Java实战项目(二)——简单计算器
#一.项目目标
利用Java swing技术设计一个简单的计算器,界面如图所示,能够进行两个数的加、减、乘、除运算。
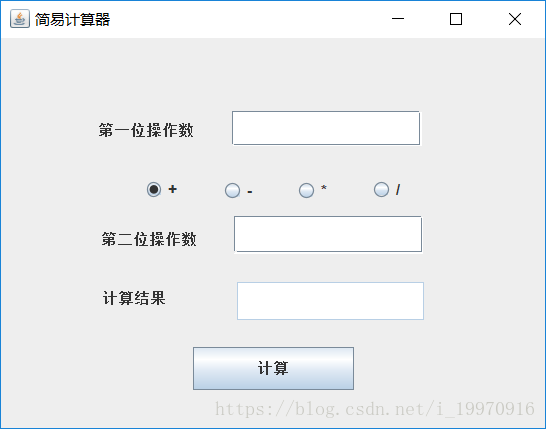
在图所示的项目运行界面上实现如下功能:
- 用户输入合法数字后,选择相应的运算符,单击【计算】按钮,计算出相应的结果,并显示在对应的文本框中。
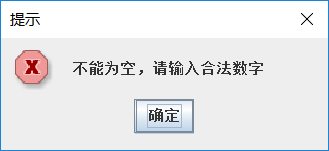
- 如果在相应的文本框中没有输入数字,单击【计算】按钮,则弹出如下图所示的提示对话框。
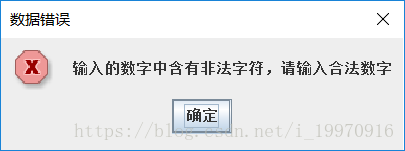
- 如果在相应的文本框中输入的是非数字,单击【计算】按钮,则弹出如下图所示的提示对话框。
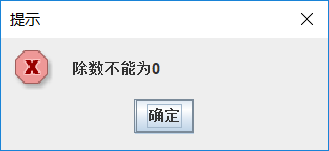
- 如果进行除法时,除数为0,单击【计算】按钮,则弹出如下图所示的提示对话框。
- 用户不能修改运算后的结果。
#二.项目分析
项目的操作过程如下:
- 在【第一操作数】文本框中输入计算的第一个数字。
- 单击运算符号执行相应运算法则。
- 在【第二操作数】文本框中输入计算的下一个数字。
- 单击【计算】按钮,把结果送到对应的文本框中。
依据项目的操作过程描述,程序对应算法如下:
- 从界面获得操作数和运算符号。
- 对操作数进行数据验证。
- 把操作数转换成double数据类型。
- 对操作数进行相应的计算。
- 把结果显示在界面上。
根据程序设计思想,本项目将分为两层结构设计:视图层和业务模型层。
视图层用来接收数据、显示结果、数据验证和调用业务逻辑等。业务模型层主要进行业务逻辑处理。下图所示为项目模型设计。
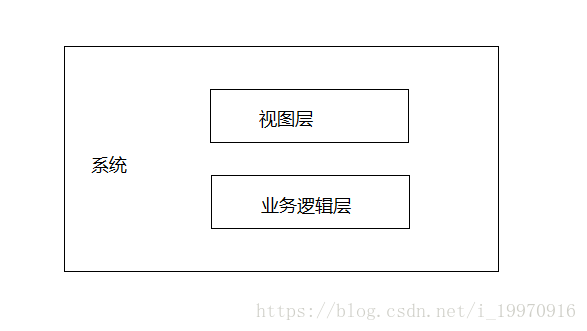
根据分层设计思想,在视图层设计了两个类,在业务逻辑层设计了一个类。类的功能如下表所示
| 序号 | 类名 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | CalFrame | 负责视图层界面显示等功能 |
| 2 | CheckData | 负责视图层数据验证功能 |
| 3 | Calculate | 负责业务逻辑层业务处理功能 |
Calculate类是对业务逻辑的抽象,其中包含一个cal方法,功能是对两个数据进行加减乘除计算,格式如下:
public double cal(double d1, double d2, String op)
其中,参数d1和d2代表运算数,参数op代表运算符。判断参数op的内容,决定进行相应的计算。
CheckData类是对数据进行验证,其中包含一个check方法,功能使判断数据是否为空,是否含有非数字字符等。格式如下:
public boolean check(String s)
对于判断是否为数字,有两种方法:
第一种方法是对字符串的每一位字符进行判断是否是0~9或是“.”子非鱼,不是则跳出判断,标志此字符串中含有非法字符。
第二种方法是利用Double类提供的parseDouble方法来判断是否是数字。即把字符串转换成double类型数据,含有非法字符,该方法将抛出异常。
CalFrame类是用来搭建界面,并调用CheckData、Calculate对象。该类继承了JFrame,实现了ActionListener接口,拥有CalFrame()、Init()、main(String[] atgs)、actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)方法。CalFrame()方法是构造方法,负责调用Init();Init()方法主要是在Frame上加载各种组件,设置Frame大小等功能;actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)方法实现命令按钮单击事件完成的动作;main(String[] atgs)方法来运行CalFrame类。
#代码实现
Calculate.java:
package calculator;
public class Calculate {
public double cal(double data1, double data2, String op) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
double rel = 0;
switch (op) {
case "+":
rel = data1 + data2;
break;
case "-":
rel = data1 - data2;
break;
case "*":
rel = data1 * data2;
break;
case "/":
rel = data1 / data2;
break;
default:
break;
}
return rel;
}
}
CheckData.java:
package calculator;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class CheckData {
public CheckData() {
}
public boolean check(String s) {
//判断数字是否合法
if (s.equals("")) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "不能为空,请输入合法数字", "提示", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return false;
}
else {
try {
double d = Double.parseDouble(s);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "输入的数字中含有非法字符,请输入合法数字", "数据错误", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
CalFrame.java:
package calculator;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.*;
public class CalFrame extends JFrame implements ActionListener{
JLabel label1 = new JLabel("第一位操作数");
JLabel label2 = new JLabel("第二位操作数");
JLabel label3 = new JLabel("计算结果");
JTextField textField1 = new JTextField();
JTextField textField2 = new JTextField();
JTextField textField = new JTextField();
JRadioButton radioButton1 = new JRadioButton("+");
JRadioButton radioButton2 = new JRadioButton("-");
JRadioButton radioButton3 = new JRadioButton("*");
JRadioButton radioButton4 = new JRadioButton("/");
ButtonGroup buttonGroup1 = new ButtonGroup();
ButtonGroup buttonGroup2 = new ButtonGroup();
JButton button = new JButton("计算");
public CalFrame() {
try {
Init();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void Init() throws Exception{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
getContentPane().setLayout(null);
label1.setBounds(new Rectangle(78, 60, 105, 31));
label2.setBounds(new Rectangle(80, 146, 87, 32));
textField1.setBounds(new Rectangle(185, 59, 152, 28));
textField2.setBounds(new Rectangle(187, 143, 151, 30));
button.addActionListener(this);
textField.setEnabled(false);
textField.setBounds(new Rectangle(189, 196, 150, 30));
label3.setBounds(new Rectangle(81, 196, 10745, 26));
radioButton1.setBounds(new Rectangle(113, 111, 44, 23));
radioButton2.setBounds(new Rectangle(176, 112, 48, 23));
radioButton3.setBounds(new Rectangle(235, 112, 43, 23));
radioButton4.setBounds(new Rectangle(295, 110, 38, 24));
button.setBounds(new Rectangle(154, 248, 129, 34));
this.getContentPane().add(label1);
this.getContentPane().add(label3);
this.getContentPane().add(textField);
this.getContentPane().add(label2);
this.getContentPane().add(textField2);
this.getContentPane().add(textField1);
this.getContentPane().add(radioButton3);
this.getContentPane().add(radioButton2);
this.getContentPane().add(radioButton1);
this.getContentPane().add(radioButton4);
this.getContentPane().add(button);
radioButton1.setSelected(true);
buttonGroup1.add(radioButton1);
buttonGroup1.add(radioButton2);
buttonGroup1.add(radioButton3);
buttonGroup1.add(radioButton4);
this.setTitle("简易计算器");
this.setVisible(true);
this.setSize(450, 350);
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//获取数据
String d1 = textField1.getText(); //第一位数
String d2 = textField2.getText(); //第二位数
String op = ""; //运算符号
if (radioButton1.isSelected()) {
op = radioButton1.getActionCommand();
} else if (radioButton2.isSelected()) {
op = radioButton2.getActionCommand();
} else if (radioButton3.isSelected()) {
op = radioButton3.getActionCommand();
} else if (radioButton4.isSelected()) {
op = radioButton4.getActionCommand();
}
//验证数据
CheckData cd = new CheckData();
boolean flag;
flag = cd.check(d1);
//第一位数不满足条件
if (!flag) {
textField1.setText("");
textField1.requestFocus();
return;
}
flag = cd.check(d2);
//第二位数不满足条件
if (!flag) {
textField2.setText("");
textField2.requestFocus();
return;
}
//验证除数为0的问题
if (d2.equals("0") && op.equals("/")) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "除数不能为0", "提示", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
}
//将数据转换为double类型进行计算
double data1 = Double.parseDouble(d1);
double data2 = Double.parseDouble(d2);
Calculate calculate = new Calculate();
double result = calculate.cal(data1, data2, op);
textField.setText(String.valueOf(result));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CalFrame calFrame = new CalFrame();
}
}