Redis源码阅读
Redis源码阅读
文章目录
- Redis源码阅读
- 1 数据结构
- 1.1 动态字符串SDS
- 1.2 双向链表ADLIST
- 1.3 字典 DICT
- 1.4 跳跃表
- 1.5 hyperloglog
- 2 内存编码
- 2.1 整数集合intset
- 2.2 压缩列表ziplist
- 3 数据类型的实现
- 3.1 Object
- 4 数据库的实现
- 5 客户端和服务器
1 数据结构
1.1 动态字符串SDS
Redis自己实现了动态字符串,相关的源码包含在sds.c和sds.h两个文件中,先来看sds.h中的相关定义。
- 为了和C语言中的字符串兼容,redis中SDS的定义其实就是
char*
typedef char *sds;
- SDS完整的内存结构则是将字符串的头部分隐藏在了之际字符串的前面,以sdshdr8为例来看
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr8 {
uint8_t len;
uint8_t alloc;
unsigned char flags;
char buf[];
};
len即是当前字符串已经占用的长度。alloc用于表示当前给字符串分配的长度。flags低三位用来区分当前结构的具体类型。- 各个header的定义中最后有一个
char buf[]。我们注意到这是一个没有指明长度的字符数组,这是C语言中定义字符数组的一种特殊写法,称为柔性数组(flexible array member),只能定义在一个结构体的最后一个字段上。它在这里只是起到一个标记的作用,表示在flags字段后面就是一个字符数组,或者说,它指明了紧跟在flags字段后面的这个字符数组在结构体中的偏移位置。而程序在为header分配的内存的时候,数组本身并不占用内存空间。如果计算sizeof(struct sdshdr8)的值,那么结果是3个字节。 - 结构体采用
__attribute__ ((__packed__))的定义方式是为了让编译器紧凑地分配空间,而不是按照字节对齐地方式,这样做的目的是为了让结构体内的所有变量能在内存种上下紧密排列,以便快速寻址。
SDS_HDR_VAR和SDS_HDR这两个宏用于获取SDS头的位置
#define SDS_TYPE_5 0
#define SDS_TYPE_8 1
#define SDS_TYPE_16 2
#define SDS_TYPE_16 2
#define SDS_TYPE_32 3
#define SDS_TYPE_64 4
#define SDS_HDR_VAR(T,s) struct sdshdr##T *sh = (void*)((s)-(sizeof(struct sdshdr##T)));
#define SDS_HDR(T,s) ((struct sdshdr##T *)((s)-(sizeof(struct sdshdr##T))))
#define SDS_TYPE_5_LEN(f) ((f)>>SDS_TYPE_BITS)
- SDS的基本操作封装
static inline size_t sdslen(const sds s); /*获取sds字符串长度*/
static inline void sdssetlen(sds s, size_t newlen); /*设置sds字符串长度*/
static inline void sdsinclen(sds s, size_t inc); /*增加sds字符串长度*/
static inline size_t sdsalloc(const sds s); /*获取sds字符串容量*/
static inline void sdssetalloc(sds s, size_t newlen); /*设置sds字符串容量*/
static inline size_t sdsavail(const sds s); /*获取sds字符串空余空间*/
static inline int sdsHdrSize(char type); /*获取当前类型type的头长度*/
static inline char sdsReqType(size_t string_size); /*获取请求长度size对应的类型*/
/*
获取当前sds的已使用长度
*/
static inline size_t sdslen(const sds s) {
unsigned char flags = s[-1];
switch(flags&SDS_TYPE_MASK) {
case SDS_TYPE_5:
return SDS_TYPE_5_LEN(flags);
case SDS_TYPE_8:
return SDS_HDR(8,s)->len;
case SDS_TYPE_16:
return SDS_HDR(16,s)->len;
case SDS_TYPE_32:
return SDS_HDR(32,s)->len;
case SDS_TYPE_64:
return SDS_HDR(64,s)->len;
}
return 0;
}
-
flags的获取使用了
s[-1]的方式,这与之前进行结构体声明是的紧凑分配内存息息相关。 -
inline关键字是在C语言中表示内联函数。在c中,为了解决一些频繁调用的小函数大量消耗栈空间或是叫栈内存的问题,特别的引入了inline修饰符,表示为内联函数。inline函数仅仅是一个建议,对编译器的建议,所以最后能否真正内联,看编译器的意思,它如果认为函数不复杂,能在调用点展开,就会真正内联,并不是说声明了内联就会内联,声明内联只是一个建议而已。
- sds.c中定义了一些对sds的申请,设置长度,更新长度,新分配长度等操作
len = sdslen(s);
sh = (char*)s-sdsHdrSize(oldtype);
newlen = (len+addlen);
if (newlen < SDS_MAX_PREALLOC)
newlen *= 2;
else
newlen += SDS_MAX_PREALLOC;
有趣的是,当需要扩充长度时,如果新的长度不足SDS_MAX_PREALLOC=1024*1024时,会将申请的长度乘以2作为新分配的长度,而当新长度超过SDS_MAX_PREALLOC时则再新长度后扩增一段SDS_MAX_PREALLOC。
1.2 双向链表ADLIST
双向链表的实现相对来说比较直白
typedef struct listNode {
struct listNode *prev;
struct listNode *next;
void *value;
} listNode;
typedef struct listIter {
listNode *next;
int direction;
} listIter;
typedef struct list {
listNode *head;
listNode *tail;
void *(*dup)(void *ptr);
void (*free)(void *ptr);
int (*match)(void *ptr, void *key);
unsigned long len;
} list;
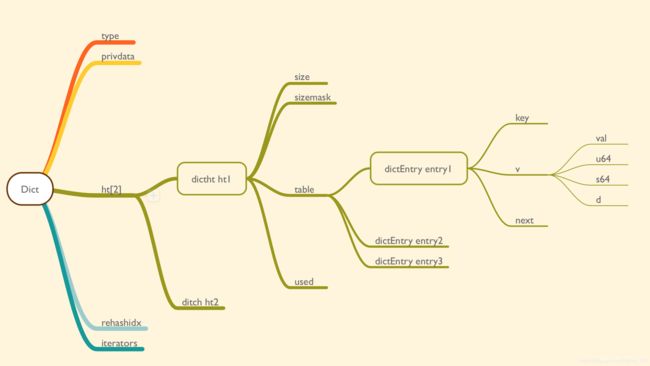
1.3 字典 DICT
Redis对字典的实现,首先是字典单个条项的定义:
typedef struct dictEntry {
void *key;
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;
struct dictEntry *next;
} dictEntry;
dictEntry是字典的一条记录,也就是所谓的桶(bucket)key是键v是值next是指向筒内下一条记录的指针
字典类型的定义则包含了本类型的字典对应的相关处理函数,包括哈希计算函数和元素比较函数等。
typedef struct dictType {
/*哈希函数定义*/
uint64_t (*hashFunction)(const void *key);
void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key);
void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj);
/*比较函数定义*/
int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2);
void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key);
void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj);
} dictType;
字典本身的定义以及哈希表的定义如下:
/* This is our hash table structure. Every dictionary has two of this as we
* implement incremental rehashing, for the old to the new table. */
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table;
unsigned long size;
unsigned long sizemask;
unsigned long used;
} dictht;
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type;
void *privdata;
dictht ht[2];
long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */
unsigned long iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */
} dict;
ditcht是哈希表的定义,包括了一个指向若干个*dictEntry类型的数组头指针table,以及当前哈希表的大小size,还有用于计算索引项的sizemask,used是当前哈希表中已经占用的数量。- 字典本身定义在
dict中,包括当前字典的类型type,两张哈希表ht[2],渐进式哈希的进度标识rehashidx,iterators则表示当前绑定到该字典上的遍历体个数。
dict在内存中的结构如下图:
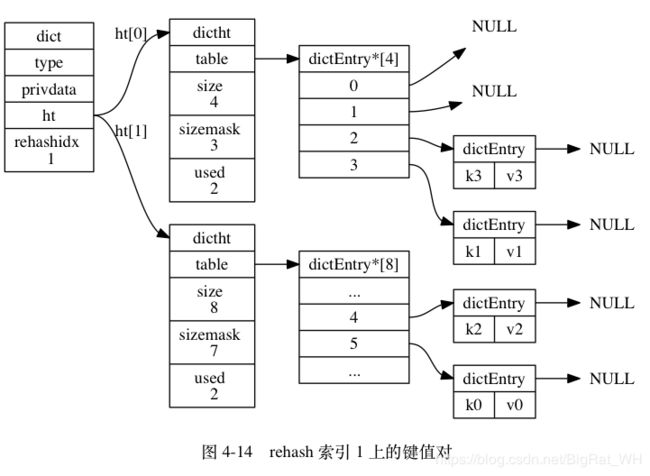
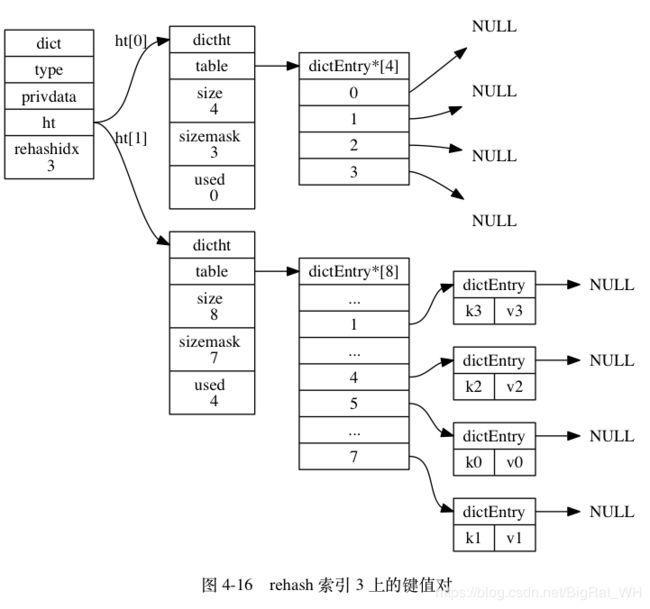
Redis对于字典的设计里,一大特点就是采用了两张哈希表,并且在使用过程中不断地通过dictRehash方法将一张哈希表的数据迁移到另一张表中,以达到扩容的目的,具体代码如下:
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) {
int empty_visits = n*10; /* Max number of empty buckets to visit. */
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0;
while(n-- && d->ht[0].used != 0) {
dictEntry *de, *nextde;
/* Note that rehashidx can't overflow as we are sure there are more
* elements because ht[0].used != 0 */
assert(d->ht[0].size > (unsigned long)d->rehashidx);
while(d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] == NULL) {
d->rehashidx++;
if (--empty_visits == 0) return 1;
}
de = d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx];
/* Move all the keys in this bucket from the old to the new hash HT */
while(de) {
uint64_t h;
nextde = de->next;
/* Get the index in the new hash table */
h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & d->ht[1].sizemask;
de->next = d->ht[1].table[h];
d->ht[1].table[h] = de;
d->ht[0].used--;
d->ht[1].used++;
de = nextde;
}
d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] = NULL;
d->rehashidx++;
}
/* Check if we already rehashed the whole table... */
if (d->ht[0].used == 0) {
zfree(d->ht[0].table);
d->ht[0] = d->ht[1];
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);
d->rehashidx = -1;
return 0;
}
/* More to rehash... */
return 1;
}
-
传入的参数
n表示了本次做rehash动作中,遍历的空桶上限为n*10个 -
开始进行rehash后,字典结构体域中
d->rehashidx将被设置为当前已经从旧哈希表迁移到新哈希表的索引最大值,而d->rehashidx=-1时表明当前哈希表未进行迁移。迁移开始后所有的插入操作将在新表中进行。 -
依次将旧哈希表中的数据在新表中进行插入。
-
旧表的数据全部插入到新表之后
-
将旧表的空间
free掉 -
将
ht[0]重新指向新表ht[1]原本指向的空间,d->rehashidx设置为-1 -
将
ht[1]中的指针都清空,此时ht[1]成为一张空表,需要在下次重新分配。
-
通过渐进式哈希的设计方法,Redis能在原哈希表需要进行扩容时,逐步将旧表的内容迁移到新表,下图是相关过程。
1.4 跳跃表
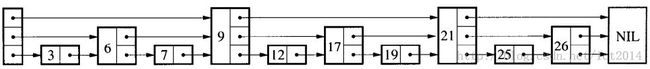
跳跃表是一种随机化的数据结构,在查找、插入和删除这些字典操作上,其效率可比拟于平衡二叉树(如红黑树),大多数操作只需要**O(log n)**平均时间。跳跃表基于有序单链表,在链表的基础上,每个结点不只包含一个指针,还可能包含多个指向后继结点的指针,这样就可以跳过一些不必要的结点,从而加快查找、删除等操作。如下图就是一个跳跃表:
Redis的跳跃表实现跟WilliamPugh在《Skip Lists: A Probabilistic Alternative to Balanced Trees》中描述的跳跃表算法类似,只是有三点不同:
-
允许重复分数;
-
排序不止根据分数,还可能根据成员对象(当分数相同时);
-
有一个前继指针,因此在第1层,就形成了一个双向链表,从而可以方便的从表尾向表头遍历,用于ZREVRANGE命令的实现。
有序集合使用两种数据结构来实现,从而可以使插入和删除操作达到O(log(N))的时间复杂度。这两种数据结构是哈希表和跳跃表。向哈希表添加元素,用于将成员对象映射到分数;同时将该元素添加到跳跃表,以分数进行排序。
Redis对跳跃表的相关结构定义在server.h中
#define ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL 64 /* Should be enough for 2^64 elements */
#define ZSKIPLIST_P 0.25 /* Skiplist P = 1/4 */
/* ZSETs use a specialized version of Skiplists */
typedef struct zskiplistNode {
sds ele;
double score;
struct zskiplistNode *backward;
struct zskiplistLevel {
struct zskiplistNode *forward;
unsigned long span;
} level[];
} zskiplistNode;
typedef struct zskiplist {
struct zskiplistNode *header, *tail;
unsigned long length;
int level;
} zskiplist;
typedef struct zset {
dict *dict;
zskiplist *zsl;
} zset;
-
跳跃表节点又使用了柔性数组
level的概念 -
ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL定义了单个节点最多存储的层数 -
ZSKIPLIST_P用于计算节点的随机层数,此处设置为0.25。从以下代码可见,level=1的概率为0.75,而level=2的概率则为0.25*0.75,依次类推,level值越大的概率越低,这即是所谓的幂次定律(powerlaw)。
/* Returns a random level for the new skiplist node we are going to create.
* The return value of this function is between 1 and ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL
* (both inclusive), with a powerlaw-alike distribution where higher
* levels are less likely to be returned. */
int zslRandomLevel(void) {
int level = 1;
while ((random()&0xFFFF) < (ZSKIPLIST_P * 0xFFFF))
level += 1;
return (level<ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL) ? level : ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL;
}
level当中的span用来记录当前节点到该层级的下一个节点的距离,这样可以方便计算某一个节点在有序链表中的排名。
1.5 hyperloglog
有点复杂啊
2 内存编码
2.1 整数集合intset
整数集合的相关代码在intset.c和intset.h中,说到底就是一个排序的整数数组,定义如下,与redis中sds的定义类似,intset结构体主要定义了header,结构体的末尾依旧是一个柔性数组contents。
typedef struct intset {
uint32_t encoding;
uint32_t length;
int8_t contents[];
} intset;
其中encoding可能是16位、32位或者是64位,通过数据类型的不同来保证最大限度的节省内存,但是所有元素的数据类型是相同的,这意味着整个数组的数据类型取决于最大的那个数。在endianconv.c和endianconv.h中设计了几个宏用来进行大小端的转换。
#if (BYTE_ORDER == LITTLE_ENDIAN)
#define memrev16ifbe(p) ((void)(0))
#define memrev32ifbe(p) ((void)(0))
#define memrev64ifbe(p) ((void)(0))
#define intrev16ifbe(v) (v)
#define intrev32ifbe(v) (v)
#define intrev64ifbe(v) (v)
#else
#define memrev16ifbe(p) memrev16(p)
#define memrev32ifbe(p) memrev32(p)
#define memrev64ifbe(p) memrev64(p)
#define intrev16ifbe(v) intrev16(v)
#define intrev32ifbe(v) intrev32(v)
#define intrev64ifbe(v) intrev64(v)
#endif
这些宏最终都对应到以下三个函数
/* Toggle the 16 bit unsigned integer pointed by *p from little endian to
* big endian */
void memrev16(void *p) {
unsigned char *x = p, t;
t = x[0];
x[0] = x[1];
x[1] = t;
}
/* Toggle the 32 bit unsigned integer pointed by *p from little endian to
* big endian */
void memrev32(void *p) {
unsigned char *x = p, t;
t = x[0];
x[0] = x[3];
x[3] = t;
t = x[1];
x[1] = x[2];
x[2] = t;
}
/* Toggle the 64 bit unsigned integer pointed by *p from little endian to
* big endian */
void memrev64(void *p) {
unsigned char *x = p, t;
t = x[0];
x[0] = x[7];
x[7] = t;
t = x[1];
x[1] = x[6];
x[6] = t;
t = x[2];
x[2] = x[5];
x[5] = t;
t = x[3];
x[3] = x[4];
x[4] = t;
}
整数集合类型提供了一些基本的操作函数
- 标准的二分查找,用来定位
value是否在原intset中,存在则返回1,不存在则返回0,pos用来返回元素value应该插入的位置。
/* Search for the position of "value". Return 1 when the value was found and
* sets "pos" to the position of the value within the intset. Return 0 when
* the value is not present in the intset and sets "pos" to the position
* where "value" can be inserted. */
static uint8_t intsetSearch(intset *is, int64_t value, uint32_t *pos) {
int min = 0, max = intrev32ifbe(is->length)-1, mid = -1;
int64_t cur = -1;
/* The value can never be found when the set is empty */
if (intrev32ifbe(is->length) == 0) {
if (pos) *pos = 0;
return 0;
} else {
/* Check for the case where we know we cannot find the value,
* but do know the insert position. */
if (value > _intsetGet(is,max)) {
if (pos) *pos = intrev32ifbe(is->length);
return 0;
} else if (value < _intsetGet(is,0)) {
if (pos) *pos = 0;
return 0;
}
}
while(max >= min) {
mid = ((unsigned int)min + (unsigned int)max) >> 1;
cur = _intsetGet(is,mid);
if (value > cur) {
min = mid+1;
} else if (value < cur) {
max = mid-1;
} else {
break;
}
}
if (value == cur) {
if (pos) *pos = mid;
return 1;
} else {
if (pos) *pos = min;
return 0;
}
}
- 编码方式需要提升时,先对整个intset的空间进行扩容,且多分配一个元素的空间。然后从后往前依次的对原本intset中的元素的位置进行调整。这里设计精妙的地方在于,调用这个函数之前一定是知道待加入的元素
value要么是太大或者是太小,从而超过了原本encoding所能表示的范围,于是prepend用来记录value的正负值,因为value要么加在当前数组的最左侧或者是最右侧。
/* Upgrades the intset to a larger encoding and inserts the given integer. */
static intset *intsetUpgradeAndAdd(intset *is, int64_t value) {
uint8_t curenc = intrev32ifbe(is->encoding);
uint8_t newenc = _intsetValueEncoding(value);
int length = intrev32ifbe(is->length);
int prepend = value < 0 ? 1 : 0;
/* First set new encoding and resize */
is->encoding = intrev32ifbe(newenc);
is = intsetResize(is,intrev32ifbe(is->length)+1);
/* Upgrade back-to-front so we don't overwrite values.
* Note that the "prepend" variable is used to make sure we have an empty
* space at either the beginning or the end of the intset. */
while(length--)
_intsetSet(is,length+prepend,_intsetGetEncoded(is,length,curenc));
/* Set the value at the beginning or the end. */
if (prepend)
_intsetSet(is,0,value);
else
_intsetSet(is,intrev32ifbe(is->length),value);
is->length = intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(is->length)+1);
return is;
}
2.2 压缩列表ziplist
redis中的压缩列表通过特殊的内存编排方式,极大程度上做到了节约内存,实现的功能类似一个队列,可以存放数字或者string类型的元素,对于队列元素的push和pop操作都能做到O(1)的时间复杂度。但是由于push和pop操作都会触发内存的重新分配,故实际的时间复杂度与整个列表大小也是相关的。
列表的整体编排方式如下:
...
zlbytes的类型是uint32_t,用于表示整个列表所占用的字节数(包括zlbytes本身所占用的4个字节),存储整个列表的大小有利于在需要扩容时不必遍历整个列表。zltial的类型是uint32_t,用于存放列表中最后一个元素的偏移量,这样可以保证pop操作的时间复杂度为O(1)。zllen的类型是uint16_t,用于表示列表中元素的个数。当列表中的元素个数超过2^16-2的时候,zllen被设置为2^16-1,这时候就需要遍历整个列表来获取元素个数。zlend的类型是uint8_t,这是一个特殊的单字节块用于标记列表的结尾,被设置为255,其他正常的元素块均不会以255开头。
列表中的元素块
-
prevlen域用于存储的是前一个元素块的长度。- 当前一个元素块的长度小于254字节时,
prevlen只占用1个字节,存储一个0-253大小的数字。表达方式如下
- 当前一个元素块的长度大于等于254字节时,
prevlen此时占用5个字节,第一个字节被设置为0xFE,之后的4个字节用于表示前一个元素块的具体长度。表达方式如下
0xFE <4 bytes unsigned little endian prevlen>
- 当前一个元素块的长度小于254字节时,
-
encoding域用于表示当前存储的元素类型,一般分为string或者是integer。-
当
encoding用于表示string时,encoding域的第一个字节的前两个bit可以是00,01,10:|00pppppp|
当string的长度小于63个字节时,encoding占用1个字节,此时首字节的前两个bit为00,后6个bit用来表示string的具体长度。|01pppppp|qqqqqqqq|
当string的长度大于63个字节但小于16383(14bits)字节时,encoding占用两个字节,首字节的前两个bit为01,后6个bit和第二个字节一起用于表示string的具体长度。这里的14bit数字为大端表示。|10000000|qqqqqqqq|rrrrrrrr|ssssssss|tttttttt|
当string的长度大于16383时,encoding占用5个字节,首字节的前两个bit被设置为10,后6个bit被设置为0。其后的4个字节用来表示string的具体长度。这里的32bit数字为大端表示。
-
当
encoding用于表示number时,encoding域的首字节的前两个bit应该是11:|11000000|
紧随其后的2个字节用于表示一个uint16_t类型的数字。|11010000|
其后的4个字节用于表示一个uint32_t类型的数字。|11100000|
其后的8个字节用于表示一个uint64_t类型的数字。|11110000|
其后的3个字节用于表示一个24 bit signed 类型的数字。|11111110|
其后的1个字节用于表示一个8 bit signed 类型的数字。|1111xxxx|
xxxx直接用于表示一个数字,取值范围从0001到1101,但是实际上只可以表示从0-12这13个数字,这意味着次时表示的数字应该是xxxx所代表的数字减1。
-
3 数据类型的实现
3.1 Object
redis中对象的实现,首先是object的定义,redis这里为节省结构体的空间,采用了位域的用法,即type和endcoding其实分别占用同一个字节的前四位和后四位。
typedef struct redisObject {
unsigned type:4;
unsigned encoding:4;
unsigned lru:LRU_BITS; /* LRU time (relative to global lru_clock) or
* LFU data (least significant 8 bits frequency
* and most significant 16 bits access time). */
int refcount;
void *ptr;
} robj;
type 域:用于表示当前的对象实际的类型,定义如下:
#define OBJ_STRING 0 /* String object. */
#define OBJ_LIST 1 /* List object. */
#define OBJ_SET 2 /* Set object. */
#define OBJ_ZSET 3 /* Sorted set object. */
#define OBJ_HASH 4 /* Hash object. */
encoding 域为当前对象的编码方式,redis中对象的编码类型分为以下几种
#define OBJ_ENCODING_RAW 0 /* Raw representation */
#define OBJ_ENCODING_INT 1 /* Encoded as integer */
#define OBJ_ENCODING_HT 2 /* Encoded as hash table */
#define OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPMAP 3 /* Encoded as zipmap */
#define OBJ_ENCODING_LINKEDLIST 4 /* No longer used: old list encoding. */
#define OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST 5 /* Encoded as ziplist */
#define OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET 6 /* Encoded as intset */
#define OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST 7 /* Encoded as skiplist */
#define OBJ_ENCODING_EMBSTR 8 /* Embedded sds string encoding */
#define OBJ_ENCODING_QUICKLIST 9 /* Encoded as linked list of ziplists */
#define OBJ_ENCODING_STREAM 10 /* Encoded as a radix tree of listpacks */
refcount 域:这里redis使用 refcount 域来做 对象共享 , 需要注意的是当设置了服务器使用的最大内存时,共享对象会被弃用,因为每个key自身需要存储lru字段。具体的内容可以参考redis对象共享
lru 域:当设置服务器可使用的最大内存时,服务器会使用算法将一些key轮转出去,跟操作系统出现内存不足时的操作类似。
redis里面的object对象只是在基础数据类型之上封装了一层,这样可以方便底层的一些基础命令去封装接口,形式上有点类似面向接口的编程方法,对于object本身来说,ptr 域直接指向了该object对应的类型。
各种类型的对象所对应的底层实现方式如下:
robj *createQuicklistObject(void) {
quicklist *l = quicklistCreate();
robj *o = createObject(OBJ_LIST,l);
o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_QUICKLIST;
return o;
}
robj *createZiplistObject(void) {
unsigned char *zl = ziplistNew();
robj *o = createObject(OBJ_LIST,zl);
o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST;
return o;
}
/*Set集合类型的对象,在底层就是一个dict结构,对应的编码类型是HT*/
robj *createSetObject(void) {
dict *d = dictCreate(&setDictType,NULL);
robj *o = createObject(OBJ_SET,d);
o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_HT;
return o;
}
/*整型结合Intset在底层则是使用列表实现的(有序数组)*/
robj *createIntsetObject(void) {
intset *is = intsetNew();
robj *o = createObject(OBJ_SET,is);
o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET;
return o;
}
/*hash对象是一个压缩列表*/
robj *createHashObject(void) {
unsigned char *zl = ziplistNew();
robj *o = createObject(OBJ_HASH, zl);
o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST;
return o;
}
/*有序列表zset对象,底层的实现是一个dict+压缩列表*/
robj *createZsetObject(void) {
zset *zs = zmalloc(sizeof(*zs));
robj *o;
zs->dict = dictCreate(&zsetDictType,NULL);
zs->zsl = zslCreate();
o = createObject(OBJ_ZSET,zs);
o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST;
return o;
}
robj *createZsetZiplistObject(void) {
unsigned char *zl = ziplistNew();
robj *o = createObject(OBJ_ZSET,zl);
o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST;
return o;
}
robj *createStreamObject(void) {
stream *s = streamNew();
robj *o = createObject(OBJ_STREAM,s);
o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_STREAM;
return o;
}
robj *createModuleObject(moduleType *mt, void *value) {
moduleValue *mv = zmalloc(sizeof(*mv));
mv->type = mt;
mv->value = value;
return createObject(OBJ_MODULE,mv);
}