ansible 批量的在大量的主机执行相同的命令
ansible 的安装
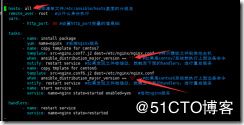
yum install ansible -y 安装包
ansible --version 查看版本信息
1. 查看主机存活不存活
模块 ping
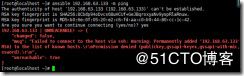
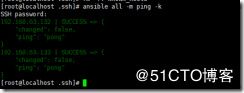
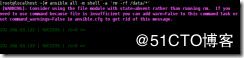
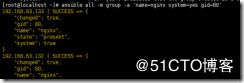
ansible 192.168.63.133 -m ping 直接查看这个ip存不存活报错显示,清单列表里面没有这个ip
[root@localhost ~]# ansible 192.168.63.133 -m ping
[WARNING]: provided hosts list is empty, only localhost is available. Note that the implicit
localhost does not match 'all'
[WARNING]: Could not match supplied host pattern, ignoring: 192.168.63.133
2. 现在将要ansible的客户机的ip加入列表
vim /etc/ansible/hosts 在文件的底部加入ip
192.168.63.133
192.168.63.132
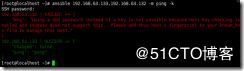
3.再次执行 ansible 192.168.63.133 -m ping 会看到这个命令是基于SSH协议的不是icmp协议
输入yes以后会提示红色的字符显示不可到达
192.168.63.133 | UNREACHABLE! => {
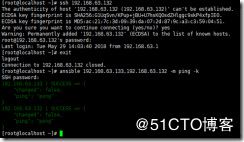
我们可以在命令 ansible 192.168.63.133 -m ping -k 后面加一个 -k :-k的意思是输入用户名密码,利用用户名密码链接
**************************************************************************************
注:我们每次用ssh登录都会特别的慢,我们可以修改配置文件
vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
UseDNS yes :把注释去掉,然后no 改成yes
GSSAPIAuthentication no 把yes改成no
*************************************************************************************
然而我们不是管理一台主机,我们管理的是多台主机,我们可以将ip写在一起,用,逗号隔开
ansible 192.168.63.133,192.168.63.132 -m ping -k
然后发现一个问题,如果两个主机的密码不一样怎么办,它不会让我们输两遍口令,它会提示一个正确,一个错误
如果密码一样,但是还是有一个地方报错
192.168.63.132 | FAILED! => {
是因为它里面有一个基于SSH登录的,一个没有基于SSH登录,所以要重新单独基于ssh的验证登录一些才可以
我们可以先用 ssh 远程登录一下ssh 192.168.63.132,然后在用ansible链接
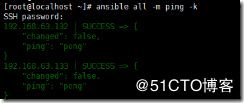
我们还可以用一种方法链接所有的主机,而不用输入ip
ansible all -m ping -k
4.主机清单还可以分组
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
在行为输入,当然ip的后面在生产中为了安全,我们加入端口号
[webservs]
192.168.63.133
[dbsrvs]
192.168.63.132
[appsrvs]
192.168.63.13[2:3]
我们可以用分组的名字ping一下
5. ansible的主配置文件
vim /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
把host_key_checking = False 注释去掉,取消key的检查,以后就不会问yes还是no
ansible all -m ping -k
启用日志,默认是不启用的,我们要记录我们的操作
找到log_path = /var/log/ansible.log这一行,然后把#号注释去掉
log_path = /var/log/ansible.log
6. ansible-doc 显示模块帮助
-l 列出当前可用的模块,的基本信息
ansible-doc -l
ansible-doc ping 查看ping模块的用法
-s 片段,大概看模块的信息
ansible-doc -s ping
7. ansible的用法
-m 指定模块
-v 显示详细过程 -vv -vvv
--list 显示主机列表 ansible all --list 查看所有的主机清单 ansible webservs --list-hosts查看webserver组的清单
-k 用用户名密码登录
-u 指定用户
ansible dbsrvs -m ping -u wang -k 用dbsrvs组的ip 用ping模块测试wang用户
用root的身份查看root家目录下的信息
ansible dbsrvs -u root -k -m command -a'ls /root' :-m command 是默认的不用写,执行命令的模块,-a是指定参数 dbsrvs是ansible清单列表里面的分组的组名
如果要用普通用户的身份查看root用户的家目录的信息,要赋予权限
-K, --ask-become-pass 提示输入sudo
-b, --become 代替旧版的sudo 切换
ansible dbsrvs -u wang -k -m command -a 'ls /root' -b -K
用这个命令执行以后会报错,他显示在客户端还没有sudo授权
我们在客户端sudo授权
visudo
## Allows people in group wheel to run all commands
%wheel ALL=(ALL) ALL
将第二行的注释#号去掉
![]()
usermod -aG wheel wang 执行这条命令,将wang用户加入wheel组
在在ansible服务器端在执行一次命令
ansible dbsrvs -u wang -k -m command -a 'ls /root' -b -K
每次输入sudo的口令,非常的麻烦。我们可以取消输入口令
在客户端输入visudo
## Same thing without a password
%wheel ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL
找到第二行把前面的注释#去掉
## Allows people in group wheel to run all commands
%wheel ALL=(ALL) ALL
在第二行的行首加注释#
8. 如果每个主机的密码都不一样,这样输入用户密码登录实在是太麻烦,我们可以基于key的验证,这样远程连接的的时候就不用输入用户名密码了
ssh-keygen 生成秘钥
ssh-copy-id 192.168.63.133 将私钥发送给133的客户端
ssh-copy-id 192.168.63.132 将私钥发送给132的客户端
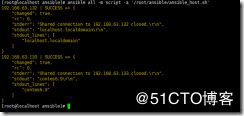
ansible all -m ping 测试,不用加-k,不用输入用户名和密码
9. ansible的主机模式 Host-pattern
all 所有清单的ip
ansible all -m ping
支持单个的分组
ansible dbsrvs -m ping
支持通配符
ansible *srvs -m ping
支持ansible清单里面的ip
ansible 192.168.63.* -m ping
支持或的关系
ansible webservs:dbsrvs -m ping
支持并且的关系,ansible清单里面的分组有相同的ip
ansible 'webservs:&dbsrvs' -m ping
支持逻辑非
ansible '!webservs:dbsrvs' -m ping 在dbsrvs里相同,但是不能在webservs里面相同
支持正则表达式
ansible '~(web|db)srvs' -m ping 以web和db开头包含srvs的行
10. ansible命令执行过程
1. 加载自己的配置文件 默认/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
2. 加载自己对应的模块文件,如command
3. 通过ansible将模块或命令生成对应的临时py文件,并将该 文件传输至远程服务器
的对应执行用户$HOME/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-数字/XXX.PY文件
4. 给文件+x执行
5. 执行并返回结果
6. 删除临时py文件, sleep 0退出
执行状态:
绿色:执行成功并且不需要做改变的操作
×××:执行成功并且对目标主机做变更
红色:执行失败
ansible all -m ping -vvv -vvv详细的过程
11.ansible的常见模块
command 默认模块,不用写
ansible all -a 'ls /root'
file 创建文件夹的模块 ,但是command 模块也可以用
ansible all -a 'removes=/etc/fs cat /data/fstab' 如果前面的命令removes=/etc/fs不存在就不执行后面的命令cat /data/fstab
ansible all -a 'creates=/etc/fs cat /etc/fstab' 如果前面的命令creates=/etc/fs 存在,将不执行后面的命令
ansible all -a 'chdir=/boot ls' 切换到boot目录 ,ls命令查看boot目录下的文件
ansible all -a '/root/f6.sh' 执行 root下的脚本
ansible all -a 'useradd test1' 创建test1的用户
shell 模块 当遇到特殊符号要用shell模块
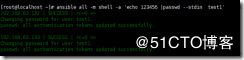
ansible all -m shell -a 'echo 123456 |passwd --stdin test1' 创建更改test1的口令
ansible all -m file -a 'rm -rf /data/*' 删除data目录下的所有数据
script 运行脚本
script不用将脚本推送到其他的主机,只要在ansible端建好脚本执行
在ansible端建好脚本
ansible all -m script -a '/root/ansible/ansible_host.sh' 执行
copy 模块将一个文件推送到其他主机
ansible all -m copy -a 'src=/root/ansible/config dest=/etc/selinux/config backup=yes'
用源文件覆盖目标文件并且备份
src 作为源的文件
dest 目标的文件
baskup=yes 备份
还可以更改权限,所属组主
ansible all -m copy -a 'src=/etc/shadow dest=/data/ mode=000 owner=wang'
将源、/etc/shadown 文件拷贝到/data/目录下,权限为000 属主为wang
ansible all -m copy -a 'content="hello\nnetstwoek\n123" dest=/data/f3'
建自己指定的内容写入f3文件
content 自己指定文件内容
dest=/data/f3 创建一个f3文件
fetch 模块:将其他主机的文件抓取到本机
只能抓取单个文件,必须是文件,不能是目录
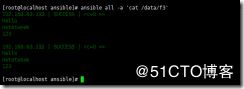
ansible all -m fetch -a 'src=/var/log/messages dest=/data'
抓取目标主机的日志文件到本机的data目录下
在fetch模块下src代表要抓取的目标
在fetch模块下dest,抓取的文件要复制的目录
如何将多个文件抓取过来
1.将多个文件打包
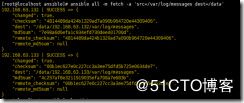
ansible all -m shell -a 'tar Jcf log.tar.xz /var/log/*.log'
2.抓取打包的文件
ansible all -m fetch -a 'src=/root/log.tar.xz dest=/data/'
将打包的文件抓取到data目录下
file模块 设置文件属性
ansible all -m file -a 'name=/data/f7 state=touch'
touch 创建文件
在data目录下创建一个f7的文件
ansible all -m file -a 'name=/data/f7 state=absent'
absent 删除文件
删除data目录下的f7文件
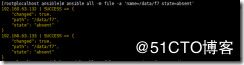
ansible all -m file -a 'name=/data/f1 state=directory'
directory 创建文件夹
在data目录创建f1文件夹
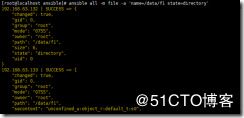
ansible all -m file -a 'src=/etc/fstab dest=/data/fstab.link state=link'
创建软链接,给/etc/fstab文件,创建一个软链接为/data/fstab.link
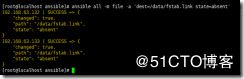
ansible all -m file -a 'dest=/data/fstab.link state=absent'
删除创建的软链接
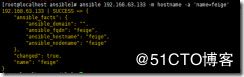
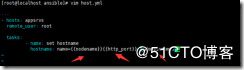
hostname模块 管理主机名
ansible 192.168.63.133 -m hostname -a 'name=feige'
更改63.133主机的主机名为feige
cron模块 计划任务
ansible all -m cron -a 'minute=* weekday=1,3,5 job="/usr/bin/wall hello" name=warnimgcron'
* 代表所有
minute 代表分钟
job 执行的任务
name 任务的名字
hour 代表小时
day 代表一天
weekday 星期几
month 月份
ansible all -m cron -a 'disabled=true job="/usr/bin/wall hello" name=warnimgcron'
或
ansible all -m cron -a 'disabled=yes job="/usr/bin/wall hello" name=warnimgcron'
注释计划任务
disabled=true true代表注释
启用计划任务
ansible all -m cron -a 'disabled=false job="/usr/bin/wall hello" name=warnimgcron'
或
ansible all -m cron -a 'disabled=no job="/usr/bin/wall hello" name=warnimgcron'
disabled=false false是和true相反的
ansible all -m cron -a 'job="/usr/bin/wall hello" name=warnimgcron state=absent'
state=absent
删除计划任务
yum模块 管理包
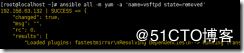
ansible all -m yum -a 'name=vsftpd'
用yum 模块安装vsftpd服务,依赖自身仓库
ansible all -m yum -a 'list=installed' 查看所有装好的包
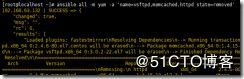
ansible all -m yum -a 'name=vsftpd state=removed'
state=removed 卸载安装好的包
安装多个包
ansible all -m yum -a 'name=vsftpd,memcached,httpd'
包之间用,逗号隔开
卸载多个包
ansible all -m yum -a 'name=vsftpd,memcached,httpd state=removed'
安装单个rpm包,在仓库里面没有
1.用模块copy将包发送到目标主机
ansible 192.168.63.132 -m copy -a 'src=/data/vsftpd-3.0.2-22.el7.x86_64.rpm dest=/root/'
'src=/data/vsftpd-3.0.2-22.el7.x86_64.rpm 要复制的文件
dest=/root/ 要复制到目标主机的目录
2.用yum模块安装包
ansible 192.168.63.132 -m yum -a 'name=/root/vsftpd-3.0.2-22.el7.x86_64.rpm'
在用yum模块安装包的时候可以忽略key的验证
ansible 192.168.63.132 -m yum -a 'name=/root/vsftpd-3.0.2-22.el7.x86_64.rpm disable_gpg_check=yes'
在yum安装包的时候有时候会因为缓存安装不成功,我们可以通过更新缓存解决
当然更新缓存的时候要安装一个包
ansible all -m yum -a 'name=dstat update_cache=yes'
service 管理服务模块
ansible all -m service -a 'name=vsftpd state=started enabled=yes'
启动vstftp的服务并设为开机启动
enabled=yes 开机启动
state=started 启动服务
ansible all -m service -a 'name=vsftpd state=restarted' 重启服务
state=restarted' 重启服务
user 创建用户模块
ansible all -m user -a 'name=nginx shell=/sbin/nologin system=yes home=/var/nginx groups=root uid=80 comment=nginx'
创建一个nginx服务的账号,由于是服务账号,一般都设置成系统账号
系统账号的shell类型是 shell=/sbin/nologin
system=yes 表示这是一个系统账号
home=/var/nginx nginx服务的home家目录是/var/nginx
groups=root 属组是root
uid=80 UID是80
comment=nginx 描述
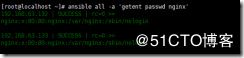
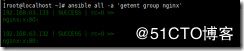
ansible all -a 'getent passwd nginx' 查看结果
ansible all -m user -a 'name=nginx state=absent'
删除用户
ansible all -m user -a 'name=nginx state=absent remove=yes'
删除用户并删除家目录
group 管理组的模板
ansible all -m group -a 'name=nginx system=yes gid=80'
创建一个组nginx
system=yes 是系统组
gid=80 gid是80
ansible all -a 'getent group nginx' 查看创建组的结果
ansible all -m group -a 'name=nginx state=absent'
删除组state=absent
name=nginx 组的名字
ansible-galaxy
连接 https://galaxy.ansible.com 下载相应的roles 角色
Ø 列出所有已安装的galaxy
ansible-galaxy list
Ø 安装galaxy
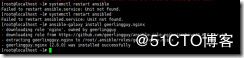
ansible-galaxy install geerlingguy.redis
Ø 删除galaxy
ansible-galaxy remove geerlingguy.redis
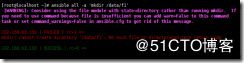
ansible-galaxy install geerlingguy.nginx 在互联网下载角色
[root@localhost ~]# ansible-galaxy install geerlingguy.nginx
- downloading role 'nginx', owned by geerlingguy
- downloading role from https://github.com/geerlingguy/ansible-role-nginx/archive/2.6.0.tar.gz
- extracting geerlingguy.nginx to /root/.ansible/roles/geerlingguy.nginx
- geerlingguy.nginx (2.6.0) was installed successfully
提示存放的位置是 /root/.ansible/roles/geerlingguy.nginx
ansible-galaxy list geerlingguy.nginx 查看版本
ansible-galaxy remove geerlingguy.nginx 删除
#############################################################################
ansible-playbook
ansible-playbook类似脚本,调用的是模块
剧本的英文名称为playbook,只需要将要做的事情编写成playbook,把不同的模块按顺序编排在剧本中,ansible就会按照剧本一步一步的执行,但剧本并不是简单的将命令按照顺序堆砌在一个可执行文件中,
编写剧本要遵循YAML语法
建议后缀是 .yml
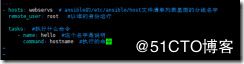
例:vim hello.yml
---
- hosts: webservs # ansible的/etc/ansible/host文件清单列表里面的分组名字
remote_user: root #以谁的身份运行
tasks: #执行什么命令
- name: hello #这个名字是说明
command: hostname #执行的命令
ansible-playbook hello.yml 运行写好的playbook
ansible-vault 加密playbook
ansible-vault encrypt hello.yml 对hello.yum 加密
![]()
ansible-vault view hello.yml 查看hello.yml 加密的内容
ansible-vault edit hello.ym 编辑hello.yml 加密的内容
ansible-vault rekey hello.yml 修改hello.yml 的口令
ansible-vault decrypt hello.yml 解密hello.yml
![]()
ansible-vault create htllo2.yml 创建一个新的加密的playbook的文件
ansible-console 交互式命令
playbook的具体使用
例:
vim file.yml
---
- hosts: webservs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: create new fiel
file: name=/data/newfile state=touch #创建一个文件
- name: create new user
user: name=test2 system=yes shell=/sbin/nologin #创建一个用户,是系统用户,指定shell类型
- name: install
yum: name=httpd #安装一个http服务
- name: copy
copy: src=/var/www/html/index.html dest=/var/www/html/ #复制一个文件到别的主机
- name: start service
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes #启动http服务
ansible-playbook -C file.yml 加-C是测试一次不执行
ansible-playbook file.yml 执行命令
如果playbook某条命令执行错误,后续的命令就不会执行
如果命令或脚本的退出码不为零,可以使用如下方式替代
tasks:
- name: run this command and ignore the result
shell: /usr/bin/somecommand || /bin/true
u或者使用ignore_errors来忽略错误信息:
tasks:
- name: run this command and ignore the result
shell: /usr/bin/somecommand
ignore_errors: True
ansible appsrvs -a 'getent passwd test2' --limit 192.168.63.133
指定对某个主机执行命令
ansible appsrvs -a 'getent passwd test2' --limit 192.168.63.133
ansible-playbook file.yml --list-tasks 查看任务列表
当我们把已经把文件发送给其他主机,但是我们在ansible端又修改了这个文件,我们把这个文件在把这个文件发送给其他主机,会覆盖之前发送的文件,但是这个文件所在的服务已经启动了,该怎么重启这个服务?
handlers
是task列表,这些task与前述的task并没有本质上的不同,用于当关注的资源发生
变化时,才会采取一定的操作
notify这个action可用于在每个play的最后被触发,这样可以避免多次有改变发
生时每次都执行指定的操作,仅在所有的变化发生完成后一次性地执行指定操
作。在notify中列出的操作称为handler,也即notify中调用handler中定义的操
作
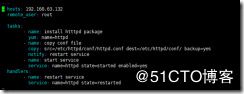
例:我们要实现文件发生变化就重启服务
http.yml
---
- hosts: 192.168.63.132 #目标主机的ip或/etc/ansible/host分组的名字
remote_user: root #以什么用户执行
tasks:
- name: install htttpd package #提示
yum: name=httpd #执行的命令,用yum模块,安装httpd
- name: copy conf file
copy: src=files/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf.d/ backup=yes #用copy模块复制文件到其他主
notify: restart service #如果这个源文件发生变化,并发送给其他主机,则触发下面的handlers
- name: start service
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes #启动服务。并设为开机启动
handlers:
- name: restart service
service: name=httpd state=restarted #当上面的文件修改被触发就重新启动服务
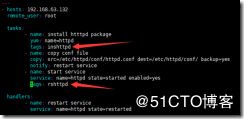
tsgs 标签
通过指定标签执行特定的动作
- hosts: 192.168.63.132
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install htttpd package
yum: name=httpd
tags: inshttpd #安装httpd的标签
- name: copy conf file
copy: src=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/ backup=yes
notify: restart service
- name: start service
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
tags: rshttpd #重启http的标签
handlers:
- name: restart service
service: name=httpd state=restarted
ansible-playbook -t rshttpd httpd.yml 针对单个标签
ansible-playbook -t inshttpd,rshttpd httpd.yml 针对多个标签
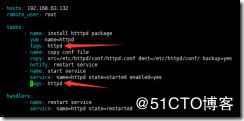
也可以多个动作用一个标签
---
- hosts: 192.168.63.132
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install htttpd package
yum: name=httpd
tags: httpd #安装的标签
- name: copy conf file
copy: src=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/ backup=yes
notify: restart service
- name: start service
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
tags: httpd 启动的标签
handlers:
- name: restart service
service: name=httpd state=restarted
ansible-playbook -t httpd httpd.yml 执行标签
playbook中使用变量
setup模块,里面内置了变量
ansible 192.168.63.129 -m setup
ansible 192.168.63.129 -m setup -a 'filter=ansible_eth0' 查看eth0的变量
例:vim app.yml
---
- hosts: appsrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install package
yum: name={{ pkname }} #大括号里面的自定义变量
- name: start service
service: name={{ pkname }} state=started enabled=yes
ansible-playbook -e 'pkname=vsftpd' app.yml 调用pkname的变量为vsftpd的包
如果装多个包 例: 变量为pkname1 pkname2
ansible-playbook -e 'pkname1=vsftpd pkname2=httpd ' app.yml
可以直接在playbook里面定义变量 用vars
vim app.yml
---
- hosts: appsrvs
remote_user: root
vars:
- pkname: vsftpd
tasks:
- name: install package
yum: name={{ pkname }}
- name: start service
service: name={{ pkname }} state=started enabled=yes
ansible-playbook app.yml 由于在playbook里面定义了变量,在这边自己执行app.yml
也可以在ansible的清单里面定义变量 /etc/ansible/hosts
一种是单独的变量
一种是组有效
对不同主机单独赋值, 132的变量http_port的值81, 129的变量http_port的值82
192.168.63.132 http_port=81
192.168.63.129 http_port=82
调用指定的变量
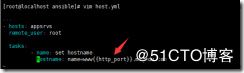
---
- hosts: appsrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: set hostname #声明
hostname: name=www{{http_port}}.magedu.com #hostname的模块是更改主机名
ansible-playbook host.yml 执行
定义组的变量
[appsrvs:vars]
nodename=www
domainname=magedu.com
在playbook中调用
[root@localhost ansible]# vim host.yml
---
- hosts: appsrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: set hostname
hostname: name={{nodename}}{{http_port}}.{{domainname}}
ansible-playbook host.yml 测试
如果在主机清单已经指定了变量的值,但是我们在命令行里面又指定了一个值,这时候是
命令行里面的优先级比清单里面的变量赋值高, ansible-playbook -e 'pkname=vsftpd' app.yml -e指定变量赋值
在清单里面单个主机赋值,不分组的辅助优先级高
我们可以直接调用内置的变量 ansible appsrvs -m setup 查看内置变量
ansible appsrvs -m setup -a "filter=ansible_fqdn" 查看ansible_fqdn变量
例:
[root@localhost ansible]# vim var.yml
---
- hosts: appsrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: create log file #创建一个文件
file: name=/data/{{ ansible_fqdn }}.log state=touch mode=600 #在data目录下创建主机名开头以.log结尾的文件 权限是600
ansible-playbook var.yml 执行playbook
ansible all -m shell -a 'ls /data/' 查看结果
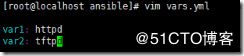
我们可以把定义的变量集中在一个文件里面
[root@localhost ansible]# vim vars.yml
#将定义的变量写入文件
var1: httpd #var1变量的值是httpd
var2: tftpd #var2变量的值是tftpd
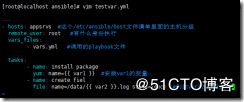
[root@localhost ansible]# vim testvar.yml
---
- hosts: appsrvs #这个/etc/ansible/host文件清单里面的主机分组
remote_user: root #有什么身份执行
vars_files:
- vars.yml #调用的playbook文件
tasks:
- name: install package
yum: name={{ var1 }} #安装var1的变量
- name: create fiel
file: name=/data/{{ var2 }}.log state=touch #创建var2的变量文件
ansible-playbook testvar.yml 执行testvar.yml文件
****************************************************************************************************************************
templates 模板
例如我有两个主机,两个主机的CPU个数不同。然后根据不同的CPU数量生成不同的文件
虽然对模板文件的存放位置没有要求,但是建议放在一个文件夹下例如ansible创建了 一个ansible的文件夹,我们可以在ansible的文件夹下放一个templates的文件夹,ansible不能调用templates
当模板的文件名是有要求的文件名后面要 .j2的后缀例:nginx.conf.j2
例如:将nginx服务的文件当模板拷入templates的文件夹
cp /etc/nginx/nginx.conf /root/ansible/templates/nginx.conf.j2
我们不修改模板文件也能直接调用
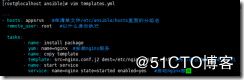
[root@localhost ansible]# vim templates.yml
---
- hosts: appsrvs #在清单文件/etc/ansible/hosts里面的分组名
remote_user: root #以什么身份执行
tasks:
- name: install package
yum: name=nginx #安装nginx服务
- name: copy template
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf #拷贝模板文件到其他主机
- name: start service
service: name=nginx state=started enabled=yes #启动nginx服务
ansible-playbook -C templates.yml 加-C 是测试一次不执行
***************************************************************************************************************************
现在我们修改模板文件,我们要根据CPU 的个数生成不同的配置文件
1.找出CPU的变量
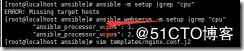
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -m setup |grep "cpu"
ERROR! Missing target hosts
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible webservs -m setup |grep "cpu"
"ansible_processor_vcpus": 1,
2.修改模板文件
vim templates/nginx.conf.j2
worker_processes {{ ansible_processor_vcpus**2 }} **2代表2的2次方
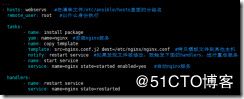
[root@localhost ansible]# vim templates.yml
---
- hosts: webservs #在清单文件/etc/ansible/hosts里面的分组名
remote_user: root #以什么身份执行
tasks:
- name: install package
yum: name=nginx #安装nginx服务
- name: copy template
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf #拷贝模板文件到其他主机
notify: restart service #如果发现文件被修改,就触发下面的handlers,进行重启服务
- name: start service
service: name=nginx state=started enabled=yes #启动nginx服务
handlers:
- name: restart service
service: name=nginx state=restarted
****************************************************************************************************************************
例如:我们想在一个主机里面的nginx的端口是81,另一个主机的nginx的端口是82
1.我们在主机清单里面设置主机的变量,分别是 81和82
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
192.168.63.132 http_port=81
192.168.63.128 http_port=81
2.在到我们复制到template下的nginx文件更改端口的位置。添加变量http_port
vim /root/ansible/templates/nginx.conf.j2
server {
listen {{ http_port }} default_server;
listen [::]:{{ http_port }} default_server;
server_name _;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
当然我们也可以在playbook里面设置变量
vim templates.yml
---
- hosts: webservs #在清单文件/etc/ansible/hosts里面的分组名
remote_user: root #以什么身份执行
vars:
- http_port: 88 #设置http_port变量的值是88
tasks:
- name: install package
yum: name=nginx #安装nginx服务
- name: copy template
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf #拷贝模板文件到其他主机
notify: restart service #如果发现文件被修改,就触发下面的handlers,进行重启服务
- name: start service
service: name=nginx state=started enabled=yes #启动nginx服务
handlers:
- name: restart service
service: name=nginx state=restarted
还可以在命令里面添加变量
ansible-playbook -e "http_port=80" templates.yum
****************************************************************************************************************************
注:我们可以得出结论,变量在命令中优先级最高,在playbook中次之,在主机清单中在次之
************************************************************************************************************************
3.执行playbook
vim templates.yml
---
- hosts: webservs #在清单文件/etc/ansible/hosts里面的分组名
remote_user: root #以什么身份执行
tasks:
- name: install package
yum: name=nginx #安装nginx服务
- name: copy template
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf #拷贝模板文件到其他主机
notify: restart service #如果发现文件被修改,就触发下面的handlers,进行重启服务
- name: start service
service: name=nginx state=started enabled=yes #启动nginx服务
handlers:
- name: restart service
service: name=nginx state=restarted
ansible-playbook templates.yml
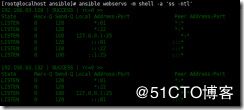
ansible webservs -m shell -a 'ss -ntl' 检查端口
********************************************************************************************************************88
例如:我们要一次性根据版本是centos6还是centos7的系统,进行不同的修改。注意他们的配置文件是不同的
when条件判断
1.在playbook里面写入,when判断语句,如果是centos6执行什么,如果centos7执行什么
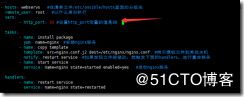
[root@localhost ansible]# vim templates.yml
---
- hosts: all #在清单文件/etc/ansible/hosts里面的分组名。all代表所有的主机
remote_user: root #以什么身份执行
vars:
---
- hosts: webservs #在清单文件/etc/ansible/hosts里面的分组名
remote_user: root #以什么身份执行
vars:
- http_port: 88 #设置http_port变量的值是88
tasks:
- name: install package
yum: name=nginx #安装nginx服务
- name: copy template for centos7
template: src=nginx.conf7.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf #拷贝模板文件到其他主机
when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "7" #如果是centos7系统就执行上面这条命令
notify: restart service #如果发现文件被修改,就触发下面的handlers,进行重启服务
- name: copy tmplate for centos6
template: src=nginx.conf6.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "6" #如果是centos6系统就执行上面这条命令
notify: restart service #如果发现文件被修改,就触发下面的handlers,进行重启服务
- name: start service
service: name=nginx state=started enabled=yes #启动nginx服务
handlers:
- name: restart service
service: name=nginx state=restarted
2.将centos6的nginx服务的配置文件发送给ansible服务器的templates文件夹下并改名为nginx.conf6.j2
scp /etc/nginx/nginx.conf 192.168.63.128:/root/ansible/templates/nginx.conf6.j2
在文件里面修改要修改的内容
3.ansible-playbook templates.yml 执行playbook
****************************************************************************************************************************
with_items 迭代
当我们进行重复性的任务时,可以使用迭代机制
例如:创建多个文件和安装多个包
vim testitem.yml
--- #可写可不写
- hosts: dbsrvs #是ansible的清单列表/etc/ansible/hosts里面的分组的名字
remote_user: root #以什么身份执行
tasks:
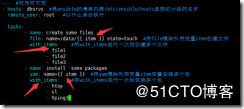
- name: create some files
file: name=/data/{{ item }} state=touch #用file模块引用变量itme创建文件
with_items: #用with_items迭代一次性创建多个文件
- file1
- file2
- file3
- name: install some packages
yum: name={{ item }} #用yum模块利用变量item变量安装多个包
with_items: #用with_items迭代一次性安装多个包
- htop
- sl
- hping3
****************************************************************************************************************************
例如创建多个组
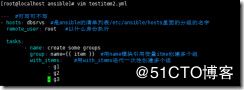
[root@localhost ansible]# vim testitem2.yml
--- #可写可不写
- hosts: dbsrvs #是ansible的清单列表/etc/ansible/hosts里面的分组的名字
remote_user: root #以什么身份执行
tasks:
- name: create some groups #提示的作用
group: name={{ item }} #用name模块引用变量itme创建多个组
with_items: #用with_items迭代一次性创建多个组
- g1
- g2
- g3
****************************************************************************************************************************
例如:我想创建三个组,还想创建三个用户,并将用户加入组
这时候我们就要用到迭代嵌套子变量
--- #可写可不写
- hosts: dbsrvs #是ansible的清单列表/etc/ansible/hosts里面的分组的名字
remote_user: root #以什么身份执行
tasks:
- name: create some groups
group: name={{ item }} #用name模块引用变量itme创建多个组
with_items: #用with_items迭代一次性创建多个组
- g1 #组g1
- g2 #组g2
- g3 #组g2
- name: create some users
user: name={{item.name}} group={{item.group}} #用user模块利用变量item.name创建用户,并将用户加入item.group变量组
with_items:
- { name: 'user1', group: 'g1' } #将用户user1加入 g1组
- { name: 'user2', group: 'g2' } #将用户user2加入 g2组
- { name: 'user3', group: 'g3' } #将用户user3加入 g3组
****************************************************************************************************************************
也可以在模板中做for循环
for循环是重复性的执行一段代码
例如我们想利用for循环生成这样的一个文件
{
server {
listen 81
}
}
{
server {
listen 82
}
}
{
server {
listen 83
}
}
1.创建playbook
[root@localhost ansible]# vim testfor.yml
---
- hosts: dbsrvs
remote_user: root
vars: # 创建变量
ports: #变量的名字
- 81 #变量的值
- 82 #变量的值
- 83 #变量的值
tasks:
- name: copy conf #提示要拷贝
template: src=for1.conf.j2 dest=/data/for1.conf # 原文件是ansible服务器下的templatest目录下的for1.conf.j2模板文件,复制到其他主机的data目录>下并改名为for1.conf
2.创建模板文件
{% for port in ports %} #ports是在playbook文件里面定义的变量名字,port是for循环的变量
server{
listen {{ port }} #调用for循环的变量
}
{% endfor %} #结束时用的符号
4. ansible-playbook testfor.yml 执行playbook
**************************************************************************************************************************8
我们可以在playbook中写入字典,列表嵌套列表
vim testfor2.yml
---
- hosts: dbsrvs
remote_user: root
vars: # 创建函数
ports: #函数的名字
- web1:
port: 81
name: web1.magedu.com
rootdir: /data/website1
- web2:
port: 82
name: web2.magedu.com
rootdir: /data/website2
- web3:
port: 83
name: web3.magedu.com
rootdir: /data/website3
tasks:
- name: copy conf #提示要拷贝
template: src=for1.conf.j2 dest=/data/for2.conf
# 原文件是ansible服务器下的templatest目录下的for1.conf.j2模板文件,复制到其他主机的data目录>下并改名为for1.conf
更改模板文件
vim templates/for1.conf.j2
{% for p in ports %}
server{
listen {{ p.port }}
servername {{ p.name }}
documentroot {{ p.rootdir }}
}
{% endfor %}
****************************************************************************************************************************
我们也可以用if
if是有值就生成,没值就不生成
设置playbook文件里面的字典一个有值一个没值
[root@localhost ansible]# vim testfor3.yml
---
- hosts: dbsrvs
remote_user: root
vars: # 创建函数
ports: #函数的名字
- web1:
port: 81
#name: web1.magedu.com
rootdir: /data/website1
- web2:
port: 82
name: web2.magedu.com
rootdir: /data/website2
- web3:
port: 83
#name: web3.magedu.com
rootdir: /data/website3
tasks:
- name: copy conf #提示要拷贝
template: src=for1.conf.j2 dest=/data/for3.conf
# 原文件是ansible服务器下的templatest目录下的for1.conf.j2模板文件,复制到其他主机的data目录>下并改名为for1.conf
配置模板文件
[root@localhost ansible]# vim templates/for1.conf.j2
{% for p in ports %}
server{
listen {{ p.port }}
{% if p.name is defined %}
servername {{ p.name }}
{% endif %}
documentroot {{ p.rootdir }}
}
{% endfor %}
ansible-playbook testfor3.yml 执行playbook
#############################################################################
roles 角色,适合大型的环境
将原来在一个playbook剧本里面的内容分到其他的文件,可以重复调用
我们可以创建一个roles角色,,里面有各种角色,以后要用直接调用
mkidr roles
mkdir roles/{httpd,mysql,memcache} -pv 创建httpd和MySQL和memcache的角色
/roles/project/ :项目名称,有以下子目录
Ø files/ :存放由copy或script模块等调用的文件
Ø templates/: template模块查找所需要模板文件的目录
Ø tasks/:定义task,role的基本元素,至少应该包含一个名为main.yml的文件;其它的文
件需要在此文件中通过include进行包含
Ø handlers/:至少应该包含一个名为main.yml的文件;其它的文件需要在此文件中通过
include进行包含
Ø vars/:定义变量,至少应该包含一个名为main.yml的文件;其它的文件需要在此文件
中通过include进行包含
Ø meta/:定义当前角色的特殊设定及其依赖关系,至少应该包含一个名为main.yml的文
件,其它文件需在此文件中通过include进行包含
Ø default/:设定默认变量时使用此目录中的main.yml文件
例如:我们要安装nginx服务
1. 创建nginx的组
2. 创建nginx的用户
3. yum安装nginx服务
4.拷贝nginx的配置文件 到template目录下
5.启动nginx服务
1.在roles角色下创建nginx的目录
mkdir roles/nginx
工具要求在nginx下面创建子目录,tasks用来存放.yml文件 和temolates,用来放模板文件
mkdir tasks templates
2.在tasks目录下创建group.yml创建组文件和user.yml创建用户文件还有yum.yml安装包文件, start.yml启动服务文件,restart.yml重新启动服务文件, templ.yml调用模板文件并copy的文件,main.yml 定义了文件该先执行哪个.yml文件,后执行哪个yml文件
vim group.yml
- name: create group
group: name=nginx gid=80 #创建组名为nginx
[root@localhost tasks]# vim user.yml
- name: create user # 创建nginx的用户 组是nginx ,是系统用户,shell类型是/sbin/nologin
user: name=nginx uid=80 gruop=nginx system=yes shell=/sbin/nologin
[root@localhost tasks]# vim yum.yml
- name: install package
yum: name=nginx #安装nginx包
[root@localhost tasks]# vim start.yml
- name: start service #启动nginx服务,并开机启动
service: name=nginx state=started enabled=yes
[root@localhost tasks]# vim restart.yml
- name: restart service #重新启动nginx服务
service: name=nginx state=restarted
[root@localhost tasks]# vim templ.yml
- name: copy copy #调用模板文件,复制到其他主机
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
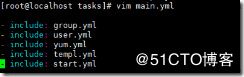
[root@localhost tasks]# vim main.yml 定义所有的文件该先执行什么,后执行什么
- include: group.yml
- include: user.yml
- include: yum.yml
- include: templ.yml
- include: start.yml
3.在templates/ 修改配置文件
cd /root/ansible/roles/nginx/templates/
cp /etc/nginx/nginx.conf /root/ansible/roles/nginx/templates/nginx.conf.j2 将我们原有的nginx文件拿过来修改
以CPU个数的不同来生成不同的配置文件
vim nginx.conf.j2
user nginx;
worker_processes {{ ansible_processor_vcpus+2 }}; #引用cpu的变量
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
4.要调用剧本文件要和roles目录平级,剧本文件就是.yml文件
写调用剧本的剧本文件
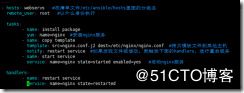
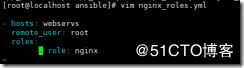
[root@localhost ansible]# vim nginx_roles.yml
- hosts: webservs
remote_user: root
roles:
- role: nginx
5. 测试
ansible-playbook -C nginx_roles.yml -C是空跑一次不执行
****************************************************************************************************************************
实现httpd角色服务,我们实现的编译安装,我们已经在一台主机安装好了,我们把已经安装好的文件打包
1. cd /root/ansible/roles/httpd/ 切换目录
mkdit ansible/roles/httpd/file 创建一个文件
cp /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf /root/ansible/roles/httpd/file/ 将httpd打包的文件传到这个文件
2.创建Apache用户
[root@localhost tasks]# vim user.yml
- name: create user
user: name=apache system=yes shell=/sbin/nologin
3.[root@localhost tasks]# vim copy.yml
- name: copy file #将http的文件发送给其他主机
copy: src=src=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf dest=/data/ owner=apache
3.定义先执行哪个剧本
[root@localhost tasks]# vim main.yml
- include: user.yml
- include: copy.yml
4.在roles平级的目录创建,要调用剧本的剧本
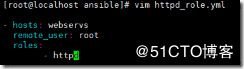
[root@localhost ansible]# vim httpd_role.yml
- hosts: webservs
remote_user: root
roles:
- httpd
5.测试
ansible-playbook -C httpd_role.yml
***************************************************************************************************************************
调用两个角色
[root@localhost ansible]# vim some_roles.yml
- hosts: webservs
remote_user: root
roles:
- role: httpd
- role: nginx
************************************************************************************************************
在一个角色调用另一个角色的剧本
我们可以在nginx角色里面的task目录下main.yml剧本里面添加一行
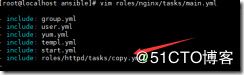
[root@localhost ansible]# vim roles/nginx/tasks/main.yml
- include: group.yml
- include: user.yml
- include: yum.yml
- include: templ.yml
- include: start.yml
- include: roles/httpd/tasks/copy.yml
****************************************************************************************************************************
我们也可以针对不同的角色加标签
[root@localhost ansible]# vim nginx_roles2.yml
- hosts: webservs
remote_user: root
roles:
- { role: httpd, tags: ['web','httpd'] } #web代表执行所有 http代表只执行http的服务
- { role: nginx, tags: ['web','nginx'] } #web代表执行所有 nginx代表只执行nginx的服务
ansible-playbook -t web nginx_roles2.yml -t指定标签
******************************************************************************************************************
还可以如果满足下面条件就执行什么命令
[root@localhost ansible]# vim nginx_roles2.yml
- hosts: webservs
remote_user: root
roles:
- { role: httpd, tags: ['web','httpd'] }
- { role: nginx, tags: ['web','nginx'],when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "7" }
****************************************************************************************************************************
综合性的实验,以http服务为例
1.在roles目录下创建角色app
mkdir /root/ansible/roles/app
2. 切换到app目录
cd /root/ansible/roles/app
3. 创建task目录用来放剧本文件,创建template目录用来放模板文件,vars目录用来放变量,handlers目录用来放触发器 ,files用来放文件
mkdir task template vars handlers files
4.切换到task目录创建playbook剧本文件
cd task/
[root@localhost task]# vim group.yml
- name: create group
group: name=app system=yes gid=79
[root@localhost task]# vim user.yml
- name: create user #创建用户app
user: name=app group=app system=yes shell=/sbin/nologin uid=79
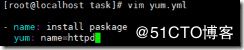
[root@localhost task]# vim yum.yml
- name: install paskage #安装httpd包
yum: name=httpd
vim vars/main.yml 在vars变量目录下创建main.yml 文件定义变量
[root@localhost app]# vim vars/main.yml
username: app #username变量的值是app
groupname: app #groupname变量的值是app
vim task/templ.yml 在存放剧本文件的目录task下创建 templ.yml剧本文件
[root@localhost app]# vim tasks/templ.yml
- name: copy conf #将模板文件拷贝到其他主机
template: src=httpd.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: restart service #触发重启服务
[root@localhost app]# vim tasks/start.yml
- name: start service #启动服务
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
vim handlers/restart.yml 在hanglers用来存放触发器的目录下创建一个/restart.yml 重启服务的脚本文件
[root@localhost app]# vim handlers/main.yml
- name: restart service #重启服务
service: name=httpd state=restarted
5.将http的配置拷贝到模板文件/template/目录下并改名字/httpd.conf.j2
cp /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf /root/ansible/roles/app/templates/httpd.conf.j2
修改模板文件
vim httpd.conf.j2
#Listen 12.34.56.78:80
Listen {{ ansible_processor_vcpus*10 }} 修改监听端口,为ansible的CPU变量乘10
![]()
User {{ username }} 修改用户的名字为变量username
Group {{ groupname }} 修改组的名字为变量groupname
6. 例如files下有一个配置文件
touch files/vhosts.conf
在tasks目录下创建剧本文件
[root@localhost app]# vim task/copyfiles.yml
- name: cpoy file #拷贝配置文件到hppd的目录下,使用主是App
copy: src=vhosts.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf.d/ owner=app
7.我们要定义剧本文件先执行什么剧本在执行什剧本
[root@localhost task]# vim main.yml
- include: group.yml
- include: user.yml
- include: yum.yml
- include: templ.yml
- include: copyfiles.yml
- include: start.yml
8.在和roles平级的目录下调用角色
[root@localhost ansible]# vim app_role.yml
- hosts: webservs
remote_user: root
roles:
- role: app
ansible-playbook app_role.yml