在当今全球CS界中,相信没有人不知道Fei-Fei Li(李飞飞)这个名字,她是CS界的女神级大咖,也是世界顶尖的华裔AI人工智能专家!
因为Fei-Fei Li和Ruicy都曾于2005年毕业于Caltech,哈哈,只不过当年Fei-Fei Li是博士毕业,我只是本科毕业。不过,当我2005年开始读CS Ph.D时,惊喜地发现她却成为了我其中一门专业课的助教老师(李飞飞老师),哈哈,所以当年让我非常幸运地认识了这位美丽、聪慧、谦逊、上进地学姐。她是CS界中我非常敬仰和佩服的女性,也是我超级喜欢(崇拜)的一位飞飞姐姐,嗯,也长得非常美丽!
☞首先,我必须先要非常隆重地向各位同学们介绍下这位全身都散发着“金灿灿”耀眼光芒的CS女神大咖背景介绍:
李飞飞 (Fei-Fei Li)
❈1999年本科毕业于美国普林斯顿大学
❈2005年获得加州理工学院电子工程博士学位
❈2005年-2006年在UIUC伊利诺伊大学厄巴纳-香槟分校担任助教
❈2007年-2008年在普林斯顿大学担任助教
❈2009年加入斯坦福大学任助理教授,2012年担任副教授,并且成为斯坦福大学终身教授,以及斯坦福人工智能实验室与视觉实验室主任,主要研究方向为机器学习、计算机视觉、认知计算神经学,侧重大数据分析为主。已在Nature、PNAS、Journal of Neuroscience、CVPR、ICCV、NIPS、ECCV、IJCV、IEEE-PAMI等顶级期刊与会议上发表了100余篇学术论文。
❈2016年11月15日加入谷歌公司任人工智能研究院,管理和领导谷歌全新的机器学习部门,在进行Visual Genome(视觉基因组)计划。(解释说明:Visual Genome是一个数据集和知识库,致力于将结构化的图像概念和语言连接起来。教会计算机解析视觉图像是人工智能非常重要的任务,这能带来更多有用的视觉算法,也能训练计算机更为高效的沟通——毕竟,在表达真实世界的时候,语言总是受到很大的限制。)
李飞飞老师自任职美国斯坦福大学以来,她主讲的CS231n课程就一直受到学生们的认可和推崇,这门课程是深度学习和计算机视觉方面的重要基础课,对于学习CS专业且分支方向为AI、Computer
Vision和Neural Network相关的学生们是非常有帮助的,也是建议必听课程!
惊喜的是今年4月(Spring 2017),李飞飞老师再次在斯坦福大学教授此门课程,并且对于课件内容进行了调整和内容更新,Ruicy特意将这门课程最新的每个章节内容和线上观看视频链接都仔细认真地帮同学们都整理好了,所以CS专业的同学们记得要抽空记笔记完整学习哦,不要辜负了我这一番苦心哦~
【斯坦福大学CS231n课程全称】
Lecture Collection | Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition
(Spring 2017)
【关于这门斯坦福大学CS231n课程简介】
随着搜索应用程序,图像识别、App应用、成像、医学、无人机和无人驾驶汽车,计算机视觉在我们的社会中已经变得无处不在。许多这样的应用程序,比如:图片分类、定位和检测的核心功能任务都是视觉识别技术完成的。最新发现的神经网络方法(又名“深度学习”),极大地提升了视觉识别系统的先进性能。
李飞飞老师的这门课程总共有16节课程,开设在Stanford
University School of Engineering斯坦福大学工程学院下。主讲人是李飞飞老师,还有2位助手分别是Justin
Johnson和SerenaYeung。在这门课程中,主要讲授深度学习中以图像分类为主要代表的深入探究细节介绍,通过学习这门课程让学生可以详细了解计算机视觉的尖端研究发展。
Computer Vision has
become ubiquitous in oursociety, with applications in search, image
understanding, apps, mapping,medicine, drones, and self-driving cars. Core to
many of these applications arevisual recognition tasks such as image
classification, localization anddetection. Recent developments in neural
network (aka “deep learning”)approaches have greatly advanced the performance
of these state-of-the-artvisual recognition systems. This lecture collection is
a deep dive into detailsof the deep learning architectures with a focus on
learning end-to-end modelsfor these tasks, particularly image classification.
From this lecturecollection, students will learn to implement, train and debug
their own neuralnetworks and gain a detailed understanding of cutting-edge
research in computervision.
【李飞飞老师和两位助手的斯坦福大学主页介绍】
Fei-Fei Li:http://vision.stanford.edu/feifeili/
Justin Johnson:http://cs.stanford.edu/people/jcjohns/
Serena Yeung:http://ai.stanford.edu/~syyeung/
【关于这门课程每节课的主要内容介绍】
Lecture 1 |
Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition
第一节:整体课程介绍,包括计算机视觉概述、历史背景以及课程组织等内容。
课程链接:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vT1JzLTH4G4&list=PL3FW7Lu3i5JvHM8ljYj-zLfQRF3EO8sYv
〼Lecture 1 gives an introduction to the field of computer
vision, discussing its history and key challenges. We emphasize that computer
vision encompasses a wide variety of different tasks, and that despite the
recent successes of deep learning we are still a long way from realizing the
goal of human-level visual intelligence.
➷Keywords: Computer vision, Cambrian Explosion, Camera
Obscura, Hubel and Wiesel, Block World, Normalized Cut, Face Detection, SIFT,
Spatial Pyramid Matching, Histogram of Oriented Gradients, PASCAL Visual Object
Challenge, ImageNet Challenge
Lecture 2 |
Image Classification
第二节:图像分类(数据驱动方法、K-最近邻、线性分类I)
课程链接:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OoUX-nOEjG0&list=PL3FW7Lu3i5JvHM8ljYj-zLfQRF3EO8sYv&index=2
〼Lecture 2 formalizes the problem of image classification.
We discuss the inherent difficulties of image classification, and introduce
data-driven approaches. We discuss two simple data-driven image classification
algorithms: K-Nearest Neighbors and Linear Classifiers, and introduce the
concepts of hyperparameters and cross-validation.
➷Keywords: Image classification, K-Nearest Neighbor,
distance metrics, hyperparameters, cross-validation, linear classifiers
Lecture 3 | Loss
Functions and Optimization
第三节:损失函数和优化:包括线性分类II,高阶表征、图像特点,优化、随机梯度下降等内容。
课程链接:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h7iBpEHGVNc&index=3&list=PL3FW7Lu3i5JvHM8ljYj-zLfQRF3EO8sYv
〼Lecture 3 continues our discussion of linear classifiers.
We introduce the idea of a loss function to quantify our unhappiness with a
model’s predictions, and discuss two commonly used loss functions for image
classification: the multiclass SVM loss and the multinomial logistic regression
loss. We introduce the idea of regularization as a mechanism to fight
overfitting, with weight decay as a concrete example. We introduce the idea of
optimization and the stochastic gradient descent algorithm. We also briefly
discuss the use of feature representations in computer vision.
➷Keywords: Image classification, linear classifiers, SVM
loss, regularization, multinomial logistic regression, optimization, stochastic
gradient descent
Lecture 4 |
Introduction to Neural Networks
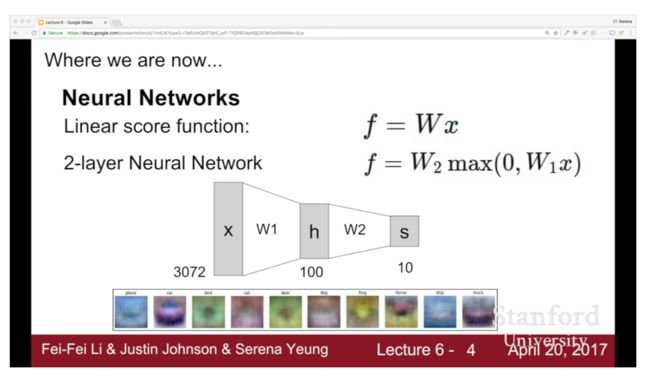
第四节:神经网络:介绍反向传播、多层感知器、神经元的概念。
课程链接:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d14TUNcbn1k&index=4&list=PL3FW7Lu3i5JvHM8ljYj-zLfQRF3EO8sYv
〼In Lecture 4 we progress from linear classifiers to
fully-connected neural networks. We introduce the backpropagation algorithm for
computing gradients and briefly discuss connections between artificial neural
networks and biological neural networks.
➷Keywords: Neural networks, computational graphs,
backpropagation, activation functions, biological neurons
Lecture 5 |
Convolutional Neural Networks
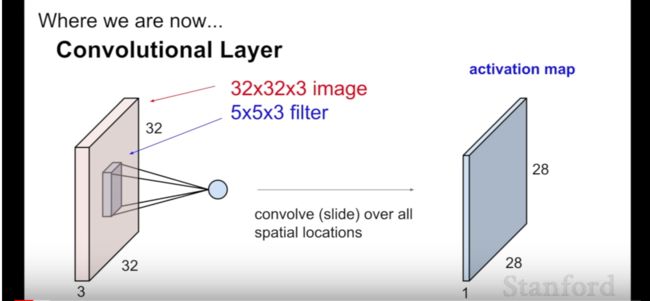
第五节:卷积神经网络:卷积神经网络的历史、卷积和池化、卷积神经网络的前瞻和愿景。
课程链接:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bNb2fEVKeEo&index=5&list=PL3FW7Lu3i5JvHM8ljYj-zLfQRF3EO8sYv
〼In Lecture 5 we move from fully-connected neural networks
to convolutional neural networks. We discuss some of the key historical
milestones in the development of convolutional networks, including the
perceptron, the neocognitron, LeNet, and AlexNet. We introduce convolution,
pooling, and fully-connected layers which form the basis for modern
convolutional networks.
➷Keywords: Convolutional neural networks, perceptron,
neocognitron, LeNet, AlexNet, convolution, pooling, fully-connected layers
Lecture 6 |
Training Neural Networks I
第六节:训练神经网络(I):包括激活函数、权重初始化、批量归一化等内容。
课程链接:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h7iBpEHGVNc&index=3&list=PL3FW7Lu3i5JvHM8ljYj-zLfQRF3EO8sYv
〼In Lecture 6 we discuss many practical issues for
training modern neural networks. We discuss different activation functions, the
importance of data preprocessing and weight initialization, and batch
normalization; we also cover some strategies for monitoring the learning
process and choosing hyperparameters.
➷Keywords: Activation functions, data preprocessing,
weight initialization, batch normalization, hyperparameter search
Lecture 7 |
Training Neural Networks II
第七节:训练神经网络(II):优化方法、模型集成、正则化、数据扩张和迁移学习等。
课程链接:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_JB0AO7QxSA&list=PL3FW7Lu3i5JvHM8ljYj-zLfQRF3EO8sYv&index=7
〼Lecture 7 continues our discussion of practical issues
for training neural networks. We discuss different update rules commonly used
to optimize neural networks during training, as well as different strategies
for regularizing large neural networks including dropout. We also discuss
transfer learning and finetuning.
➷Keywords: Optimization, momentum, Nesterov momentum,AdaGrad, RMSProp, Adam, second-order optimization, L-BFGS, ensembles,regularization, dropout, data augmentation, transfer learning, finetuning
Lecture 8 | Deep
Learning Software
第八节:深度学习软件:Caffe、Torch、Theano、TensorFlow、Keras、PyTorch等。
课程链接:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6SlgtELqOWc&list=PL3FW7Lu3i5JvHM8ljYj-zLfQRF3EO8sYv&index=8
〼In Lecture 8 we discuss the use of different software
packages for deep learning, focusing on TensorFlow and PyTorch. We also discuss
some differences between CPUs and GPUs.
➷Keywords: CPU vs GPU, TensorFlow, Keras, Theano, Torch,
PyTorch, Caffe, Caffe2, dynamic vs static computational graphs
Lecture 9 | CNN
Architectures
第九节:CNN架构:AlexNet,VGG,GoogLeNet,ResNet等。
课程链接:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DAOcjicFr1Y&list=PL3FW7Lu3i5JvHM8ljYj-zLfQRF3EO8sYv&index=9
〼In Lecture 9 we discuss some common architectures for
convolutional neural networks. We discuss architectures which performed well in
the ImageNet challenges, including AlexNet, VGGNet, GoogLeNet, and ResNet, as
well as other interesting models.
➷Keywords: AlexNet, VGGNet, GoogLeNet, ResNet, Network in
Network, Wide ResNet, ResNeXT, Stochastic Depth, DenseNet, FractalNet,
SqueezeNet
Lecture 10 |
Recurrent Neural Networks
第十节:循环神经网络:主要包括RNN,LSTM,GRU,从语言建模、图像描述、视觉问答系统等方面进行描述
课程链接:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6niqTuYFZLQ&index=10&list=PL3FW7Lu3i5JvHM8ljYj-zLfQRF3EO8sYv
〼In Lecture 10 we discuss the use of recurrent neural
networks for modeling sequence data. We show how recurrent neural networks can
be used for language modeling and image captioning, and how soft spatial
attention can be incorporated into image captioning models. We discuss
different architectures for recurrent neural networks, including Long Short
Term Memory (LSTM) and Gated Recurrent Units (GRU).
➷Keywords: Recurrent neural networks, RNN, language
modeling, image captioning, soft attention, LSTM, GRU
Lecture 11 | Detection and Segmentation
第十一节:检测和分割:语义分割、目标检测、实例分割。
课程链接:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nDPWywWRIRo&list=PL3FW7Lu3i5JvHM8ljYj-zLfQRF3EO8sYv&index=11
〼In Lecture 11 we move beyond image classification, and
show how convolutional networks can be applied to other core computer vision
tasks. We show how fully convolutional networks equipped with downsampling and
upsampling layers can be used for semantic segmentation, and how multitask
losses can be used for localization and pose estimation. We discuss a number of
methods for object detection, including the region-based R-CNN family of
methods and single-shot methods like SSD and YOLO. Finally we show how ideas
from semantic segmentation and object detection can be combined to perform
instance segmentation.
➷Keywords: Semantic segmentation, fully convolutional
networks, unpooling, transpose convolution, localization, multitask losses,
pose estimation, object detection, sliding window, region proposals, R-CNN,
Fast R-CNN, Faster R-CNN, YOLO, SSD, DenseCap, instance segmentation, Mask
R-CNN
Lecture 12 |
Visualizing and Understanding
第十二节:可视化和理解:特征可视化和反演、对抗样本、DeepDream(深度梦想)和风格转移。
课程链接:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6wcs6szJWMY&list=PL3FW7Lu3i5JvHM8ljYj-zLfQRF3EO8sYv&index=12
〼In Lecture 12 we discuss methods for visualizing and
understanding the internal mechanisms of convolutional networks. We also
discuss the use of convolutional networks for generating new images, including
DeepDream and artistic style transfer.
Keywords: Visualization, t-SNE,
saliency maps, class visualizations, fooling images, feature inversion,
DeepDream, style transfer
Lecture 13 | Generative Models
第十三节:生成模型:PixelRNN / CNN、变分自编码器、生成式对抗网络。
课程链接:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5WoItGTWV54&list=PL3FW7Lu3i5JvHM8ljYj-zLfQRF3EO8sYv&index=13
〼In Lecture 13 we move beyond supervised learning, and
discuss generative modeling as a form of unsupervised learning. We cover the
autoregressive PixelRNN and PixelCNN models, traditional and variational
autoencoders (VAEs), and generative adversarial networks (GANs).
➷Keywords: Generative models, PixelRNN, PixelCNN,
autoencoder, variational autoencoder, VAE, generative adversarial network, GAN
Lecture 14 |
Deep Reinforcement Learning
第十四节:强化学习:策略梯度,hard attention模型;Q-Learning和Actor-Critic学习。
课程链接:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lvoHnicueoE&index=14&list=PL3FW7Lu3i5JvHM8ljYj-zLfQRF3EO8sYv
〼In Lecture 14 we move from supervised learning to
reinforcement learning (RL), in which an agent must learn to interact with an
environment in order to maximize its reward. We formalize reinforcement
learning using the language of Markov Decision Processes (MDPs), policies,
value functions, and Q-Value functions. We discuss different algorithms for
reinforcement learning including Q-Learning, policy gradients, and Actor-Critic.
We show how deep reinforcement learning has been used to play Atari games and
to achieve super-human Go performance in AlphaGo.
➷Keywords: Reinforcement learning, RL, Markov decision
process, MDP, Q-Learning, policy gradients, REINFORCE, actor-critic, Atari
games, AlphaGo
Lecture 15 |
Efficient Methods and Hardware for Deep Learning
第十五节:现实世界使用:卷积算法,CPU / GPU、低精度模型压缩。
课程链接:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eZdOkDtYMoo&list=PL3FW7Lu3i5JvHM8ljYj-zLfQRF3EO8sYv&index=15
〼In Lecture 15, guest lecturer Song Han discusses
algorithms and specialized hardware that can be used to accelerate training and
inference of deep learning workloads. We discuss pruning, weight sharing,
quantization, and other techniques for accelerating inference, as well as parallelization,
mixed precision, and other techniques for accelerating training. We discuss
specialized hardware for deep learning such as GPUs, FPGAs, and ASICs,
including the Tensor Cores in NVIDIA’s latest Volta GPUs as well as Google’s
Tensor Processing Units (TPUs).
➷Keywords: Hardware, CPU, GPU, ASIC, FPGA, pruning, weight
sharing, quantization, low-rank approximations, binary networks, ternary
networks, Winograd transformations, EIE, data parallelism, model parallelism,
mixed precision, FP16, FP32, model distillation, Dense-Sparse-Dense training,
NVIDIA Volta, Tensor Core, Google TPU, Google Cloud TPU
Lecture 16 |
Adversarial Examples and Adversarial Training
第十六节:对抗性样本和对抗性训练:该部分由lan goodfellow主讲,详细讲解了对抗性样本和对抗性训练。
课程链接:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CIfsB_EYsVI&list=PL3FW7Lu3i5JvHM8ljYj-zLfQRF3EO8sYv&index=16
〼In Lecture 16, guest lecturer Ian Goodfellow discusses
adversarial examples in deep learning. We discuss why deep networks and other
machine learning models are susceptible to adversarial examples, and how
adversarial examples can be used to attack machine learning systems. We discuss
potential defenses against adversarial examples, and uses for adversarial
examples for improving machine learning systems even without an explicit
adversary.
➷Keywords: Adversarial examples, Fooling images, fast
gradient sign method, Clever Hans, adversarial defenses, adversarial examples
in the physical world, adversarial training, virtual adversarial training,
model-based optimization
特别声明:本篇文章为裴若希原创文章,首发内容来自微信公众号:若希北美留学工作室,微信号:ruoxiliuxue,文章版权归原作者及原出处所有。欢迎各位家长和学生们阅读与转发,请其他留学中介公司及同业老师不要抄袭和盗用内容,如需转载请与我们联系,否则必追究相关法律责任!经我们官方授权后,必须在发布文章开头添加:“该文章系转载自微信公众号:若希北美留学工作室,微信号:ruoxiliuxue,文章版权归原作者及原出处所有。”的内容,如您会在公众平台发布,请特别说明为您开启白名单。