SpringBoot+Thymeleaf+JPA的基本使用
GitHub源码 https://github.com/zehuawong/SpringBoot-JPA-Thymeleaf-Demo
项目属性配置
application.yml文件
#cupSize: CD
#age: 18
#content: "cupSize: ${cupSize},age: ${age}" #在当前配置里面再使用配置
#
#girl:
# cupSize: C
# age: 20
spring:
profiles:
active: dev #使用dev这个配置,区分生产环境和开发环境
resources目录下新建application-dev.yml文件代表开发环境
server:
port: 8081
servlet:
#context-path: "/url"
cupSize: CD
age: 18
content: "cupSize: ${cupSize},age: ${age}" #在当前配置里面再使用配置
girl:
cupSize: C
age: 20
resources目录下新建application-prod.yml文件代表生产环境,可以使用和开发环境不一样的配置
server:
port: 8081
servlet:
#context-path: "/url"
cupSize: CD
age: 18
content: "cupSize: ${cupSize},age: ${age}" #在当前配置里面再使用配置
girl:
cupSize: C
age: 20
GirlProperties类
@Component //如果使用@Autowired还需要使用@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "girl") //前缀属性是girl的映射到这个类
public class GirlProperties {
private String cupSize;
private Integer age;
public String getCupSize() {
return cupSize;
}
public void setCupSize(String cupSize) {
this.cupSize = cupSize;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
注入属性到类GirlProperties中
@Value("${cupSize}")
private String cupSize; //通过注解将配置文件里面的属性注入到此
@Value("${age}")
private Integer age;
@Value("${content}")
private String content;
@Autowired
private GirlProperties girlProperties;
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String sayHi() {
return girlProperties.getCupSize();
}
@RestController
spring4之后新加的注解,原来返回json需要@ResponseBody配合@Controller
Controller和Thymeleaf模板的使用
1、第一步首先需要在pom.xml中配置Thymeleaf依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId>
dependency>
2、在application.yml文件中增加thymeleaf配置
#thymelea模板配置
thymeleaf:
prefix: classpath:/templates/
suffix: .html
mode: HTML5
encoding: UTF-8
servlet:
content-type: text/html
cache: false #开发阶段务必关闭缓存
resources:
chain:
strategy:
content:
enabled: true
paths: /**
3、Controller的配置
/**
* Created by wzh-zhua on 2018/9/30.
*/
//@RestController //spring4之后新加的注解,原来返回json需要@ResponseBody配合@Controller
@Controller //配合模板使用
public class HelloController {
public String hello() {
return "/index";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "hello",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView index(ModelAndView mv) {
mv.setViewName("/index");
mv.addObject("title","欢迎使用Thymeleaf");
return mv;
}
}
4、在templates目录下新建index.html文件
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Hello Springtitle>
head>
<body>
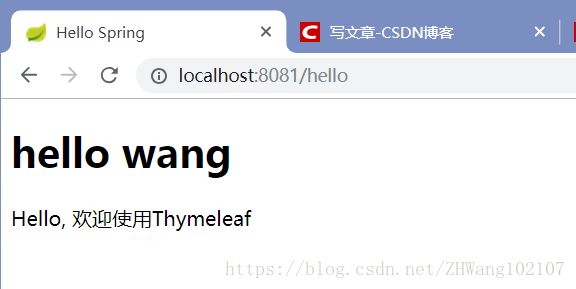
<h1>hello wangh1>
<p th:text="'Hello, ' + ${title}" /><br/>
body>
html>
最后在浏览器中访问http://localhost:8081/hello即可看到以下结果
Thymeleaf列表的使用
User.java
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
}
UserController.java
@Controller
@RequestMapping("user")
public class UserController {
//@RequestMapping(value = "/list", method = RequestMethod.GET)或者
@GetMapping("list")
public String listUser(Model model, @RequestParam(value = "id", required = false, defaultValue = "0") Integer id) {
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<User>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(i);
user.setUsername("username" + i + i);
userList.add(user);
}
model.addAttribute("users", userList);
model.addAttribute("id", id);
return "user/list";
}
// @RequestMapping(value = "/list/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
// public String getUserID(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
// return "id"+ id;
// }
}
user/list.html文件
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Hello Springtitle>
head>
<body>
<span th:text="'参数中的用户id为'+${id}">span>
<h2>用户列表h2>
<div>
<ul>
<li th:each="user:${users}">
<p>ID:<span th:text="${user.id}">span>p>
<p>名字:<span th:text="${user.username}">span>p>
li>
ul>
div>
body>
html>
结果
JPA数据库操作
JPA定义
JPA顾名思义就是Java Persistence API的意思,是JDK 5.0注解或XML描述对象-关系表的映射关系,并将运行期的实体对象持久化到数据库中。
详细可参考 https://blog.csdn.net/wujiaqi0921/article/details/78789087
1、pom.xml中配置JPA
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpaartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
dependency>
2、在application.yml中配置数据库
#数据库配置
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/dbgirl?useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&allowMultiQueries=true
username: root
password: 123456
#jpa配置
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: update #注意,如果是create,每一次运行程序都会删除表再重新创建
show-sql: true
3、Girl.java bean类
@Entity //表示对应数据库中的表,没有则会创建一个表
@Table(name = "girl")
public class Girl {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
@Column(name = "name", nullable = true, length = 20)
private String name;
@Column(name = "age", nullable = true, length = 4)
private Integer age;
//getter and setter方法
}
2、JpaRepository接口
public interface GirlRepository extends JpaRepository<Girl,Long> {
List<Girl> findGirlByAge(Integer id);
}
3、 GirlController
@RestController
@RequestMapping("girl")
public class GirlController {
@Autowired
private GirlRepository girlRepository;
@Autowired
private GirlService girlService;
@GetMapping(path = "getgirlbyname/{age}")
public List<Girl> getGirlByAge(@PathVariable("age") Integer age){
return girlRepository.findGirlByAge(age);
}
@GetMapping(path = "findgirl/{id}")
public Girl findOneGirl(@PathVariable("id") Long id){
return girlRepository.findById(id).orElse(null);
}
@GetMapping(path = "girllist")
public List<Girl> getGirl( ) {
return girlRepository.findAll();
}
@PostMapping(path = "addgirl")
public Girl addGirl(@RequestParam("name") String name, @RequestParam("age") Integer age) {
Girl girl = new Girl();
girl.setAge(age);
girl.setName(name);
girlRepository.save(girl);
return girl;
}
@DeleteMapping(path = "deletegirl")
public void deleteGirl(Long id) {
girlRepository.deleteById(id);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "inserttwo")
public void insertTwo() {
girlService.insertTwo();
}
}
4、用postman请求后的结果
事务管理
1、 @Transactional 数据库事务注解
@Service
public class GirlService {
@Autowired
private GirlRepository girlRepository;
@Transactional //数据库事务注解
public void insertTwo() {
Girl girlA=new Girl();
girlA.setName("A");
girlA.setAge(18);
girlRepository.save(girlA);
Girl girlB=new Girl();
girlB.setName("B");
girlB.setAge(19);
girlRepository.save(girlB); //如果没有开启事务注解,可能出现A已经插入,而B失败的情况,这是不合理的
}
}
2、Controller中url配置
@RequestMapping(value = "inserttwo")
public void insertTwo() {
girlService.insertTwo();
}