最优二叉搜索树(Optimal BST)-算法导论
问题描述:
维基百科定义:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Optimal_binary_search_tree
In the static optimality problem as defined by Knuth we are given a set of n ordered elements and a set of 2n+1 probabilities. We will denote the elements a1 through an and the probabilities A1 through An and B0 through Bn . Ai is the probability of a search being done for element ai . For 1≤i<n , define the probability of bi is Bi is the probability of a search being done for an element between ai and ai+1 , B0 is the probability of a search being done for an element strictly less than a0 , and Bn is the probability of a search being done for an element strictly greater than an . These 2n+1 probabilities cover all possible searches, and therefore add up to one.
( ∑ni=1Ai+∑ni=0Bi=1 )
The static optimality problem is the optimization problem of finding the binary search tree that minimizes the expected search time, given the 2n+1 probabilities. As the number of possible trees on a set of n elements is (2nn)1n+1(2nn)1n+1 , which is exponential in n , brute-force search is not usually a feasible solution.
需要说明的是静态的最优二叉搜索树不一定是高度最矮的二叉搜索树。
O(n3) 的动态规划算法:
期望搜索代价
E[T]=∑ni=1(depth(ai)+1)∗Ai+∑ni=0(depth(bi)+1)∗Bi
=1+∑ni=1depth(ai)∗Ai+∑ni=0depth(bi)∗Bi
最优子结构
观察一颗最优二叉搜索树的子树 T′ 必然包含连续的节点 <ai<ai+1<...<aj> 而且我们用“剪贴法”证明 T′ 必定是包含节点 <ai,ai+1,...,aj>
的一颗最优二叉搜索树,如果说 T′ 不是包含节点 ai,...,aj 的 Optimal BST,则我们可以将用包含 ai,...,aj 的另外一颗Optimal BST T′′ 将其替换掉。
子问题的递归描述
定义 eij 为包含节点 <ai,...,aj>(n≥j≥i−1) 的一颗最优二叉搜索树的期望搜索代价
当一颗子树成为一个节点的子树时,由于每个节点的深度增加了一,因此增加的期望搜索代价为
wi,j=∑jm=iAm+∑jn=iBi
ei,j 的递归公式为
ei,j=Ar+(ei,r−1+wi,r−1)+(er+1,j+wr+1,j)
而
wi,j=Ar+wi,r−1+wr+1,j
所以
ei,j=ei,r−1+er+1,j+wi,j
ei,j 的递归公式
>
而 wi,j=wi,j−1+Aj+Bj
编程实现
下面给出一个接收 <q1,...,qn> 及 <p0,...,pn> 作为节点 a1,...,an 与 b0,...bn 的概率作为输入返回期望 e 及 root 子树树根的代码
#include
#define INF DBL_MAX
#define maxn 100
using namespace std;
double e[maxn][maxn];int root[maxn][maxn];
void optimal_BST(double p[],double q[],int n)//p[1,n],q[0,n ]
{
double w[n+2][n+2];
for(int i=1 ; i<=n+1 ; i++)
{
e[i][i-1] = q[i-1];
w[i][i-1] = q[i-1];
}
for(int l =1 ; l<=n ; l++)
{
for(int i= 1 ; i<=n-l+1 ; ++i)
{
int j = i+l-1;
e[i][j] = INF;
w[i][j] = w[i][j-1] +p[j]+q[j];
for(int r = i;r<=j ; r++)
{
double t = e[i][r-1]+e[r+1][j]+w[i][j];
if(t递归输出子树
void print(int i,int j,int p)// 输出最优二叉树
{
if(i-j==1)
{
if(jprintf("b%d是a%d的左孩子\n",j,p);
else printf("b%d是a%d的右孩子\n",j,p);
return;
}
if(p==0)
{
p = root[i][j];
printf("a%d是根\n",p);
print(i,p-1,p);
print(p+1,j,p);
}else if(root[i][j] printf("a%d是a%d的左孩子\n",root[i][j],p);
p = root[i][j];
print(i,p-1,p);
print(p+1,j,p);
}else
{
printf("a%d是a%d的右孩子\n",root[i][j],p);
p = root[i][j];
print(i,p-1,p);
print(p+1,j,p);
}
} 测试
int main()
{
//cout<
double A[] = {0,0.15,0.10,0.05,0.10,0.20};
double B[] = {0.05,0.10,0.05,0.05,0.05,0.10};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0])-1;
optimal_BST( A,B,n);
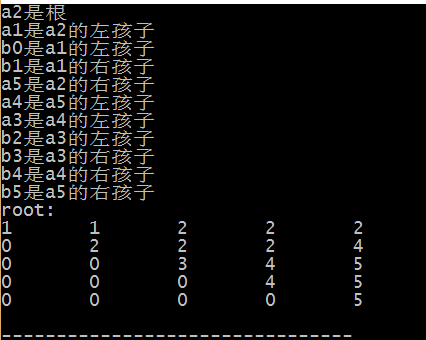
print( 1,n,0);
printf("root:\n");
for(int i=1 ; i<=n ; ++i)
{
for(int j=1 ; j<=n ; ++j)
printf("%d \t",root[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
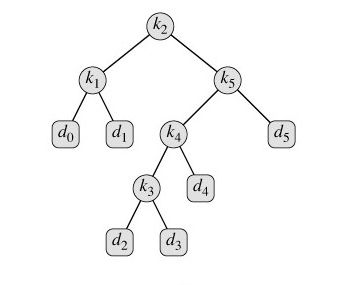
} 对应数据及最优二叉搜索树图
| i | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ai | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.20 | |
| Bi | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.10 |