1,LinearLaout;(常用属性,Weight权重,divider分割线)
1.1,常用属性
->orientation:horizontal、vertical;
->gravity:控制组件所包含的子元素的对齐方式;
->layout_gravity:控制该组件在父容器里的对其方式;
->layout_width:通常是wrap_content(组件实际大小)和match_parent(填满父容器);
->layout_height:布局的高度,类比
layout_width;
->id:为该组件设置一个资源id,Java中通过findViewById找到该组件;
->background:为该组件设置一个背景图片,或者直接用颜色覆盖。
1.2,Weight,用来等比例的划分区域
->等比例划分,分谁,谁为0,Weight按比例即可
->[http://labs.udacity.com/android-visualizer/#/android/linear-layout](http://labs.udacity.com/android-visualizer/#/android/linear-layout),XML可视化在线工具;
1.3,divider分割线,用于为LinearLayout设置分割线图片,通过showDividers来设置分割线的所在位置,有四个可选值:none,middle,beginning,end;
->divider,为LinearLayout设置分割线的图片;
->showDividers,设置分割线所在的位置,四个值可选;
->dividerPadding,设置分割线的padding。
布局代码:
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
android:text="罗路"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:textSize="48sp"
android:paddingTop="40dp"
android:background="#0000"/>
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:background="#000000" />
android:text="吴佑炫"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="48sp"
android:paddingTop="40dp"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:background="#98FB00"/>
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:background="#000000" />
android:text="丁俊康"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="48sp"
android:paddingTop="40dp"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:background="#00FB98"/>
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:background="#000000" />
android:text="赵丹阳"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="48sp"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:paddingTop="40dp"
android:background="#966B98"/>
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:background="#000000" />
android:text="赵潞"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="48sp"
android:paddingTop="40dp"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:background="#98F532"/>
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:background="#000000" />
2,RelativeLayout,控件之间的相对位置或相对父容器位置进行排列;
2.1,常用属性
->子类控件相对子类控件,值是另外一个控件的id;
->android:layout_above,位于给定ID控件之上;
->android:layout_below;
->android:layout_toLeftOf位于给定控件左边;
->android:layout_toRightOf;
->android:layout_alignLeft,左边与给定ID控件的左边对其;
->android:layout_alignRight;
->android:layout_alignTop上边与给定ID控件的上边对其;
->android:layout_alignBottom;
->android:layout_alignBaseLine对齐到控件基准线;
->相对父容器,值是true或false;
->android:layout_alignParentLeft,相对于父靠左;
->android:layout_alignParentRight;
->android:layout_alignParentTop;
->android:layout_alignParentBottom;
->android:layout_centerInParent=“true”,相对于父,垂直且水平居中;
->android:layout_centerHorizontal=“true”;
->android:layout_centerVertical=“true”;
->相对父容器位置;
->android:layout_margin=“3dp”
->android:layout_marginLeft
->android:layout_marginRight
->android:layout_marginTop
->android:layout_marginBottom
->4.2以上相对布局的新特性
->android:layout_alignStart,将控件对齐给定的id控件的头部;
->android:layout_alignEnd;
->android:layout_alignParentStart,将控件对齐到父控件的头部;
->android:layout_alignParentEnd;
布局示例代码:
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="26dp">
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" />
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" />
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true" />
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true" />
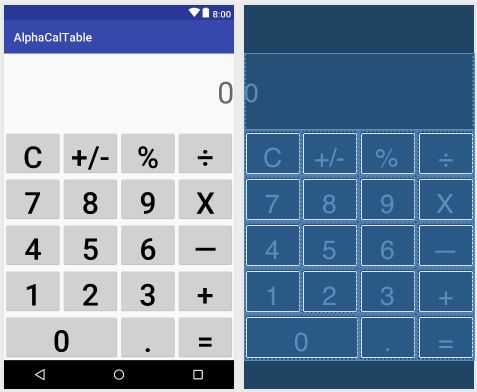
3,TableLayout,Tablelayout以行和列的形式对控件进行管理,每一行为一个TableRow对象,或一个View控件。当为TableRow对象时,可在TableRow下添加子控件,默认情况下,每个子控件占据一列。有多少个子控件就有多少列;当为View时,该View将独占一行。
3.1,属性
->android:layout_colum,指定该单元格在第几列显示;
->android:layout_span,指定该单元格占据的列数(未指定,默认为1)
->android:stretchColums,设置可伸展的列,该列可向行方向伸展,最多可占据一整行;
->android:shrinkColums,设置可收缩的列,当该列挤满所在行,该子控件的内容将往列方向显示。
计算器示例代码:
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools";
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.example.luolu.alphacaltable.MainActivity">
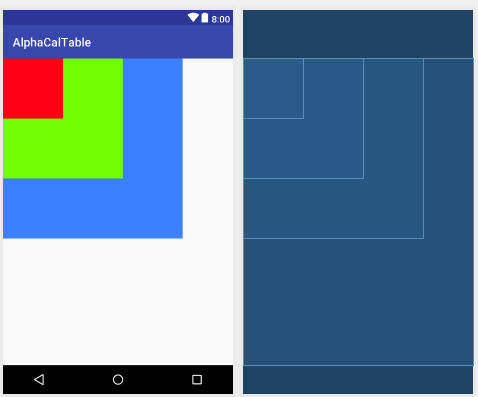
4,FrameLayout,这个布局直接在屏幕上开辟出一块空白的区域,当我们往里面添加控件的时候,会默认把他们放到这块区域的左上角,帧布局的大小由控件中最大的子控件决定,如果控件的大小一样大的话,那么同一时刻就只能看到最上面的那个组件!后续添加的控件会覆盖前一个!虽然默认会将控件放置在左上角,但是我们也可以通过layout_gravity属性,指定到其他的位置!
常用属性:
->android:foreground,设置帧布局容器的前景图像;
->android:foregroundGravity,设置前景图像显示的位置。
布局示例代码:
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools";
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.example.luolu.alphacaltable.MainActivity">
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:background="#438bff" />
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:background="#7BFE00" />
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="#ff0015" />
5,GridLayout,是4.0中引进的新布局控件,支持控件在行、列上都交错排列的情景。优点:1)减少布局嵌套层次从而提高性能;2)适用于需要复杂对齐的布局。
5.1,行列数
->android:rowCount=“8”
->android:columnCount=“8”
5.2,布局方向
->分为水平和垂直两种方式,默认是水平布局
->设置行数或列数之后,控件会自动按行或列进行排列
5.3,单元格属性
->android:layout_column,指定该单元格在第几列显示
->android:layout_row,指定单元格在第几行显示
->android:layout_columnSpan,指定单元格占据的列数
->android:layout_rowSpan,
->android:layout_gravity,指定单元格在容器中的位置
->android:layout_columnWeght,api21加入,列权重
->android:layout_rowWeight,api21加入,行权重
5.4,平均分配行、列问题
->android:layout_columnWeight=“1”
->android:layout_rowWeight=“1”
->占据多行或多列时填满问题
->android:layout_gravity=“fill"
Q:GridLayout 与 GridLayout v7的区别?
主要是解决GridLayout在安卓4.0(API14)以下版本兼容的问题;
1,将此工程拷到你的项目的同级目录下,
(这一点需要注意,很多人导入子工程后,在自己项目add library时不能成功,显示x号,就是这个原因)
2,将gridlayout工程import进来
3,在自己的项目上右键-->属性-->android-->library里gridlayout的子工程
4,xml中的
5.再然后,在java文件里,import android.support.v7.widget.GridLayout;
6,最后android:minSdkVersion改成低版本的,应用就可以在2.3,2.2上面使用了。
计算器布局文件示例代码:
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools";
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.example.luolu.alphacaltable.MainActivity">
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="0"
android:gravity="center_vertical|end"
android:textSize="50sp"
android:id="@+id/resultText" />
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="3"
android:id="@+id/tableLayout"
android:rowCount="5"
android:columnCount="4"
>
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_rowWeight="1"
android:text="C"
android:textSize="50sp"/>
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_rowWeight="1"
android:text="+/-"
android:textSize="50sp"/>
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_rowWeight="1"
android:text="%"
android:textSize="50sp"/>
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_rowWeight="1"
android:text="÷"
android:textSize="50sp"/>
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_rowWeight="1"
android:text="7"
android:textSize="50sp"/>
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_rowWeight="1"
android:text="8"
android:textSize="50sp"/>
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_rowWeight="1"
android:text="9"
android:textSize="50sp"/>
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_rowWeight="1"
android:text="x"
android:textSize="50sp"/>
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_rowWeight="1"
android:text="4"
android:textSize="50sp"/>
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_rowWeight="1"
android:text="5"
android:textSize="50sp"/>
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_rowWeight="1"
android:text="6"
android:textSize="50sp"/>
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_rowWeight="1"
android:text="—"
android:textSize="50sp"/>
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_rowWeight="1"
android:text="1"
android:textSize="50sp"/>
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_rowWeight="1"
android:text="2"
android:textSize="50sp"/>
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_rowWeight="1"
android:text="3"
android:textSize="50sp"/>
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_rowWeight="1"
android:text="+"
android:textSize="50sp"/>
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_rowWeight="1"
android:text="0"
android:layout_columnSpan="2"
android:textSize="50sp"/>
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_rowWeight="1"
android:text="."
android:textSize="50sp"/>
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_rowWeight="1"
android:text="="
android:textSize="50sp"/>