Nginx+Tomcat实现反向代理与负载均衡入门
【1】反向代理
反向代理(Reverse Proxy)方式是指以代理服务器来接受internet上的连接请求,然后将请求转发给内部网络上的服务器,并将从服务器上得到的结果返回给internet上请求连接的客户端,此时代理服务器对外就表现为一个服务器,该服务器就可称之为代理服务器。
由于代理服务器处在最终处理请求访问的服务器之前,因此可以在代理服务器上做负载均衡。实际上,互联网中也大量的存在反向代理服务器提供代理功能的同时也提供负载均衡的功能。
首先需要安装好Tomcat和Nginx,可以参考博文。
Centos7下安装tomcat:http://blog.csdn.net/j080624/article/details/78626523;
Centos7下安装Nginx:http://blog.csdn.net/j080624/article/details/79240685。
修改nginx.conf如下:
#user nobody nobody;
worker_processes 4;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
use epoll;
multi_accept on;
worker_connections 65535;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
server_tokens off;
server_names_hash_bucket_size 128;
client_header_buffer_size 32k;
large_client_header_buffers 4 32k;
client_max_body_size 1000m;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 120;
send_timeout 10;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#gzip on;
server {
// 监听本地 80端口的请求
listen 80;
// 多个域名用空格隔开
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
// 将80端口的请求转发到Tomcat监听的8080端口
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}其中反向代理其他配置:
proxy_set_header Host $host; 后端的Web服务器可以通过X-Forwarded-For获取用户真实IP。
proxy_connect_timeout 90; Nginx跟后端服务器连接超时时间。
proxy_read_timeout 90; 连接成功后,后端服务器响应时间。
proxy_buffer_size 4k; 设置代理服务器保存用户头信息的缓冲区大小。
proxy_buffers 6 32k; proxy_buffers缓冲区。
proxy_busy_buffers_size 64k; 高负荷下缓冲大小。
proxy_temp_file_write_size 64k; 设定缓存文件夹大小。【2】负载均衡
随着业务不断拓展、用户量不断增多,原本一台Nginx代理的服务器已经显得吃力,不论在性能、响应速度等都显得力不从心,所以需要对后台服务器做负载均衡,缓解一台或几台服务器的高并发请求压力。
① Upstream
负载均衡需要使用Nginx支持的HTTP Upstream模块,该模块通过一个简单的算法调度来实现客户端ip到服务端负载均衡。
Upstream目前支持4种调度算法:
A、默认的轮循
默认的调度算法,在处理客户端的每次请求时,按照时间顺序逐一分配到均衡服务器,可以设定服务器的权重(weight)比值,比值越大访问的几率越大,一般用在后台服务器列表访问性能不均匀情况。
B、ip_hash
记录每次访客的ip地址,固定分配给指定的服务器,有效的解决了不同服务器网页Session的问题。
C、fair
根据后端服务器响应的时间长短来分配,响应时间越短被分配几率越大,它属于第三方插件,Nginx本身并不支持,如需使用必须下载Nginx的upstream_fair模块。
D、url_hash
按访问的地址url的hash值结果分配, 使每个url定向到指定的服务器,可以提高后端服务器的缓存效率,同样的,Nginx本身也不支持该算法,需要第三方的hash软件。
② Upstream支持的状态参数
在Nginx的Upstream模块中,除了可以通过server指定到特定服务器和端口,还可以设置服务器在负载均衡中的状态。
目前的状态如下:
A、down
代表当前的服务器server不参与负载均衡。
B、backup
预留的备用设备,也就是当其它的服务器故障或忙时才会分配它给客户请求,所以它的压力最小。
C、max_fails
服务器server允许请求失败的次数,默认为1次,当失败次数超过限定的次数,就会返回proxy_next_upstream错误信息。
D、fail_timeout
当经历了max_fails的次数后,暂停服务的时间,一般与max_fails配合使用。
注意:
当服务器的调度算法为ip_hash时,服务器在负载均衡中的状态不能是weight和backup。
③ 修改nginx.conf文件如下:
#user nobody nobody;
worker_processes 4;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
use epoll;
multi_accept on;
worker_connections 65535;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
server_tokens off;
server_names_hash_bucket_size 128;
client_header_buffer_size 32k;
large_client_header_buffers 4 32k;
client_max_body_size 1000m;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 120;
send_timeout 10;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
#gzip on;
// 配置服务器集群
upstream tomcat80_server{
# ip_hash;//这里使用默认算法
server 127.0.0.1:8080 weight=1;
server 127.0.0.1:8081 weight=2;//权重越高表示被分配到的几率越大
# server 127.0.0.1:8081 backup;//不配置备用服务器
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost www.test.com;//多个域名用空格隔开
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
proxy_pass http://tomcat80_server;//将请求转发到集群
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
upstream详细设置:
upstream balance {
server 192.168.88.190:8081 weight=1 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=30s;
server 192.168.88.39:8081 weight=1 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=30s;
server 127.0.0.1:8081 down;
#server 192.168.88.152:8080 backup;
} 参数说明如下:
weight : 值越大,负载权重越大,请求次数越多 ;
~
max_fails : 允许请求失败的次数,超过失败次数后,转发到下一个服务器,当有max_fails个请求失败,就表示后端的服务器不可用,默认为1,将其设置为0可以关闭检查 ;
~
fail_timeout : 指定时间内无响应则失败, 在以后的fail_timeout时间内nginx不会再把请求发往已检查出标记为不可用的服务器 ;
~
down : 表示当前server不参与负载 ;
~
backup : 其他非backup server都忙的时候,backup server作为备用服务器,将请求转发到backup服务器 。
上述配置,默认拦截了所有的请求,并转发到Tomcat集群。
实际应用中可以根据需求做详细配置,参考如下两个示例。
① JSP页面请求交给Tomcat处理
具体的,在nginx.conf中新建一个location,用正则表达式将所有JSP的请求匹配到该location中:
其中最核心的就是”proxy_pass http://localhost:8080;”这条配置,它将匹配到的请求都转发给Tomcat去处理。
其他的配置:
proxy_set_header Host $host; 后端的Web服务器可以通过X-Forwarded-For获取用户真实IP。
client_max_body_size 10m; 允许客户端请求的最大单文件字节数。
client_body_buffer_size 128k; 缓冲区代理缓冲用户端请求的最大字节数。
proxy_connect_timeout 90; Nginx跟后端服务器连接超时时间。
proxy_read_timeout 90; 连接成功后,后端服务器响应时间。
proxy_buffer_size 4k; 设置代理服务器保存用户头信息的缓冲区大小。
proxy_buffers 6 32k; proxy_buffers缓冲区。
proxy_busy_buffers_size 64k; 高负荷下缓冲大小。
proxy_temp_file_write_size 64k; 设定缓存文件夹大小。② 静态文件直接交给nginx处理,并做缓存
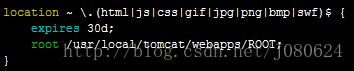
对于静态文件的请求,我们也新建一个location,将常见图片、css、js等请求匹配到该location中。
如图所示,配置非常简单,通过root关键字,将匹配到的请求都到tomcat/webapps/ROOT目录下直接查找。而expires 30d则表示使用expires缓存模块,缓存到客户端30天。实际应用中可能会将图片,html,css,js等分开为单独文件夹,思想同上。
上面两个举例只是一种思想,可能不需要。但是在大型项目中,动静分离是一种很好的思想方式!