的封装类型,tb_user即为数据库中的表 --> //查询
3.4 测试类
1 public class Test2 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { 3 SqlSessionFactory factory = null; 4 try { 5 //指定全局配置的文件xml再读取配置文件 6 //(这里可以比喻成一个建筑图 工程师要建房子首先要先看图纸,我们现在把config.xml看做是一张图纸) 7 InputStream inputStream= Resources.getResourceAsStream("config.xml"); 8 // 构建sqlSessionFactory(创建一个工厂) 9 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(); 10 factory = builder.build(inputStream); 11 System.out.println("1.配置的config.xml"+inputStream); 12 System.out.println("2.创建出一个工厂"+factory); 13 } catch (IOException e) { 14 e.printStackTrace(); 15 } 16 // 获取sqlSession(打开工厂) 17 SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession(); 18 System.out.println("3.session"+sqlSession); 19 //StudentMapper层(将东西放进工厂生产) 20 StudentDao studentDao = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class); 21 System.out.println("4.获得实现类的实例:"+studentDao); 22 Student student = studentDao.findStudentByid(1); 23 System.out.println(student); 24 25 sqlSession.close(); 26 } 27 }
删除操作:
第一步:接口写入一个方法(findStudenrdelete()):
package com.nf; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.List; public interface StudentDao { // 查询 public Student findStudentByid(int stuid) throws SQLException; // 删除 public boolean findStudentdelete(int stuid);
第二步: 配置文件 StudentMapper.xml
1 2 3 4 56 7 8 13 14 //查询 15 19 20 //删除 id:与接口的方法名要一致 Student的实体类 219 10 11 12 22 DELETE FROM students WHERE stuid=#{Id} 23
24
第三步:测试类(Testdelete.java)
1 package com.nf; 2 3 import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; 4 import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; 5 import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; 6 import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; 7 8 import java.io.IOException; 9 import java.io.InputStream; 10 11 12 //删除 13 public class Test4 { 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 SqlSessionFactory factory = null; 16 try { 17 InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("config.xml"); 18 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(); 19 factory = builder.build(inputStream); 20 } catch (IOException e) { 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 } 23 SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession(); 24 StudentDao studentDao = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class); 25 26 boolean ok = studentDao.findStudentdelete(1);//点接口方法名 27 if(ok){ 28 System.out.println("删除成功"); 29 }else{ 30 System.out.println("删除失败"); 31 } 32 sqlSession.commit(); 33 } 34 }
添加操作:
第一步:接口写入一个方法(findStudenrdelete()):
package com.nf; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.List; public interface StudentDao { // 查询 public Student findStudentByid(int stuid) throws SQLException; // 删除 public boolean findStudentdelete(int stuid); // 添加 public boolean findStudentInsert(Student student); }
第二步:第二步: 配置文件 StudentMapper.xml
1 2 3 4 56 7 8 13 14 15 19 20 219 10 11 12 22 delete from students where stuid=#{Id} 23 24 //添加 2526 INSERT INTO students(name,email,dob) value(#{name},#{email},#{dob}) 27 28
第三步:测试类(TestInsert.java)
1 package com.nf; 2 3 import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; 4 import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; 5 import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; 6 import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; 7 8 import java.io.IOException; 9 import java.io.InputStream; 10 import java.sql.Date; 11 import java.sql.SQLException; 12 import java.text.ParseException; 13 import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; 14 15 //添加 16 public class Test3 { 17 public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { 18 SqlSessionFactory factory = null; 19 try { 20 InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("config.xml"); 21 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(); 22 factory = builder.build(inputStream); 23 System.out.println("配置xml"+inputStream); 24 System.out.println("创建出一个工厂"+factory); 25 } catch (IOException e) { 26 e.printStackTrace(); 27 } 28 SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession(); 29 StudentDao studentDao = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class); 30 Student student = new Student(); 31 //student.setStuid(4); 32 student.setName("小华"); 33 student.setEmail("[email protected]"); 34 // 日期转类型 35 SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"); 36 java.util.Date date = null; 37 try { 38 date= simpleDateFormat.parse("2055-6-2"); 39 } catch (ParseException e) { 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 } 42 //new java.sql.Date(date.getTime()); 43 student.setDob( new java.sql.Date(date.getTime())); 44 //不严谨 45 //student.setDob(Date.valueOf("2055-6-2")); 46 boolean ok =studentDao.findStudentInsert(student); 47 if(ok){ 48 System.out.println("添加成功"); 49 }else{ 50 System.out.println("添加失败"); 51 } 52 studentDao.findStudentInsert(student); 53 54 sqlSession.commit(); 55 System.out.println(student.getStuid()); 56 sqlSession.close(); 57 } 58 }