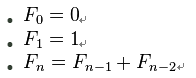一、(6分)
实现type函数用于识别标准类型和内置对象类型,语法如下:
var t = type(obj);
使用举例如下:
var t = type(1) // t==="number"
var t = type(new Number(1)) // t==="number"
var t = type("abc") // t==="string"
var t = type(new String("abc")) // t==="string"
var t = type(true) // t==="boolean"
var t = type(undefined) // t==="undefined"
var t = type(null) // t==="null"
var t = type({}) // t==="object"
var t = type([]) // t==="array"
var t = type(new Date) // t==="date"
var t = type(/\d/) // t==="regexp"
var t = type(function(){}) // t==="function"
解:
/*方法一:识别标准类型和内置类型的*/
function type(obj){
return obj.prototype.toString.call.slice(8,-1);
}
/*方法二:识别所有类型*/
function type(obj){
if(obj){
return obj.constructor.toString().match(/function\s*([^(]*)/)[1]
}else{
return Object.prototype.toString.call(obj).slice(8,-1)
}
}
二、(10分)
ES5中定义的Object.create(proto)方法,会创建并返回一个新的对象,这个新的对象以传入的proto对象为原型。
语法如下:
Object.create(proto) (注:第二个参数忽略)
proto —— 作为新创建对象的原型对象
使用示例如下:
var a = Object.create({x: 1, y: 2});
alert(a.x);
Object.create在某些浏览器没有支持,请给出Object.create的兼容实现。
解:
Object.create=Object.create||function(obj){
var F=function(){};
F.prototype=obj;
return new F();
}
var a = Object.create({x: 1, y: 2});
console.log(a.x);
三、(10分)
高版本的firefox,chrome及ie10以上的浏览器实现了Function.prototype.bind方法,bind方法调用语法为:
functionObj.bind(thisArg[, arg1[, arg2[, ...]]])
使用范例参考如下:
function move(x, y) {
this.x += x;
this.y += y;
}
var point = {x:1, y:2};
var pointmove = move.bind(point, 2, 2);
pointmove(); // {x:3, y:4}
但是低版本浏览器中并未提供该方法,请给出兼容低版本浏览器的bind方法的代码实现。
解:
Function.prototype.bind=function(obj){
var aa=this, args=arguments;
return function(){
aa.apply(obj,Array.prototype.slice.call(args,1))
}
}
function move(x, y) {
this.x += x;
this.y += y;
}
var point = {x:1, y:2};
var pointmove = move.bind(point, 2, 2);
pointmove();
console.log(point);
// {x:3, y:4}
四、(10分)
斐波那契数列(Fibonacci Sequence)由 0 和 1 开始,之后的斐波那契数就由之前的两数相加。在数学上,斐波那契数列是以递归的方法来定义的:
请实现一个函数,参数为n,返回结果为以n为下标的斐波那契数。函数语法为
var num = fibonacci(n);
使用举例如下
var num = fibonacci(3); // num值等于2
var num = fibonacci(5); // num值等于5
解:
function fibonacci(n){
if(n==0){
return 0;
}else if(n==1) {return 1;
}
else{return (arguments.callee(n-1)+arguments.callee(n-2));}
}
var num = fibonacci(3);
console.log(num);//2
var num = fibonacci(5);
console.log(num);//5