ThreadLocal源码解读和内存泄露分析
什么是TheadLocal
在多线程环境下,每个线程可以将自己的私有值存储到ThreadLocal,使用时从ThreadLocal中取出,起到一个数据隔离,保证线程安全的作用。
public
class Thread implements Runnable {
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;每个线程都有一个关联的ThreadLocalMap,ThreadLocalMap中存储了多个ThreadLocal-value的键值组。
ThreadLocalMap源码
static class ThreadLocalMap {
static class Entry extends WeakReference {
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
private Entry[] table; ThreadLocalMap内部维护一个弱引用的Entry[]数组,存放ThreadLocal - value 的键值对组。
ThreadLocal的get方法
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null)
return (T)e.value;
}
return setInitialValue();
}ThreadLocalMap的getEntry方法
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal key) {
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
Entry e = table[i];
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
return e;
else
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
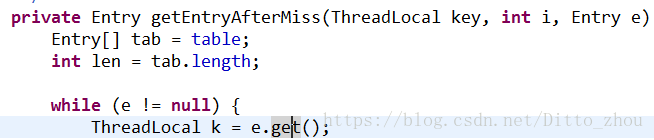
private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal key, int i, Entry e) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
while (e != null) {
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
if (k == key)
return e;
if (k == null)
expungeStaleEntry(i);
else
i = nextIndex(i, len);
e = tab[i];
}
return null;
}private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = null;
size--;
Entry e;
int i;
for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
if (k == null) {
e.value = null;
tab[i] = null;
size--;
} else {
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);
if (h != i) {
tab[i] = null;
while (tab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, len);
tab[h] = e;
}
}
}
return i;
}1.根据TheadLocal的hash值,计算出在数组中下表,找到key相同的entry
2. 否则,向下遍历找下一个,直到找到ThreadLocal相同的entry
3. 遍历过程中,如果key为null,将当前的entry回收,并且重新处理Entry数组,将key为null的Entry清除。
ThreadLocal的set方法
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}ThreadLocalMap的set方法
private void set(ThreadLocal key, Object value) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);//当前索引位置,设置新的entry,并清除过期的entry
return;
}
}
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
//清除过期的entry,并按照原来的两倍大小扩容
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
private boolean cleanSomeSlots(int i, int n) {
boolean removed = false;
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
do {
i = nextIndex(i, len);
Entry e = tab[i];
if (e != null && e.get() == null) {
n = len;
removed = true;
i = expungeStaleEntry(i);
}
} while ( (n >>>= 1) != 0);
return removed;
}1. 根据key的hash值,确定到Entry数组的下标,如果下标在数组中,并且key相同,就替换
2. 如果当前下标的entry为空,就会新设置一个entry到这个索引位置,并会清除过期的entry
3. 如果下标不在当前数组中,就新增entry,并清除过期的entry,如没有过期的entry并且size>=threshold,就会按照两倍length大小扩容。
ThreadLocal的remove方法
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}获取线程绑定的ThreadLocalMap,调用remove方法
private void remove(ThreadLocal key) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
if (e.get() == key) {
e.clear();
expungeStaleEntry(i);
return;
}
}
}public void clear() {
this.referent = null;
}找到key相同的entry,将引用置null,使得gc回收这个entry,并会清除过期的entry.
注意,ThreadLocal的get/set/remove方法都去清除过期的entry
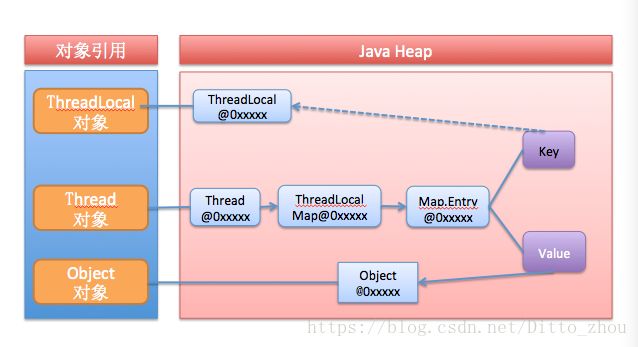
ThreadLocal导致的内存泄露分析
栈中线程引用通过强引用指向堆中的Thread对象和ThreadLocalMap(value实际存放在ThreadLocalMap里面的Entry)
Entry类的源码:
获取到的引用是弱引用,也就是当ThreadLocal被GC回收的时候,entry可能没有被GC,这就造成了内存泄露
那entry什么时候被回收呢?
只有当current thread终止时候,ThreadLocalMap被gc了,这个entry才会被回收。
如何解决
ThreadLocal的get/set/remove方法都会将过期的entry删除,只要调用其中一个方法就行。
一般的解决方法是,在get到值后,调用ThreadLocal的remove方法,将entry主动清除。