简介
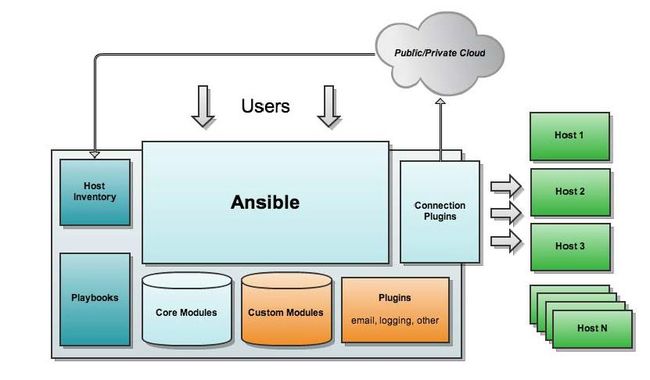
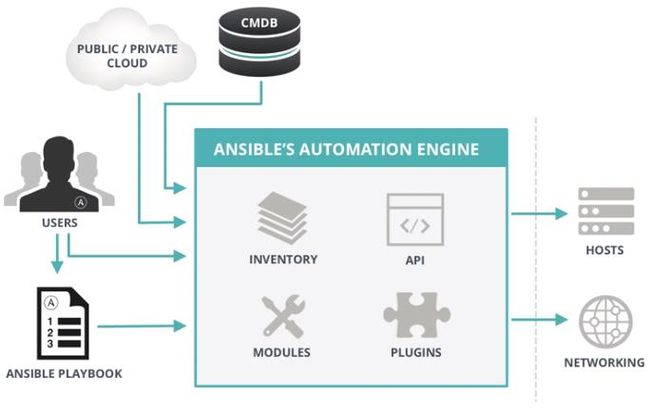
架构
原理
组成
ANSIBLE PLAYBOOKS:任务剧本(任务集),编排定义Ansible任务集的配置文件,由Ansible顺序依次执行,通常是JSON格式的YML文件
INVENTORY:Ansible管理主机的清单/etc/anaible/hosts
MODULES:Ansible执行命令的功能模块,多数为内置核心模块,也可自定义
PLUGINS:模块功能的补充,如连接类型插件、循环插件、变量插件、过滤插件等,该功能不常用
API:供第三方程序调用的应用程序编程接口
ANSIBLE:组合INVENTORY、API、MODULES、PLUGINS的绿框,可以理解为是ansible命令工具,其为核心执行工具
安装
rpm包安装
基于epel:yum install ansible
编译安装
- yum -y install python-jinja2 PyYAMLpython-paramikopython-babelpython-crypto
- tar xfansible-1.5.4.tar.gz
- cdansible-1.5.4
- python setup.pybuild
- python setup.pyinstall
- mkdir/etc/ansible
- cp -r examples/* /etc/ansible
git安装
- gitclone git://github.com/ansible/ansible.git --recursive
- cd ./ansible
- source ./hacking/env-setup
pip安装
pip是安装Python包的管理器,类似yum
- yum install python-pip python-devel
- yum install gccglibc-develzibl-develrpm-bulidopenssl-devel
- pip install --upgrade pip
- pip install ansible--upgrade
inventory
主机清单,ansible的主要功用在于批量主机操作,为了便捷地使用其中的部分主机,可以在inventory file中将其分组命名
默认的inventory file为/etc/ansible/hosts
inventory file可以有多个,且也可以通过Dynamic Inventory来动态生成
/etc/ansible/hosts
ntp.magedu.com
[webservers] # 分组名称
www1.magedu.com:2222 # 默认是ssh的22端口,如果不是22端口需要指定端口号
www2.magedu.com
[dbservers]
db1.magedu.com
db2.magedu.com
db3.magedu.com
[websrvs]
www[01:100].example.com # 列表方式表示主机
[dbsrvs]
db-[a:f].example.com
/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
主配置文件,一般保持默认
[defaults]
#inventory = /etc/ansible/hosts # 主机列表配置文件
#library = /usr/share/my_modules/ # 库文件存放目录
#remote_tmp= $HOME/.ansible/tmp # 临时py命令文件存放在远程主机目录
#local_tmp= $HOME/.ansible/tmp # 本机的临时命令执行目录
#forks = 5 # 默认并发数
#sudo_user= root # 默认sudo用户
#ask_sudo_pass= True # 每次执行ansible命令是否询问ssh密码
#ask_pass= True
#remote_port= 22
#host_key_checking= False # 检查对应服务器的host_key,建议取消注释
#log_path=/var/log/ansible.log # 日志文件,建议取消注释
命令
执行过程
- 加载自己的配置文件默认/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
- 加载自己对应的模块文件,如command
- 通过ansible将模块或命令生成对应的临时py文件,并将该文件传输至远程服务器的对应执行用户$HOME/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-数字/XXX.PY文件
- 给文件+x执行
- 执行并返回结果
- 删除临时py文件,sleep 0退出
执行状态
- 绿色:执行成功并且不需要做改变的操作
- 黄色:执行成功并且对目标主机做变更
- 红色:执行失败
ansible
ansible
- --version:显示版本
- -m module:指定模块,默认位command,可通过修改/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg来修改
- -v:详细过程,-vv,-vvv
- --list-host:显示主机列表,可简写--list
- -k/--ask-pass:提示输入ssh连接密码,默认是key验证
- -K/--ask-become-pass:提示输入sudo时的口令
- -C/--check:检查,并不执行
- -T/--timeout=TIMEOUT:执行命令的超时时间,默认为10s
- -u/--user=REMOTE_user:远程执行时使用的用户
- -b/--become:代替旧版的sudo切换
Host-pattern
匹配主机的列表
All :表示所有Inventory中的所有主机
ansibleall –m ping
* :通配符
ansible "*" -m ping
ansible 192.168.1.* -m ping
ansible "*srvs" -m ping
: :逻辑或
ansible 192.168.39.129:192.168.39.140 -m ping
:& :逻辑与
ansible "websrvs:&dbsrvs" –m ping
:! :逻辑非
ansible 'websrvs:!dbsrvs' –m ping # 在websrvs组,但不在dbsrvs组中的主机。注意:此处为单引号
综合逻辑
ansible 'websrvs:dbsrvs:&appsrvs:!ftpsrvs' –m ping
正则表达式
ansible "websrvs:&dbsrvs" –m ping
ansible "~(web|db).*\.magedu\.com" –m ping
示例:
# 以wang用户执行ping存活检测
ansible all -m ping -u wang -k
# 以wang sudo至root执行ping存活检测
ansible all -m ping -u wang –b -k
# 以wang sudo至mage用户执行ping存活检测
ansible all -m ping -u wang –b -k --become-user mage
# 以wang sudo至root用户执行ls
ansible all -m command -u wang --become-user=root -a 'ls /root' -b –k -K
module
ansible-doc -l:列出所有可用模块
ansible-doc -s MODULE:先查看模块帮助
command
在远程主机执行命令,默认模块,可执行简单命令,可忽略-m选项
ansiblesrvs-m command -a 'service vsftpd start'
ansiblesrvs-m command -a 'echo magedu|passwd--stdinwang' # 不成功
注意:不支持$VARNAME<>|;& 等,用shell模块实现
shell
和command相似,用shell执行命令,调用bash执行命令
ansiblesrv-m shell -a 'echo magedu|passwd –stdin wang'
注意:即使使用shell也可能会失败(解决办法:写到脚本时,copy到远程,执行,再把需要的结果拉回执行命令的机器)
script
运行脚本
[root@centos6 app]# cat f1.sh
#!/bin/bash
touch /app/test.txt
[root@centos6 app]# ansible all -m script -a 'f1.sh'
[root@centos6 app]# ansible all -m command -a 'ls /app'
192.168.39.139 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
test.txt
192.168.39.129 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
test.txt
192.168.39.140 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
test.tx
copy
从主控端复制文件到被控端,推送
# 如目标存在,默认覆盖,此处指定先备份
ansiblesrv-m copy -a "src=/root/f1.sh dest=/tmp/f2.sh backup=yes"
# 利用内容,直接生成目标文件
ansiblesrv-m copy -a "content='test content\n' dest=/tmp/f1.txt"
注意:src可以使用相对路径,基于yml文件的相对路径
fetch
从被控端取文件到主控端,与copy相反,拉取,目录可先tar
[root@centos6 app]# ansible all -m fetch -a 'src=/app/nihao dest=/app/'
[root@centos6 app]# tree
.
├── 192.168.39.129
│ └── app
│ └── nihao
├── 192.168.39.139
│ └── app
│ └── nihao
└── 192.168.39.140
└── app
└── nihao
注意:直接拉取过来不是单文件,而是全路径的文件
file
设置文件属性
# 修改被控端文件属主和权限
ansiblesrv-m file -a "path=/root/a.sh owner=wangmode=755"
# 在被控端创建软连接
ansibleweb -m file -a 'src=/app/testfiledest=/app/testfile-link state=link'
hostname
管理主机名,修改主机名,永久生效
ansible test -m hostname -a 'name=test'
cron
计划任务
[root@centos6 ~]# ansible all -m cron -a 'minute=*/5 job="/usr/sbin/ntpdate 172.18.0.1 &> /dev/null" name=synctime' # 创建计划任务
[root@centos6 ~]# ansible all -a 'crontab -l'
192.168.39.139 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
#Ansible: synctime
*/5 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate 172.18.0.1 &> /dev/null
192.168.39.129 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
#Ansible: synctime
*/5 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate 172.18.0.1 &> /dev/null
192.168.39.140 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
#Ansible: synctime
*/5 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate 172.18.0.1 &> /dev/null
[root@centos6 ~]# ansible all -m cron -a 'state=absent name=synctime' # 删除计划任务
[root@centos6 ~]# ansible all -a 'crontab -l'
192.168.39.139 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
192.168.39.129 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
192.168.39.140 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
yum
管理包
ansible srv-m yum -a 'name=httpdstate=latest' # 安装
ansiblesrv-m yum -a 'name=httpdstate=absent' # 删除
service
管理服务
ansible srv-m service -a 'name=httpdstate=stopped' # 关闭服务
ansiblesrv-m service -a 'name=httpdstate=started' # 开启服务
ansiblesrv–m service –a 'name=httpdstate=reloaded' # 重载配置文件
ansiblesrv-m service -a 'name=httpdstate=restarted' # 重启服务
user
管理用户
# 创建用户,添加描述信息,指定uid,指定家目录,指定属组
ansible srv -m user -a 'name=user1 comment="test user" uid=2048 home=/app/user1 group=root'
# 创建系统用户,指定家目录
ansible srv -m user -a 'name=sysuser1 system=yes home=/app/sysuser1'
# 删除用户,并删除家目录
ansible srv -m user -a 'name=user1 state=absent remove=yes'
group
管理组
ansible srv -m group -a "name=testgroupsystem=yes" # 创建系统组
ansiblesrv-m group -a "name=testgroupstate=absent" # 删除组
ansible-doc
显示模块帮助,ansible-doc [options][module...],常用选项:
- -a:显示所有模块的文档
- -l/--list:列出可用模块
- -s/--snippet:显示指定模块的playbook片段
ansible-doc –l # 列出所有模块
ansible-doc ping # 查看指定模块帮助用法
ansible-doc –s ping # 查看指定模块帮助用法
ansible-galaxy
连接https://galaxy.ansible.com 下载相应的roles
列出所有已安装的galaxy:ansible-galaxy list
安装galaxy:ansible-galaxy install geerlingguy.redis
删除galaxy:ansible-galaxy remove geerlingguy.redis
ansible-pull
推送命令至远程,效率无限提升,对运维要求较高
ansible-playbook
ansible-playbook
- --check:只检测可能会发生的改变,但不真正执行操作
- --list-hosts:列出运行任务的主机
- --limit:指定主机列表,只针对主机列表中的主机执行
- -v:详细过程,-vv,-vvv
ansible-playbook file.yml--check # 只检测,不执行
ansible-playbook file.yml # 执行
ansible-playbook file.yml--limit websrvs # 指定主机列表执行
ansible-vault
管理加密解密yml文件,常用动作:
- encrypt:加密
- decrypt:解密
- view:查看
- edit:编辑机密文件
- rekey:修改口令
- create:创建新文件
ansible-console
2.0+新增,可交互执行命令,支持tab
root@all (3)[f:5]:执行用户@当前操作的主机组(当前组的主机数量)[f:并发数]
设置并发数:forks n 例如:forks 10
切换组:cd 主机组例如:cd web
列出当前组主机列表:list
列出所有的内置命令:?或help
[root@centos6 app]# ansible-console
Welcome to the ansible console.
Type help or ? to list commands.
root@all (3)[f:5]$ list
192.168.39.129
192.168.39.140
192.168.39.139
root@all (3)[f:5]$ cd webservers
root@webservers (2)[f:5]$ list
192.168.39.129
192.168.39.140
root@webservers (2)[f:5]$ yum name=httpdstate=present
root@webservers (2)[f:5]$ service name=httpdstate=started
root@webservers (2)[f:5]$ shell ss -tnl|grep :80
192.168.39.129 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
LISTEN 0 128 :::80 :::*
192.168.39.140 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
LISTEN 0 128 :::80 :::*
playbook
playbook是由一个或多个“play”组成的列表
play的主要功能在于将事先归并为一组的主机装扮成事先通过ansible中的task定义好的角色。从根本上来讲,所谓task无非是调用ansible的一个module。将多个play组织在一个playbook中,即可以让它们联同起来按事先编排的机制同唱一台大戏
Playbook采用YAML语言编写
YAML
YAML是一个可读性高的用来表达资料序列的格式。更多的内容及规范参见http://www.yaml.org
- 在单一档案中,可用连续三个连字号(——)区分多个档案。另外,还有选择性的连续三个点号( ... )用来表示档案结尾
- 次行开始正常写Playbook的内容,一般建议写明该Playbook的功能
- 使用#号注释代码
- 缩进必须是统一的,不能空格和tab混用
- 缩进的级别也必须是一致的,同样的缩进代表同样的级别,程序判别配置的级别是通过缩进结合换行来实现的
- YAML文件内容和Linux系统大小写判断方式保持一致,是区别大小写的,k/v的值均需大小写敏感
- k/v的值可同行写也可换行写。同行使用:分隔
- v可是个字符串,也可是另一个列表
- 一个完整的代码块功能需最少元素需包括name: task
- 一个name只能包括一个task
- YAML文件扩展名通常为yml或yaml
- List:列表,其所有元素均使用“-”打头。具体在ansible playbook中,列表所描述的是局部环境,它不一定要有名称,不一定要从同一个属性开始,只要使用"- ",它就表示圈定一个范围,范围内的项都属于该列表
- Dictionary:字典,通常由多个key与value构成。具体到playbook中,一般"虚拟性"的内容都可以通过字典的方式书写,而实体化的、动作性的、对象性的内容则应该定义为列表形式。
name: John Smith
age: 41
gender: Male
spouse:
name: Jane Smith
age: 37
gender: Female
children:
- name: Jimmy Smith
age: 17
gender: Male
- name: Jenny Smith
age: 13
gender: Female
hosts
用于指定要执行指定任务的主机,须事先定义在主机清单中
格式:
- 192.168.1.*
- Websrvs:dbsrvs:两个组的并集
- Websrvs:&dbsrvs:两个组的交集
- webservers:!phoenix:在websrvs组,但不在dbsrvs组
- hosts: websrvs:dbsrvs
remote_user
可用于Host和task中。也可以通过指定其通过sudo的方式在远程主机上执行任务,其可用于play全局或某任务;此外,甚至可以在sudo时使用sudo_user指定sudo时切换的用户
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: test connection
ping:
remote_user: magedu
sudo: yes # 默认sudo为root
sudo_user: wang # sudo为wang
gather_facts
ansible-playbook的第一个步骤总是执行gather_facts,不论你有没有再playbook设定这个tasks,而且通常这步时间都会比较久,因为需要家藏facts库。因此如果不需要获取被控端fact数据的话,可以关闭fact数据功能(playbook中添加 gather_facts: no 和hosts对齐即可)
---
- hosts: '7'
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: touch file
file: name=/app/test state=touch
可以设置"gather_facts: no"来禁止ansible收集facts信息,但是有时候又需要使用facts中的内容,这时候可以设置facts的缓存。例如,在空闲的时候收集facts,缓存下来,在需要的时候直接读取缓存进行引用。
先来查看一下/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg中facts的默认设置
#gathering = implicit
gathering的三种状态:
- implicit:默认收集
- explicit:默认不收集
- smart:默认收集,但facts已有的情况下不会收集,即使用缓存facts
tasks
play的主体部分是task list。task list中的各任务按次序逐个在hosts中指定的所有主机上执行,即在所有主机上完成第一个任务后再开始第二个。在运行自上而下某playbook时,如果中途发生错误,所有已执行任务都将回滚,因此,在更正playbook后重新执行一次即可
task的目的是使用指定的参数执行模块,而在模块参数中可以使用变量。模块执行是幂等的,这意味着多次执行是安全的,因为其结果均一致
每个task都应该有其name,用于playbook的执行结果输出,建议其内容尽可能清晰地描述任务执行步骤。如果未提供name,则action的结果将用于输出
# 临时禁用selinux
tasks:
- name: disable selinux
command: /sbin/getenforce 0
# 如果命令或脚本的退出码不为零,可以使用如下方式替代
tasks:
- name: run this command and ignore the result
shell: /usr/bin/somecommand || /bin/true
# 或者使用ignore_errors来忽略错误信息
tasks:
- name: run this command and ignore the result
shell: /usr/bin/somecommand
ignore_errors: true
[root@centos6 app]# cat httpd.yml
---
- hosts: webservers
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install httpd
yum: name=httpd
- name: copy httpd.conf
copy: src=/app/httpd7.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
- name: start httpd
service: name=httpd state=started
- hosts: appservers
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install httpd
yum: name=httpd
- name: copy httpd.conf
copy: src=/app/httpd6.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
- name: start httpd
service: name=httpd state=started
[root@centos6 app]# ansible-playbook httpd.yml --list-hosts
playbook: httpd.yml
play #1 (webservers): webservers TAGS: []
pattern: [u'webservers']
hosts (2):
192.168.39.140
192.168.39.129
play #2 (appservers): appservers TAGS: []
pattern: [u'appservers']
hosts (1):
192.168.39.139
[root@centos6 app]# ansible-playbook httpd.yml --check
PLAY RECAP ************************************************************************
192.168.39.129 : ok=4 changed=3 unreachable=0 failed=0
192.168.39.139 : ok=4 changed=3 unreachable=0 failed=0
192.168.39.140 : ok=4 changed=3 unreachable=0 failed=0
[root@centos6 app]# ansible-playbook httpd.yml
PLAY RECAP ************************************************************************
192.168.39.129 : ok=4 changed=3 unreachable=0 failed=0
192.168.39.139 : ok=4 changed=3 unreachable=0 failed=0
192.168.39.140 : ok=4 changed=3 unreachable=0 failed=0
[root@centos6 app]# ansible all -m shell -a 'ss -tnl |grep :8080'
192.168.39.139 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
LISTEN 0 128 :::8080 :::*
192.168.39.129 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
LISTEN 0 128 :::8080 :::*
192.168.39.140 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
LISTEN 0 128 :::8080 :::*
handles和notify
Handlers:是task列表,这些task与前述的task并没有本质上的不同,用于当关注的资源发生变化时,才会采取一定的操作
notify:用于在每个play的最后被触发,这样可避免多次有改变发生时每次都执行指定的操作,仅在所有的变化发生完成后一次性地执行指定操作。在notify中列出的操作称为handler,也即notify中调用handler中定义的操作
[root@centos6 app]# cat httpd.yml
---
- hosts: appservers
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install httpd
yum: name=httpd
- name: copy httpd.conf
copy: src=/app/httpd6.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: restart httpd
- name: start httpd
service: name=httpd state=started
handlers:
- name: restart httpd
service: name=httpd state=restarted
[root@centos6 app]# ansible-playbook httpd.yml
RUNNING HANDLER [restart httpd] ***************************************************
changed: [192.168.39.139]
PLAY RECAP ************************************************************************
192.168.39.139 : ok=5 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0
[root@centos6 app]# ansible appservers -m shell -a 'ss -tnl |grep :9527'
192.168.39.139 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
LISTEN 0 128 :::9527 :::*
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: add group nginx
tags: user
user: name=nginxstate=present
- name: add user nginx
user: name=nginxstate=present group=nginx
- name: Install Nginx
yum: name=nginxstate=present
- name: config
copy: src=/root/config.txtdest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
notify:
- Restart Nginx
- Check NginxProcess
handlers:
- name: Restart Nginx
service: name=nginxstate=restarted enabled=yes
- name: Check Nginxprocess
shell: killall-0 nginx> /tmp/nginx.log # 检查进程是否启动
tags
相当于给tasks中的action起个别名,配合ansible-lpaybook -t TAGS file.yml来执行文件中的指定标签action
注意:-t选项可以指定多个标签同时执行,多个action也可以定义为同一个标签
[root@centos6 app]# ansible appservers -m shell -a 'ss -tnl |grep :9527'
192.168.39.139 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
LISTEN 0 128 :::9527 :::*
[root@centos6 app]# cat httpd.yml
---
- hosts: appservers
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install httpd
yum: name=httpd
- name: copy httpd.conf
copy: src=/app/httpd6.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: restart httpd
tags: conf
- name: start httpd
service: name=httpd state=started
handlers:
- name: restart httpd
service: name=httpd state=restarted
[root@centos6 app]# ansible-playbook httpd.yml --list-tags
playbook: httpd.yml
play #1 (appservers): appservers TAGS: []
TASK TAGS: [conf]
[root@centos6 app]# ansible-playbook -t conf httpd.yml
PLAY [appservers] *****************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ************************************************************
ok: [192.168.39.139]
TASK [copy httpd.conf] ************************************************************
changed: [192.168.39.139]
RUNNING HANDLER [restart httpd] ***************************************************
changed: [192.168.39.139]
PLAY RECAP ************************************************************************
192.168.39.139 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0
[root@centos6 app]# ansible appservers -m shell -a 'ss -tnl |grep :80'
192.168.39.139 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
LISTEN 0 128 :::80 :::*
vars
变量命名:仅能由字母、数字和下划线组成,且只能以字母开头
变量来源:
-
ansible setup facts:远程主机的所有变量都可直接调用
ansible 192.168.39.139 -m setup # 收集关于远程主机的事实,可以看到变量[root@centos6 app]# cat var.yml --- - hosts: appservers remote_user: root tasks: - name: create log file file: name=/app/{{ ansible_fqdn }} state=touch [root@centos6 app]# ansible appservers -m setup |grep ansible_fqdn "ansible_fqdn": "test", [root@centos6 app]# ansible-playbook var.yml --check PLAY RECAP ************************************************************************ 192.168.39.139 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 [root@centos6 app]# ansible-playbook var.yml PLAY RECAP ************************************************************************ 192.168.39.139 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 [root@centos6 app]# ansible appservers -a "ls /app" 192.168.39.139 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> test -
在/etc/ansible/hosts中定义
[webservers] 192.168.39.129 http_port=81 # 普通变量,仅在当前主机生效,优先级高于公共变量 192.168.39.140 http_port=82 http_port=80 # 公共变量,组内主机都可用, -
通过命令行指定变量,优先级最高
ansible-playbook –e varname=value[root@centos6 app]# cat var.yml --- - hosts: appservers remote_user: root tasks: - name: install package yum: name={{ pkname }} state=present [root@centos6 app]# ansible-playbook -e pkname=lftp var.yml PLAY RECAP ************************************************************************ 192.168.39.139 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 [root@centos6 app]# ansible appservers -a "rpm -q lftp" [WARNING]: Consider using the yum, dnf or zypper module rather than running rpm. If you need to use command because yum, dnf or zypper is insufficient you can add warn=False to this command task or set command_warnings=False in ansible.cfg to get rid of this message. 192.168.39.139 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> lftp-4.0.9-14.el6.x86_64 -
在playbook中定义
vars: - http6_port: 8080 - http7_port: 9527[root@centos6 app]# cat var.yml --- - hosts: appservers remote_user: root vars: - username=user1 - groupname=group1 tasks: - name: create user user: name={{ username }} - group: create group group: name={{ groupname }} [root@centos6 app]# ansible-playbook var.yml [root@centos6 app]# ansible-playbook -e "username=user2 groupname=group2" var2.yml # 命令行的优先级最高 -
在独立的变量YAML文件中定义,然后再playbook中引用
[root@centos6 app]# cat vars.yml var1: httpd var2: lftp [root@centos6 app]# cat var.yml --- - hosts: appservers remote_user: root vars_files: - vars.yml tasks: - name: create httpd log file: name=/app/{{ var1 }}.log state=touch - name: create lftp log file: name=/app/{{ var2 }}.log state=touch [root@centos6 app]# ansible-playbook var.yml --check PLAY RECAP ************************************************************************ 192.168.39.139 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0 [root@centos6 app]# ansible-playbook var.yml PLAY RECAP ************************************************************************ 192.168.39.139 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0 [root@centos6 app]# ansible appservers -a 'ls /app' 192.168.39.139 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> httpd.log lftp.log 在role中定义
变量调用:
通过{{ variable_name}} 调用变量,且变量名前后必须有空格,有时用"{{ variable_name}}"才生效
-
ansible-playbook –e 选项指定
ansible-playbook test.yml-e "hosts=www user=magedu"
templates
模板,根据模块文件动态生成对应的配置文件
注意:
templates文件必须存放于templates目录下,且命名为.j2 结尾
-
yaml/yml文件需和templates目录平级,目录结构如下:
├── temnginx.yml └── templates └── nginx.conf.j2
示例:利用templates 同步nginx配置文件
[root@centos6 app]# cat temnginx.yml
---
- hosts: appservers
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: template config to remote hosts
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
notify: restart service
- name: start service
service: name=nginx state=starte
handlers:
- name: restart service
service: name=nginx state=restarted
[root@centos6 app]# ansible-playbook temnginx.yml
PLAY RECAP ************************************************************************
192.168.39.139 : ok=3 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
[root@centos6 app]# ansible appservers -a 'ps aux |grep nginx'
192.168.39.139 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
root 11997 0.0 0.4 108944 2048 ? Ss 21:18 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
nginx 11999 0.0 0.5 109368 2700 ? S 21:18 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 12062 0.0 0.2 106120 1136 pts/2 S+ 21:18 0:00 /bin/sh -c ps aux |grep nginx
root 12064 0.0 0.1 103336 848 pts/2 S+ 21:18 0:00 grep nginx
修改文件nginx.conf.j2 下面行为
worker_processes{{ ansible_processor_vcpus}};
[root@centos6 app]# ansible-playbook temnginx.yml
PLAY RECAP ************************************************************************
192.168.39.139 : ok=3 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
[root@centos6 app]# ansible appservers -a 'ps aux |grep nginx'
192.168.39.139 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
root 11997 0.0 0.4 108944 2048 ? Ss 21:18 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
nginx 11999 0.0 0.5 109368 2700 ? S 21:18 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 12062 0.0 0.2 106120 1136 pts/2 S+ 21:18 0:00 /bin/sh -c ps aux |grep nginx
root 12064 0.0 0.1 103336 848 pts/2 S+ 21:18 0:00 grep nginx
算术运算
vim nginx.conf.j2:worker_processes{{ ansible_processor_vcpus**2 }};
[root@centos6 app]# ansible-playbook temnginx.yml
PLAY RECAP ************************************************************************************************************************************************************
192.168.39.139 : ok=3 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
[root@centos6 app]# ansible appservers -a 'ps aux |grep nginx'
192.168.39.139 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
root 13307 0.0 0.4 108944 2048 ? Ss 21:27 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
nginx 13309 0.0 0.5 109368 2792 ? S 21:27 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 13310 0.0 0.5 109368 2700 ? S 21:27 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 13373 0.0 0.2 106120 1140 pts/2 S+ 21:27 0:00 /bin/sh -c ps aux |grep nginx
root 13375 0.0 0.1 103336 852 pts/2 S+ 21:27 0:00 grep nginx
vim nginx.conf.j2:worker_processes{{ ansible_processor_vcpus+2 }};
[root@centos6 app]# ansible-playbook temnginx.yml
PLAY RECAP ************************************************************************************************************************************************************
192.168.39.139 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0
[root@centos6 app]# ansible appservers -a 'ps aux |grep nginx'
192.168.39.139 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
root 13747 0.0 0.4 108944 2052 ? Ss 21:30 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
nginx 13749 0.0 0.5 109368 2796 ? S 21:30 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 13750 0.0 0.5 109368 2796 ? S 21:30 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 13751 0.0 0.5 109368 2776 ? S 21:30 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 13814 0.0 0.2 106120 1136 pts/2 S+ 21:31 0:00 /bin/sh -c ps aux |grep nginx
root 13816 0.0 0.1 103336 852 pts/2 S+ 21:31 0:00 grep nginx
for
格式如下:
{ % for VAR in LIST % }
代码块
{ % endfor % }
示例:
// temnginx.yml
---
- hosts: mageduweb
remote_user: root
vars:
nginx_vhosts:
- web1
- web2
- web3
tasks:
- name: template config
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
// templates/nginx.conf.j2
{% for vhostin nginx_vhosts%}
server {
listen {{ vhost}}
}
{% endfor%}
生成的结果:
server {
listen web1
}
server {
listen web2
}
server {
listen web3
}
// temnginx.yml
- hosts: mageduweb
remote_user: root
vars:
nginx_vhosts:
- web1:
listen: 8080
server_name: "web1.magedu.com"
root: "/var/www/nginx/web1/"
- web2:
listen: 8080
server_name: "web2.magedu.com"
root: "/var/www/nginx/web2/"
- web3:
listen: 8080
server_name: "web3.magedu.com"
root: "/var/www/nginx/web3/“
tasks:
- name: template config
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
// templates/nginx.conf.j2
{% for vhostin nginx_vhosts%}
server {
listen {{ vhost.listen}}
server_name {{ vhost.server_name}}
root {{ vhost.root}}
}
{% endfor%}
生成结果:
server {
listen 8080
server_nameweb1.magedu.com
root /var/www/nginx/web1/
}
server {
listen 8080
server_nameweb2.magedu.com
root /var/www/nginx/web2/
}
server {
listen 8080
server_nameweb3.magedu.com
root /var/www/nginx/web3/
}
if
格式如下:
{% if vhost.server_name is defined %}
server_name {{ vhost.server_name }};
{% endif %}
示例:
// temnginx.yml
- hosts: mageduweb
remote_user: root
vars:
nginx_vhosts:
- web1:
listen: 8080
root: "/var/www/nginx/web1/"
- web2:
listen: 8080
server_name: "web2.magedu.com"
root: "/var/www/nginx/web2/"
- web3:
listen: 8080
server_name: "web3.magedu.com"
root: "/var/www/nginx/web3/"
tasks:
- name: template configto
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
// templates/nginx.conf.j2
{% for vhostin nginx_vhosts%}
server {
listen {{ vhost.listen}}
{% if vhost.server_nameis defined %}
server_name {{ vhost.server_name}}
{% endif%}
root {{ vhost.root}}
}
{% endfor%}
生成的结果
server {
listen 8080
root /var/www/nginx/web1/
}
server {
listen 8080
server_nameweb2.magedu.com
root /var/www/nginx/web2/
}
server {
listen 8080
server_nameweb3.magedu.com
root /var/www/nginx/web3/
}
when
条件测试:如果需要根据变量、facts或此前任务的执行结果来做为某task执行与否的前提时要用到条件测试,通过when语句实现,在task中使用,jinja2的语法格式
示例:
- name: "shutdown RedHatflavored systems"
command: /sbin/shutdown -h now
when: ansible_os_family == "RedHat"
当系统版本为6时,重启nginx服务
[root@centos6 app]# cat when.yml
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: restart nginx
service: name=nginx state=restarted
when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "6"
[root@centos6 app]# ansible-playbook when.yml
PLAY [all] ************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ************************************************************
ok: [192.168.39.139]
ok: [192.168.39.129]
ok: [192.168.39.140]
TASK [restart nginx] **************************************************************
skipping: [192.168.39.129]
skipping: [192.168.39.140]
changed: [192.168.39.139]
PLAY RECAP ************************************************************************
192.168.39.129 : ok=1 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0
192.168.39.139 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
192.168.39.140 : ok=1 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0
[root@centos6 app]# cat when.yml
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: centos6 touch
file: name=/app/cnetos{{ ansible_distribution_major_version }} state=touch
when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "6"
- name: centos7 touch
file: name=/app/centos{{ ansible_distribution_major_version }} state=touch
when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "7"
[root@centos6 app]# ansible-playbook when.yml
PLAY [all] ************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ************************************************************
ok: [192.168.39.140]
ok: [192.168.39.129]
ok: [192.168.39.139]
TASK [centos6 touch] **************************************************************
skipping: [192.168.39.129]
skipping: [192.168.39.140]
changed: [192.168.39.139]
TASK [centos7 touch] **************************************************************
skipping: [192.168.39.139]
changed: [192.168.39.129]
changed: [192.168.39.140]
PLAY RECAP ************************************************************************
192.168.39.129 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
192.168.39.139 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
192.168.39.140 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
[root@centos6 app]# ansible all -a 'ls /app'
192.168.39.139 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
cnetos6
192.168.39.129 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
centos7
192.168.39.140 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
centos7
with_items
迭代,当有需要重复性执行的任务时,可以使用迭代机制
对迭代项的引用,固定变量名为item
示例:
- name: add several users
user: name={{ item }} state=present groups=wheel
with_items:
- testuser1
- testuser2
上面语句的功能等同于下面的语句
- name: add user testuser1
user: name=testuser1 state=present groups=wheel
- name: add user testuser2
user: name=testuser2 state=present groups=wheel
将多个文件进行copy到被控端
- name: Create rsyncd config
copy: src={{ item }} dest=/etc/{{ item }}
with_items:
- rsyncd.secrets
- rsyncd.conf
迭代嵌套子变量
---
- hosts: appservers
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: add some groups
group: name={{ item }} state=present
with_items:
- group1
- group2
- group3
- name: add some users
user: name={{ item.name }} group={{ item.group }}
with_items:
- { name: 'user1', group: 'group1' }
- { name: 'user2', group: 'group2' }
- { name: 'user3', group: 'group3' }
roles
roles就是通过分别将变量、文件、任务、模板及处理器放置于单独的目录中,并可以便捷地include它们的一种机制。角色一般用于基于主机构建服务的场景中,但也可以是用于构建守护进程等场景中
目录
结构如下:
playbook.yml
roles/
project/
tasks/
files/
vars/ 不常用
default/ 不常用
templates/
handlers/
meta/ 不常用
各目录作用:
- files/ :存放由copy或script模块等调用的文件
- templates/:template模块查找所需要模板文件的目录
- tasks/:定义task,role的基本元素,至少应该包含一个名为main.yml的文件;其它的文件需要在此文件中通过include进行包含
- handlers/:至少应该包含一个名为main.yml的文件;其它的文件需要在此文件中通过include进行包含
- vars/:定义变量,至少应该包含一个名为main.yml的文件;其它的文件需要在此文件中通过include进行包含
- meta/:定义当前角色的特殊设定及其依赖关系,至少应该包含一个名为main.yml的文件,其它文件需在此文件中通过include进行包含
- default/:设定默认变量时使用此目录中的main.yml文件
示例:
[root@centos7 .ansible]# tree
.
└── roles
└── ajsalminen.hosts
├── defaults
│ └── main.yml
├── meta
│ └── main.yml
├── README.md
├── tasks
│ ├── hostname.yml
│ ├── hosts.yml
│ └── main.yml
├── templates
│ ├── hostname.j2
│ └── hosts.j2
└── vars
└── FreeBSD.yml
创建
- 创建以roles命名的目录
- 在roles目录中分别创建以各角色名称命名的目录,如webservers等
- 在每个角色命名的目录中分别创建files、handlers、meta、tasks、templates和vars目录;用不到的目录可以创建为空目录,也可以不创建
- 在playbook文件中,调用各角色
调用角色
-
直接调用
--- - hosts: websrvs remote_user: root roles: - mysql - memcached - nginx -
传递变量给角色
--- - hosts: websrvs remote_user: root roles: - mysql - { role: nginx, username: nginx }键role用于指定角色名称,后续的k/v用于传递变量给角色
-
基于条件测试实现角色调用
roles: - { role: nginx, username: nginx, when: ansible_distribution_major_version == '7' }