Android 属性动画探究(二)——TypeEvaluator解析与自定义
1、TypeEvaluator
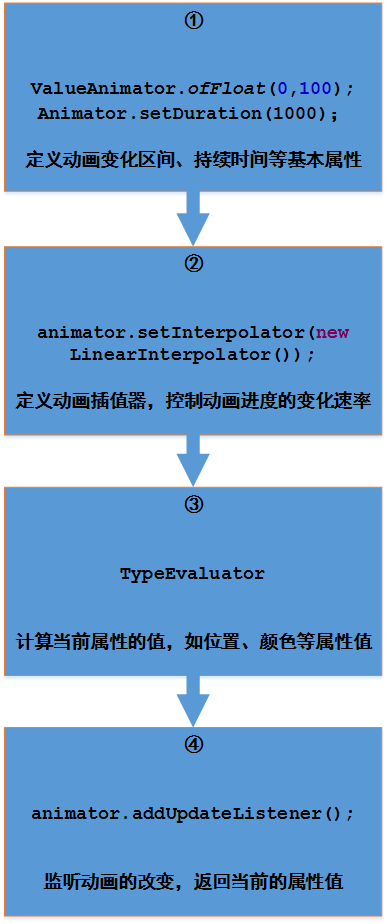
这里将主要阐述一下上图的第三步,关于TypeEvaluator的一些解析。上一篇中已经知道Interpolator的作用是控制动画的完成进度变化快慢的,那TypeEvaluator的作用又是什么?
简言之,TypeEvaluator是直接改变动画的属性值的,比如要改变颜色属性,可以直接改变其值为"#FFFFFF",而Interpolator改变的是进度,如可以直接指定瞬间完成动画整体的80%。但是两者不是孤立存在的,不是各自改变各自的东西,他们之间又有着什么样的爱恨纠葛?
2、系统实现的TypeEvaluator
先看一下上一篇用到的 ValueAnimator.ofFloat的默认实现
/**
* Internal function, called by ValueAnimator, to set up the TypeEvaluator that will be used
* to calculate animated values.
*/
void init() {
if (mEvaluator == null) {
// We already handle int and float automatically, but not their Object
// equivalents
mEvaluator = (mValueType == Integer.class) ? sIntEvaluator :
(mValueType == Float.class) ? sFloatEvaluator :
null;
}
if (mEvaluator != null) {
// KeyframeSet knows how to evaluate the common types - only give it a custom
// evaluator if one has been set on this class
mKeyframeSet.setEvaluator(mEvaluator);
}
}可见默认设置为sFloatEvaluator
private static final TypeEvaluator sFloatEvaluator = new FloatEvaluator();
**
* This evaluator can be used to perform type interpolation between float values.
*/
public class FloatEvaluator implements TypeEvaluator {
/**
* This function returns the result of linearly interpolating the start and end values, with
* fraction representing the proportion between the start and end values. The
* calculation is a simple parametric calculation: result = x0 + t * (v1 - v0),
* where x0 is startValue, x1 is endValue,
* and t is fraction.
*
* @param fraction The fraction from the starting to the ending values
* @param startValue The start value; should be of type float or
* Float
* @param endValue The end value; should be of type float or Float
* @return A linear interpolation between the start and end values, given the
* fraction parameter.
*/
public Float evaluate(float fraction, Number startValue, Number endValue) {
float startFloat = startValue.floatValue();
return startFloat + fraction * (endValue.floatValue() - startFloat);
}
} public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
cy = (Float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
// ...
}3、自己实现TypeEvaluator
ValueAnimator与ObjectAnimator中都有ofObject(TypeEvaluator evaluator, Object... values) 这个方法,其中第一个参数便可使用自己实现的TypeEvaluator。在定义Interpolator时只能使动画进度变化按特定函数关系执行,在这里便可以使得动画的属性值按特定的函数关系变化。下面描述一个使小球沿着等幅周期振荡函数进行运动的例子。
定义一个类封装坐标值(系统也有实现-- android.graphics.Point;):
/**
* 坐标点
*/
public class Point {
private float x;
private float y;
public Point(float x, float y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public float getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(float x) {
this.x = x;
}
public float getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(float y) {
this.y = y;
}
}
/**
* 等幅振荡
*/
class OscillationEvaluator implements TypeEvaluator {
@Override
public Object evaluate(float fraction, Object startValue, Object endValue) {
Point startPoint = (Point) startValue;
Point endPoint = (Point) endValue;
float x = startPoint.getX() + fraction * (endPoint.getX() - startPoint.getX());//x坐标线性变化
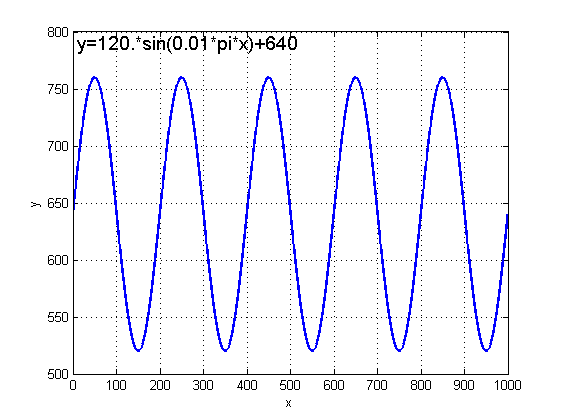
float y = 120 * (float) (Math.sin(0.01 * Math.PI * x)) + getHeight() / 2;//y坐标取相对应函数值
return new Point(x, y);
}
}
函数图像:
动画设置:
/**
* 小球动画
*/
private void startAnimationMotion() {
Point startPoint = new Point(mRadius, getHeight() / 2);
Point endPoint = new Point(getWidth() - mRadius, 0);
ValueAnimator animator = ValueAnimator.ofObject(new OscillationEvaluator(), startPoint, endPoint);
animator.setDuration(7000).setRepeatCount(3);
animator.addUpdateListener(new AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
currentPoint = (Point) animation.getAnimatedValue();
invalidate();
}
});
animator.setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator());//设置插值器
animator.start();
}这里需要设置为LinearInterpolator保证x坐标线性变化。
绘制图像:
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
width = getWidth();
height = getHeight();
mPaint.setStyle(Style.FILL);
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
if (currentPoint == null) {
startAnimationMotion();// 执行动画
}
mPaint.setColor(Color.WHITE);
canvas.drawLine(0, getHeight() / 2, getWidth(), getHeight() / 2, mPaint);
mPaint.setColor(Color.MAGENTA);
canvas.drawCircle(currentPoint.getX(), currentPoint.getY(), mRadius, mPaint);
}4、总结
以上便是对Interpolator、TypeEvaluator的一些见解。Interpolator负责调节动画进度变化快慢,TypeEvaluator负责改变动画最终的属性值,它们之间以Interpolator返回的当前进度值相联系。文中多以路径变化举例,当然属性动画是可以根据需要作用于其他属性的,通过对Interpolator、TypeEvaluator的自定义,写出丰富效果。当然,一般不需要同时自己实现两者。
下载源码