自上一篇博文以来,网站在很多地方有了改进,最直观的是将网站 UI 进行了美化,添加和完善了一些功能。该篇博文将对博客系统中的博文检索功能模块进行总结。
GitHub:DuanJiaNing/BlogSystem
简述
网站通过类别和标签将一篇博文进行归类和贴标签,同时使用了 Lucene 全文检索框架,博文检索功能可细分为如下几类:
- 通过关键字检索
- 通过类别检索
- 通过标签检索
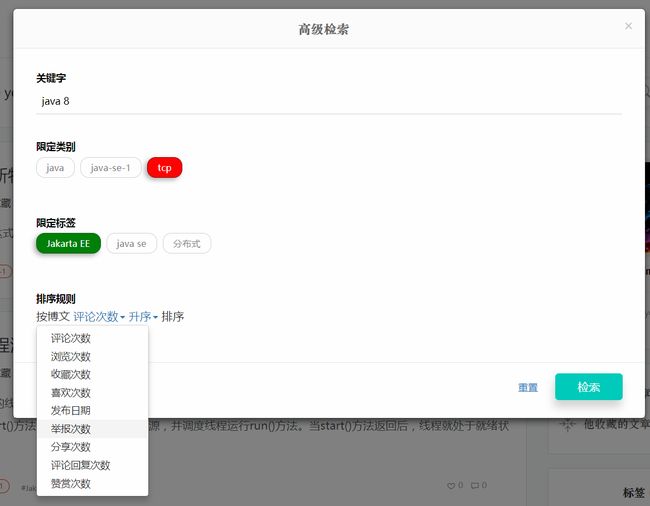
- 高级检索(即同时限定类别,标签以及关键字)
以上的检索方式都将按照默认或指定的排序规则来对结果进行排序。
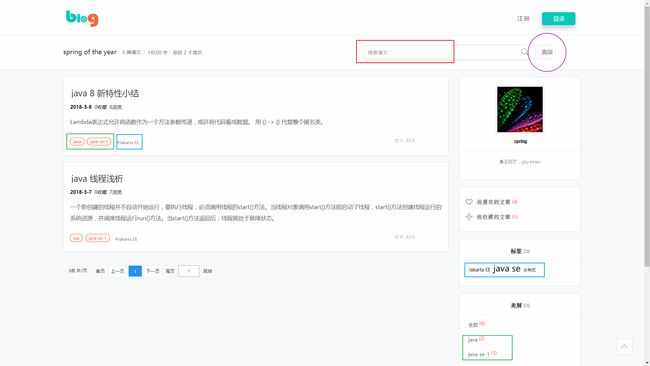
4种检索方式在博主主页都有使用。如下示意图中红绿蓝线框标记处分别为前三种检索方式的功能入口:
而高级检索的入口为紫色的圆框处,对应如下的弹出框:
接下来从前端 js 开始,分析一次检索请求是通过哪些步骤,最终获取到数据的。在此之前先看一下后端对应博文检索API:
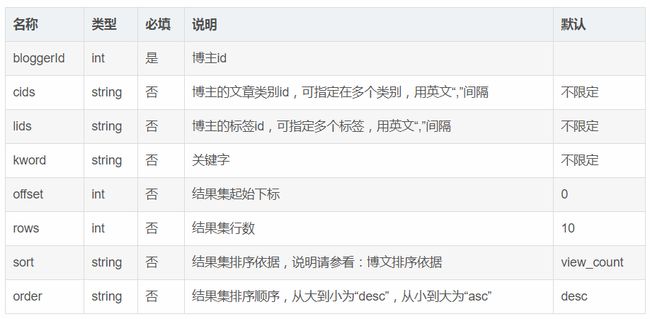
检索指定博主的博文列表 API 说明
- 接口地址:/blog
- 返回格式:json
- 请求方式:get
- 请求参数说明:
- 请求示例:
降序,博文类别id限定为1或2,博文标签限定为2,博主id为1:
http://localhost:8080/blog/1/?order=desc&cids=1,2&lids=2
JavaScript ajax 请求
下面与源码并不一致,将一些干扰代码移除,便于解读。
/**
* 重新加载博文列表
* @param offset 结果集偏移
* @param rows 行数
*/
function filterBloggerBlog(offset, rows) {
$.get(
'/blog',
{
bloggerId: pageOwnerBloggerId,
offset: offset,
rows: rows,
cids: filterData.cids,
lids: filterData.lids,
kword: filterData.kword,
sort: filterData.sort,
order: filterData.order
},
function (result) {
// ...
}, 'json'
);
}
如上代码所示,在发送检索请求时只要灵活修改 filterData 就能从后台获取到想要的数据,通过修改 offset 和 rows 的值则能实现分页功能。
比如在实现 通过博文类别检索 功能时,只需修改 filterData 的 cids (目标类别的id,多个类别用英文","分隔),将 filterData 的其他成员置为 null,发送请求后后端就能根据限定条件返回目标数据。
同理在实现 高级检索 时只需将用户给的值(关键字,类别 id 集,标签 id 集 以及排序规则)赋予 filterData,发起请求即可。
java 后端实现检索功能
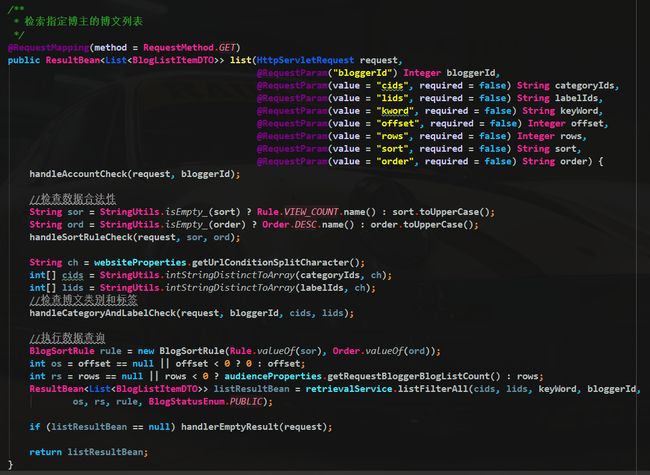
后端 API 方法如下:
方法中首先需要完成一些校验工作,账户校验,排序规则校验,类别和标签校验,所有传入数据合法后就可以调用服务进行数据获取。
检索服务
检索服务为 BlogRetrievalService,检索服务继承于 BlogFilterAbstract,该抽象类是博文检索功能 BlogFilter 接口的通用实现,BlogFilter 中定义了如下方法:
public interface BlogFilter {
/**
* 全限定检索(包括关键字)
*
* @param categoryIds 限定在博主的哪些类别之下,不做限定时传null
* @param labelIds 限定在博主的哪些标签之下,不做限定时传null
* @param keyWord 关键字,不做限定时传null
* @param bloggerId 博主id
* @param offset 结果集起始位置
* @param rows 行数
* @param sortRule 排序规则,为null则不做约束
* @param status 博文状态
* @return 查询结果
*/
T listFilterAll(int[] categoryIds, int[] labelIds, String keyWord, int bloggerId, int offset, int rows,
BlogSortRule sortRule, BlogStatusEnum status);
/**
* 标签&类别检索(无关键字)
*
* @param labelIds 限定在博主的哪些标签之下
* @param categoryIds 限定在博主的哪些类别之下
* @param bloggerId 博主id
* @param offset 结果集起始位置
* @param rows 行数
* @param sortRule 排序规则,为null则不做约束
* @param status 博文状态
* @return 查询结果
*/
T listFilterByLabelAndCategory(int[] categoryIds, int[] labelIds, int bloggerId, int offset, int rows,
BlogSortRule sortRule, BlogStatusEnum status);
/**
* 获得一次检索后的结果集总条数
*
* @return 数量
*/
int getFilterCount();
}
两个关键方法主要的区分依据是检索条件中是否包含关键字,当有关键字时需要使用到 Lucene,而没有关键字时检索流程就会简单些。
BlogFilter 定义的三个方法在 BlogFilterAbstract 中得到了实现,而 BlogFilterAbstract 中定义了一个抽象方法 constructResult ,用于构造最终结果。
/**
* 构造结果集,statistics是经过筛选而且排序了的结果,可借助 statistics 的顺序来得到最终结果
*
* @param blogHashMap 博文id为键,博文为值的map
* @param statistics 已排序的博文统计信息集合
* @param blogIdMapCategoryIds 博文id为键,对应拥有的类别id数组为值的map
* @return 最终结果
*/
protected abstract T constructResult(Map blogHashMap, List statistics, Map blogIdMapCategoryIds);
该方法用于构造最终的结果,该方法的返回值返回给 Controller ,然后 Controller 借由 SpringMVC 转为 json 格式传递给前端。
该方法的第一个参数 blogHashMap 为查询出来的所有符合条件的博文,第二个参数 statistics 为所有符合条件博文的统计信息集合(博文统计信息:博文浏览次数,评论次数,喜欢次数,收藏次数等),而且已经排好序。
在博文检索功能模块的数据获取过程中只有结果集的构建是子类会有不同实现的,而按条件检索和排序的部分是通用的,这部分通用的功能由 BlogFilterAbstract 进行实现。
检索流程
带关键字的检索:
@Override
public T listFilterAll(int[] categoryIds, int[] labelIds, String keyWord,
int bloggerId, int offset, int rows, BlogSortRule sortRule,
BlogStatusEnum status) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(keyWord)) {
//标签&类别检索
return listFilterByLabelAndCategory(categoryIds, labelIds, bloggerId, offset, rows, sortRule, status);
} else {
// 有关键字时需要依赖lucene进行检索
return filterByLucene(keyWord, categoryIds, labelIds, bloggerId, offset, rows, sortRule, status);
}
}
listFilterAll 方法会对带关键字的检索请求进行最终确认,进而调用 filterByLucene 方法进行检索。
/**
* 关键字不为null时需要通过lucene进行全文检索
*
* @param keyWord 关键字
* @param categoryIds 类别id
* @param labelIds 标签id
* @param bloggerId 博主id
* @param offset 结果偏移量
* @param rows 结果行数
* @param sortRule 排序规则
* @param status 博文状态
* @return 经过筛选、排序的结果集
*/
protected T filterByLucene(String keyWord, int[] categoryIds, int[] labelIds,
int bloggerId, int offset, int rows, BlogSortRule sortRule,
BlogStatusEnum status) {
// ------------------------关键字筛选
int[] ids;
try {
// 搜索结果无法使用类似于sql limit的方式分页,这里一次性将所有结果查询出,后续考虑使用缓存实现分页
ids = luceneIndexManager.search(keyWord, 10000);
} catch (IOException | ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new LuceneException(e);
}
//关键字为首要条件
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(ids)) return null;
// 关键字检索得到的博文集合
List filterByLuceneIds = new ArrayList<>();
// UPDATE 取最前面的rows条结果
int row = Math.min(rows, ids.length);
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) filterByLuceneIds.add(ids[i]);
// ----------------------类别、标签筛选
Map map = getMapFilterByLabelAndCategory(bloggerId, categoryIds, labelIds, status);
Integer[] mids = map.keySet().toArray(new Integer[map.size()]);
// 类别、标签检索得到的博文集合
List filterByOtherIds = Arrays.asList(mids);
//求两者交集得到最终结果集
List resultIds = filterByLuceneIds.stream().filter(filterByOtherIds::contains).collect(Collectors.toList());
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(resultIds)) return null;
//构造结果,排序并重组
count.set(resultIds.size());
List blogs = blogDao.listBlogByBlogIds(resultIds, status.getCode(), offset, rows);
return sortAndConstructResult(blogs, sortRule, map);
}
检索流程:
- 通过关键字从 Lucene 的索引库中(索引库在第一次博主创建博文时进行构建,新增、修改或删除博文时进行更新)找到符合条件的博文的 id 集合,全文检索时会通过博文标题,内容,摘要和关键字进行匹配;
- 获取目标行数(这部分代码待完善) ;
- 根据博文 id 集合获取博文,按类别和标签进行过滤;
- 查询博文统计信息,进行排序;
- 调用
constructResult构造结果并返回。
对于无关键字检索只需跳过 1~2 步,从第 4 步开始,从指定博主的所有博文中按类别和标签过滤,排序,构造结果返回即可。
对结果进行排序
// 对筛选出的博文进行排序并重组结果集
private T sortAndConstructResult(List blogs, BlogSortRule sortRule, Map map) {
//用于排序
List temp = new ArrayList<>();
//方便排序后的重组
Map blogHashMap = new HashMap<>();
for (Blog blog : blogs) {
int blogId = blog.getId();
BlogStatistics statistics = statisticsDao.getStatistics(blogId);
temp.add(statistics);
blogHashMap.put(blogId, blog);
}
BlogListItemComparatorFactory factory = new BlogListItemComparatorFactory();
temp.sort(factory.get(sortRule.getRule(), sortRule.getOrder()));
return constructResult(blogHashMap, temp, map);
}
对查询结果的排序依赖于博文统计数据,通过 java.util.Comparator 比较器来实现排序。通过比较器将博文统计信息集排序,重组时只需依据排序过的博文统计信息集就能得到目标结果。